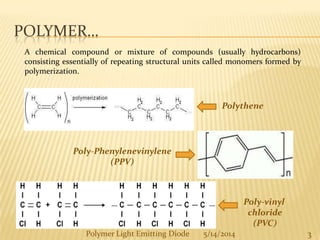
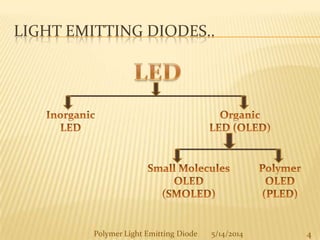
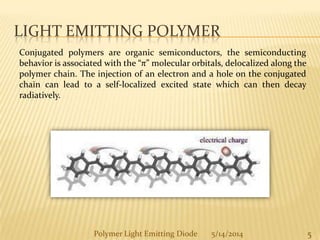
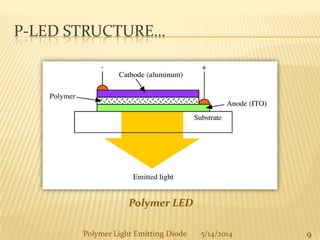
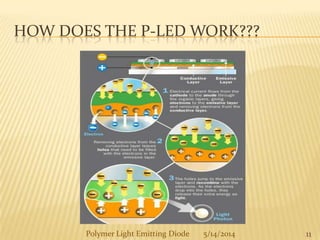
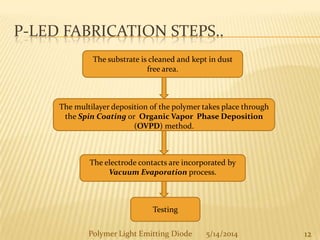
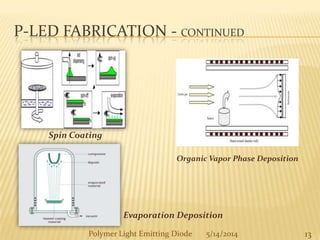
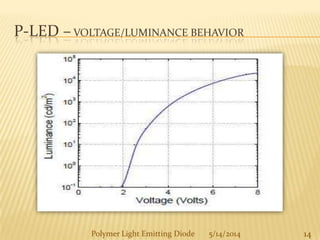
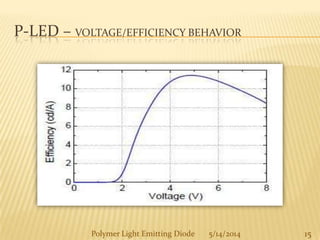
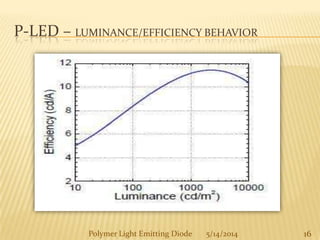
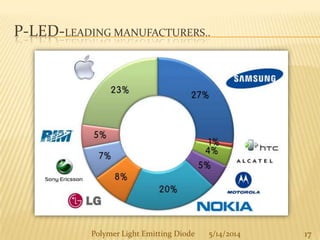
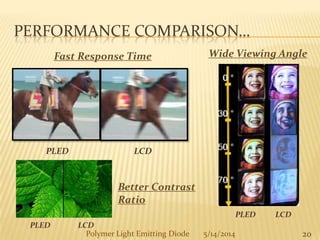
The document provides an overview of polymer light-emitting diodes (PLEDs), including their structure, operation, fabrication processes, and applications in various fields. While highlighting their advantages such as flexibility, energy efficiency, and high resolution, it also addresses challenges like limited lifespan and color balance issues. The conclusion emphasizes that despite its current limitations, PLED technology is expected to grow and evolve in the future.