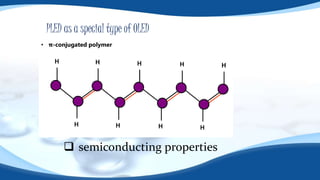
PLEDs use semiconducting polymers that emit light when electric current is applied. They can be used to create more efficient LED displays, especially for portable devices due to their flexibility. A PLED consists of a thin film of conjugated polymer sandwiched between an anode and cathode. When voltage is applied, the polymer emits light. PLEDs have advantages over LCDs like lower power consumption, thinner displays, and flexible substrates. However, they have shorter lifetimes at high brightness and are sensitive to oxidation and humidity.