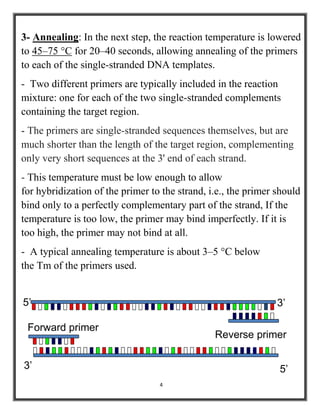
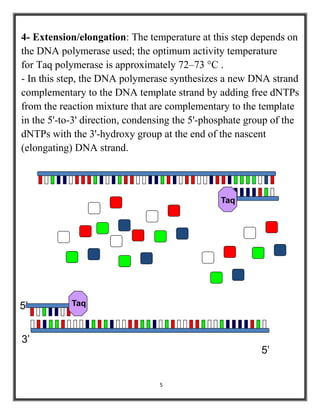
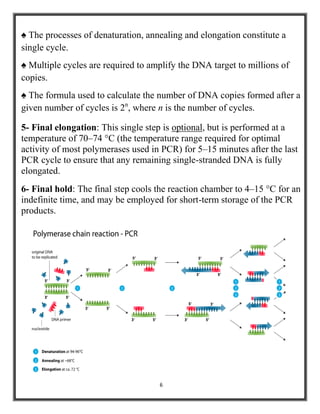
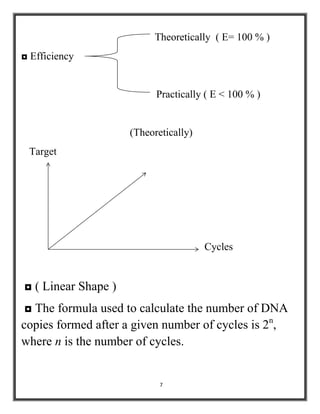
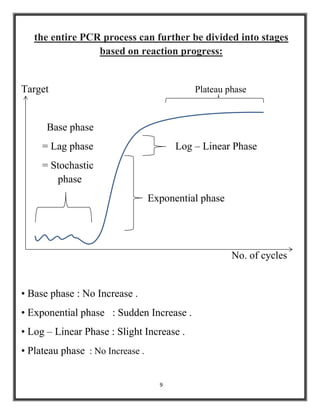
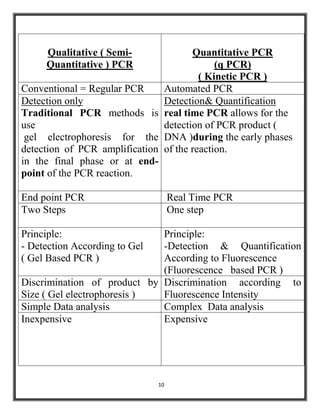
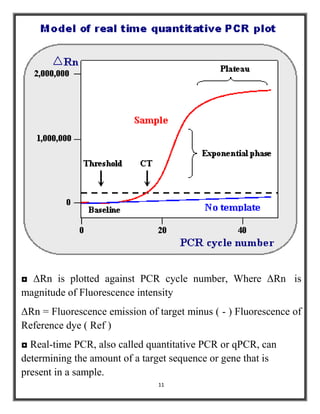
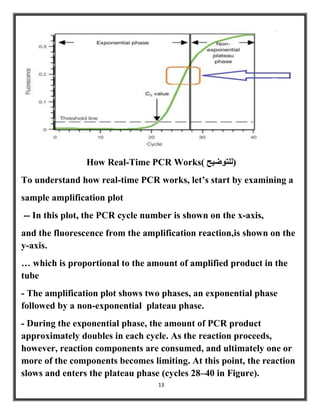
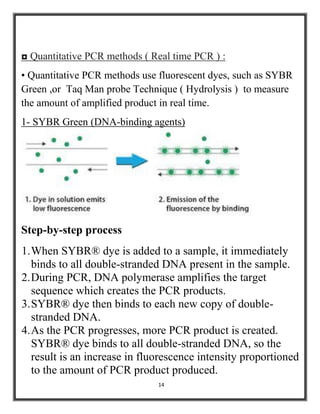
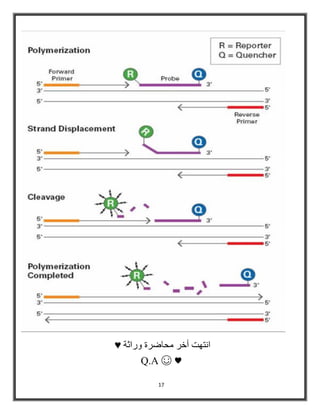
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a molecular biology technique used to amplify specific DNA sequences, allowing for thousands to millions of copies from a single or few DNA fragments. The basic PCR setup requires a DNA template, DNA polymerase, primers, nucleotides, a buffer solution, and cations, and the process includes steps of denaturation, annealing, and elongation across multiple cycles to achieve amplification. Real-time PCR enables quantification of the DNA product via fluorescence detection, providing insight into the amplification process during its early phases.