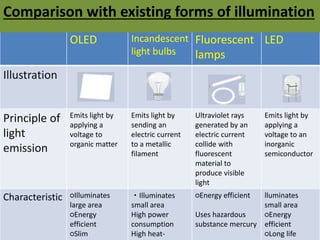
OLED (organic light-emitting diode) is a light-emitting diode made by placing a series of organic thin films between two conductors. When electrical current is applied, a bright light is emitted from a device that is 100 to 500 nm thick. There are different types of OLEDs including passive matrix OLEDs, active matrix OLEDs, and foldable OLEDs. OLEDs have advantages over traditional lighting like being lightweight, thin, flexible, more energy efficient, and having faster response times. However, their manufacturing processes are currently expensive and their organic materials have limited lifetimes. OLEDs are used in displays for phones, TVs, watches and can potentially replace traditional light bulbs