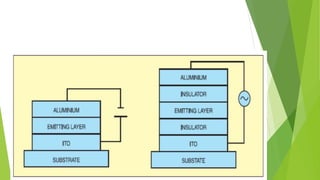
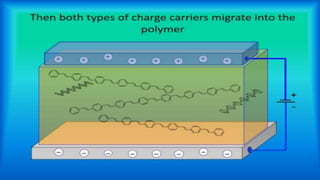
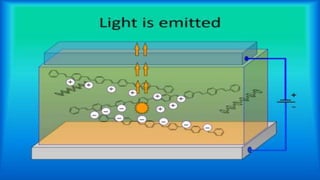
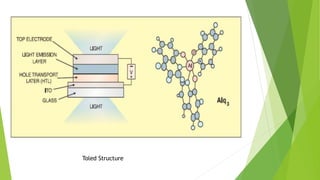
This document provides an overview of light emitting polymers (LEPs), which are a type of thin, lightweight and low-power flat panel display technology. It describes the chemistry and structure of LEPs, how they work, types including flexible and transparent polymers, manufacturing processes like spin coating, advantages over other displays, limitations such as aging, and applications including phones, TVs and electronic paper. LEPs have potential for use in many consumer electronics and displays.