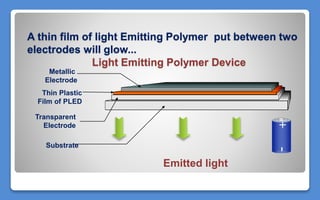
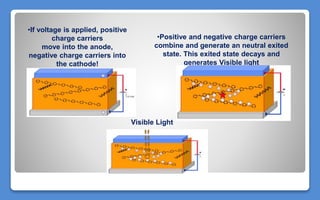
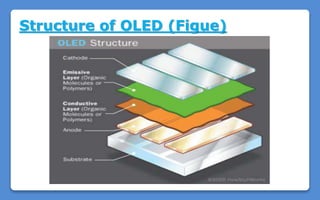
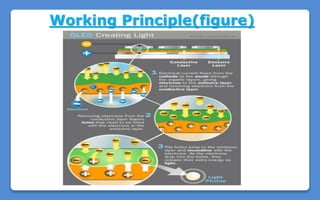
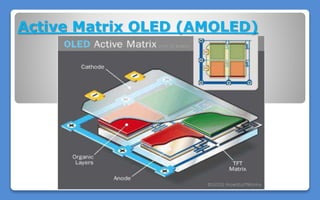
Polymer LED (PLED) technology uses a polymer as the semiconductor material between two electrodes to produce light. PLEDs offer advantages like thinner and more flexible displays compared to traditional LEDs. The first PLED was created in 1989 using polyphenylene vinylene between electrodes. PLEDs work through electroluminescence where electrons and holes recombine in the polymer to emit light. Organic LEDs (OLEDs) are similar solid state devices made of thin organic molecule films that emit light with electricity and are used in applications like phones, TVs and more due to benefits such as low energy use, thinness and high contrast.