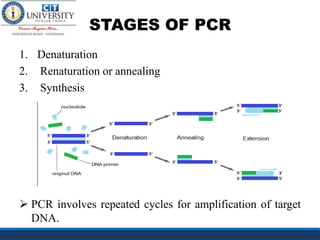
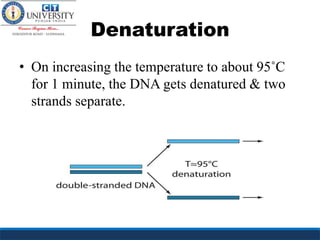
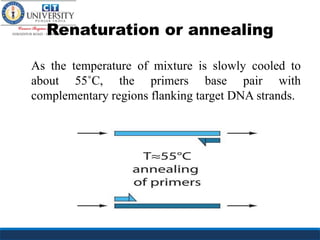
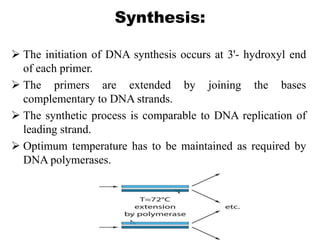
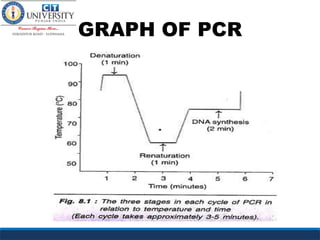
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to amplify a specific region of DNA across multiple cycles. It involves denaturing the double-stranded DNA target, annealing primers to the single strands, and extending the primers with a DNA polymerase to synthesize new strands. Repeating this process results in exponential amplification of the target DNA sequence. PCR requires a DNA template, primers, nucleotides, and a thermostable DNA polymerase. It is used for applications like prenatal diagnosis of genetic diseases, detection of infectious diseases, cancer diagnosis, and forensics.