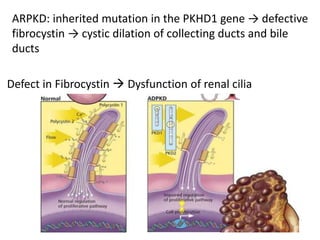
Polycystic kidney disease (PKD) is an inherited disorder characterized by multiple cysts in the kidneys. It is classified into autosomal recessive PKD and autosomal dominant PKD, which is the most common genetic cause of chronic kidney disease. Autosomal dominant PKD results from mutations in PKD1 or PKD2 genes and is characterized by cyst formation due to a two-hit mechanism. Symptoms usually occur after age 30 but can manifest earlier. Treatment involves slowing disease progression with ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and tolvaptan in some cases. Later stages may require dialysis or kidney transplantation.