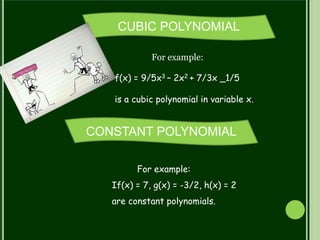
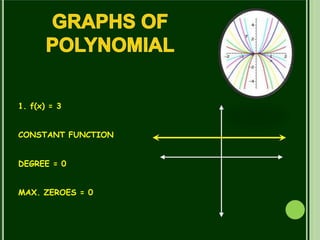
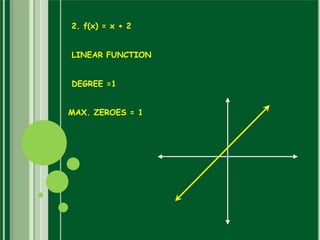
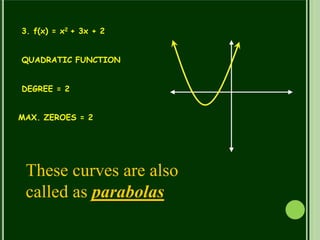
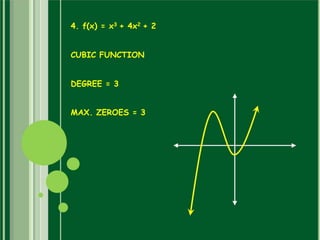
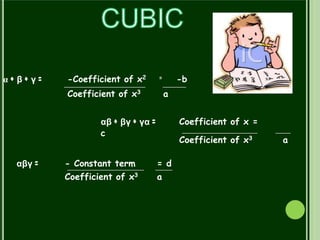
This document discusses polynomials. It defines a polynomial as an expression constructed from variables and constants using addition, subtraction, multiplication, and exponents. Polynomials appear in many areas of mathematics and science. The document then discusses the terms, coefficients, and different types of polynomials including linear, quadratic, cubic, and constant polynomials. It also discusses the degree and maximum number of zeroes of each type of polynomial. Finally, it discusses using the division algorithm to find quotients, remainders, and factors of polynomials.