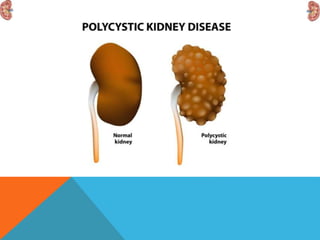
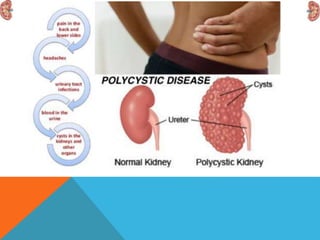
This document discusses polycystic kidney disease (PKD). It describes PKD as a common hereditary disease characterized by the development of multiple renal cysts. There are two forms: autosomal recessive PKD which is fatal in infancy, and autosomal dominant PKD which is more common and can lead to end stage renal disease in around 50% of cases by age 60. The document provides details on the clinical features, investigations, and management of autosomal dominant PKD.