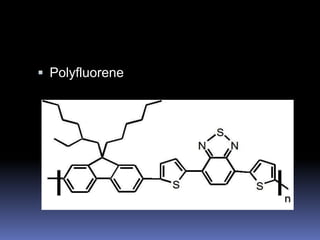
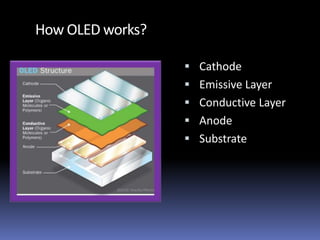
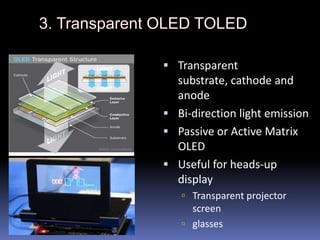
The document discusses organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), which are thin films of organic compounds that emit light when electric current is applied. It provides a brief history of OLED development from the 1950s and describes the basic working principle of OLEDs involving organic semiconductor layers and electrodes. The document also outlines different types of OLEDs and their applications, as well as advantages such as high contrast, flexibility, and energy efficiency compared to LCDs. Potential disadvantages discussed include higher manufacturing costs and limited lifespan.