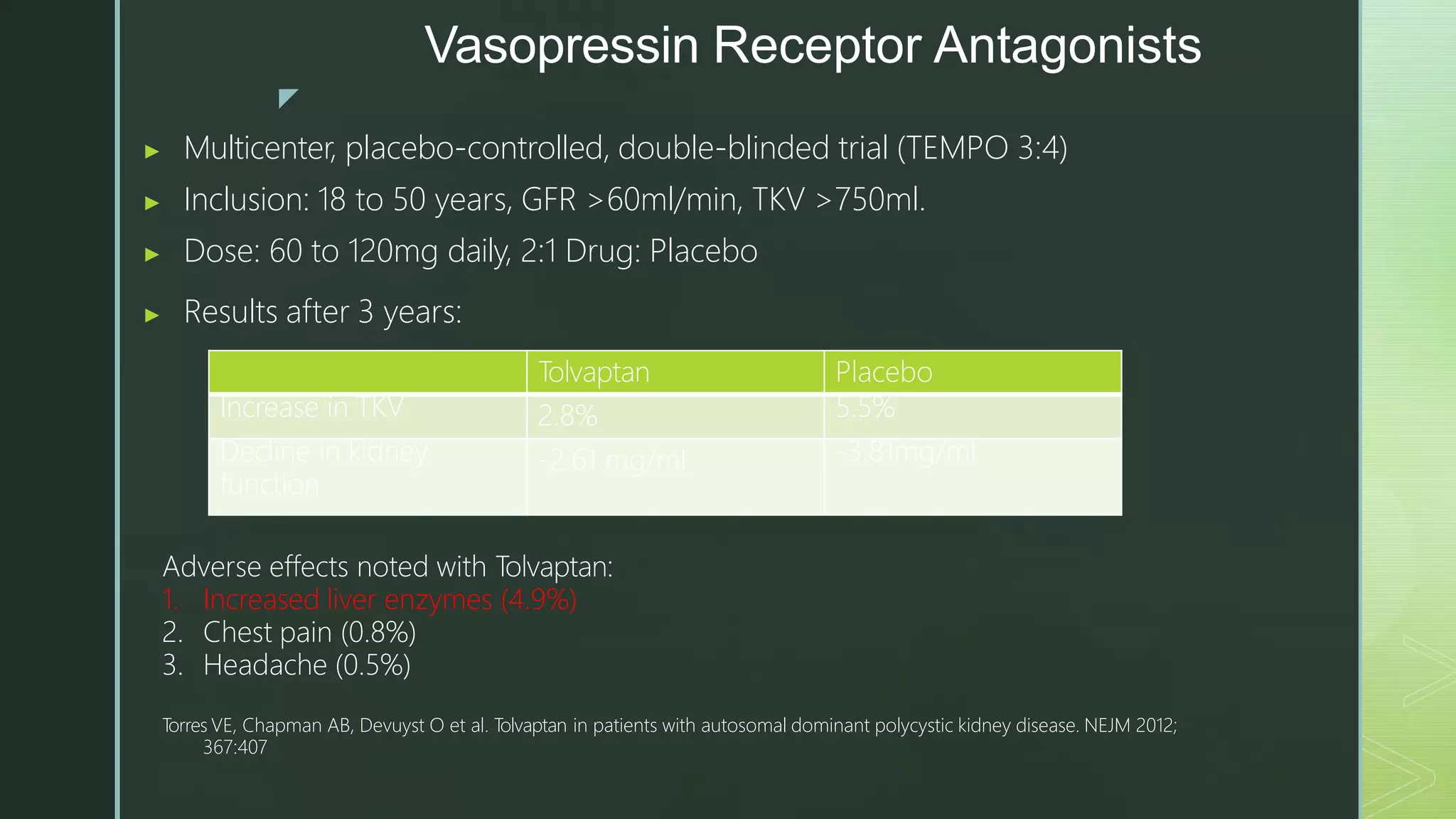
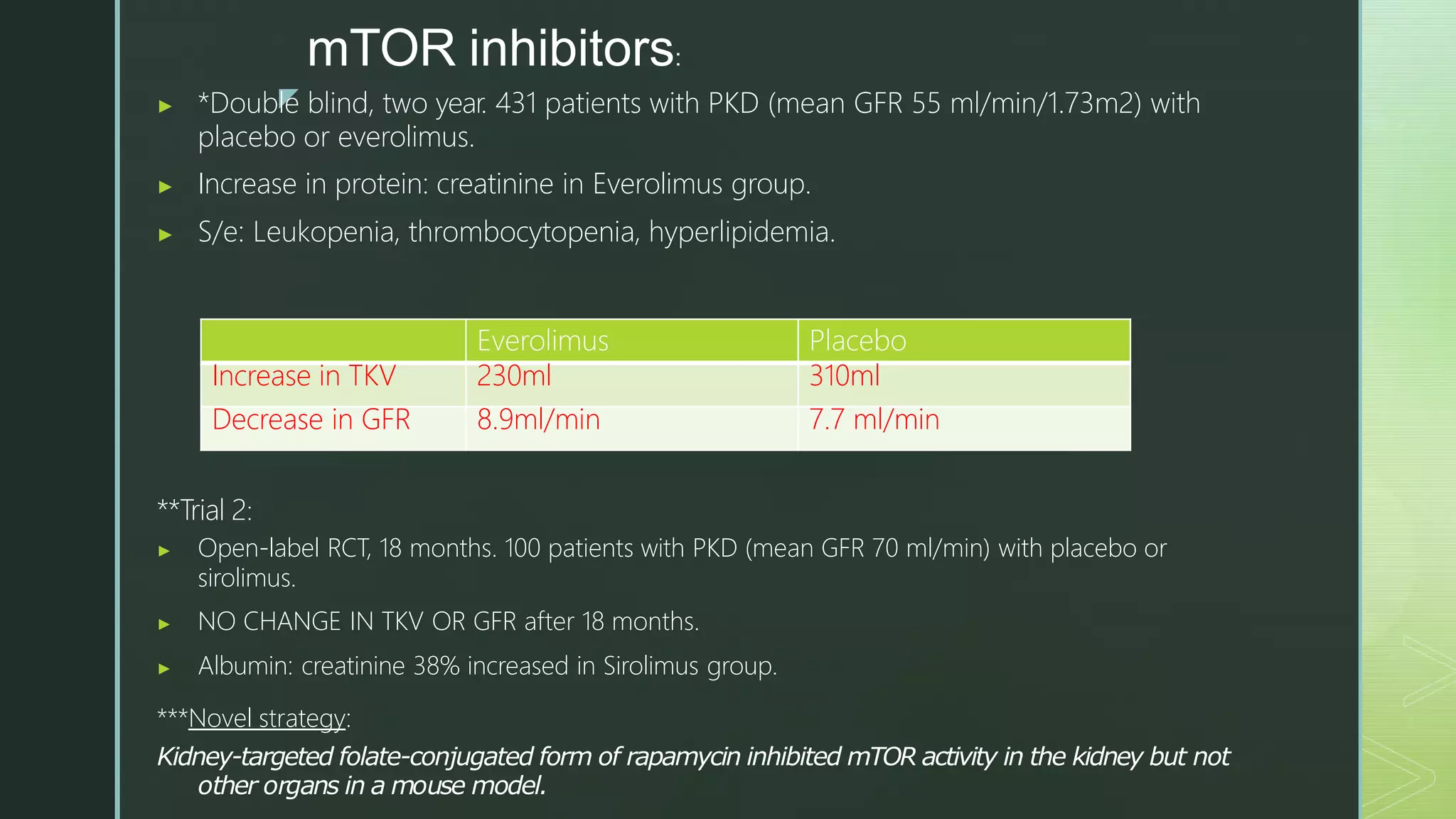
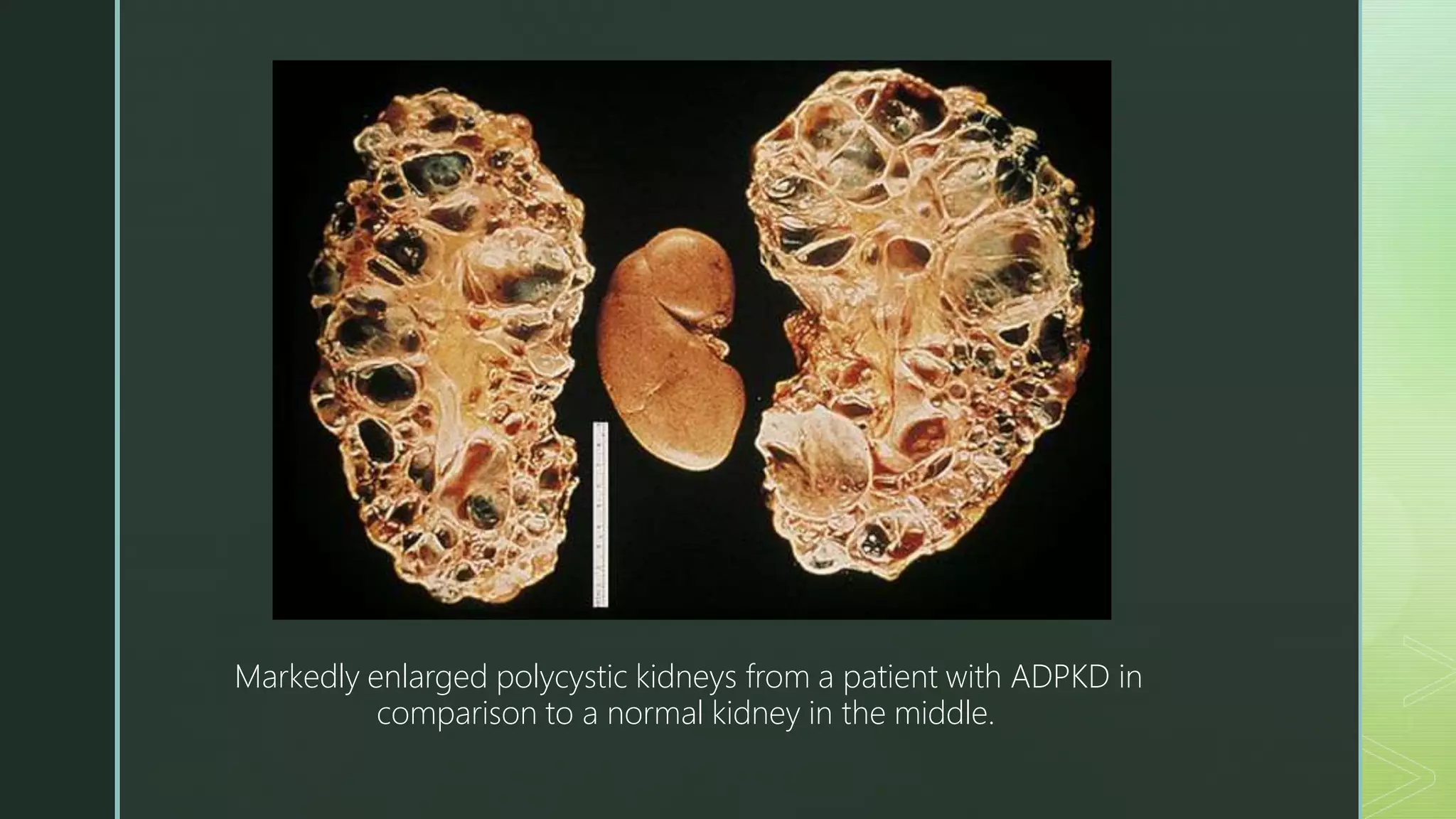
The document summarizes autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD). It describes ADPKD as a genetic disorder caused by mutations in PKD1 and PKD2 genes, resulting in multiple bilateral renal cysts and cysts in other organs. The cysts compress and replace normal kidney tissue, leading to renal failure in half of patients by age 60. Symptoms include hypertension, pain, hematuria and kidney enlargement. Management focuses on blood pressure control and treating complications such as infections and stones. New therapies targeting cyst growth include mTOR inhibitors and vasopressin receptor antagonists, but kidney transplantation remains the only cure for renal failure.




![PKD1 PKD2
Located on Chromosome 16
[16p13]
Located on Chromosome 4
[4q21-q23]
Codes for Polycystin 1 protein
(PC1)
Codes for Polycystin 2 protein
(PC2)
Associated with more severe
phenotype
Less severe phenotype
Incidence: 85% Incidence: 15%
Median age of ESRD 53 years Median age of ESRD 73 years
Code PC1: Cilia, Basolateral
membranes, inter-membrane
junctions.
Helps in cell-cell adhesions.
Code PC2: non-selective cation
channel, permeable to Calcium.
Located mainly in SER.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-230308175022-2804ec52/75/Presentation-1-pptx-6-2048.jpg)



![z
Clinical Manifestations
▶ Asymptomatic [until the fourth to fifth decade of life and are
diagnosed by incidental discoveries]
▶ Pain—in the abdomen, flank, or back—is the most common initial
complaint. [may result from renal cyst infection, hemorrhage or
nephrolithiasis]
▶ Gross hematuria [resulting from cyst rupture occurs in ~40% of
patients and many of them will have recurrent episodes.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-230308175022-2804ec52/75/Presentation-1-pptx-10-2048.jpg)

![z
Complications
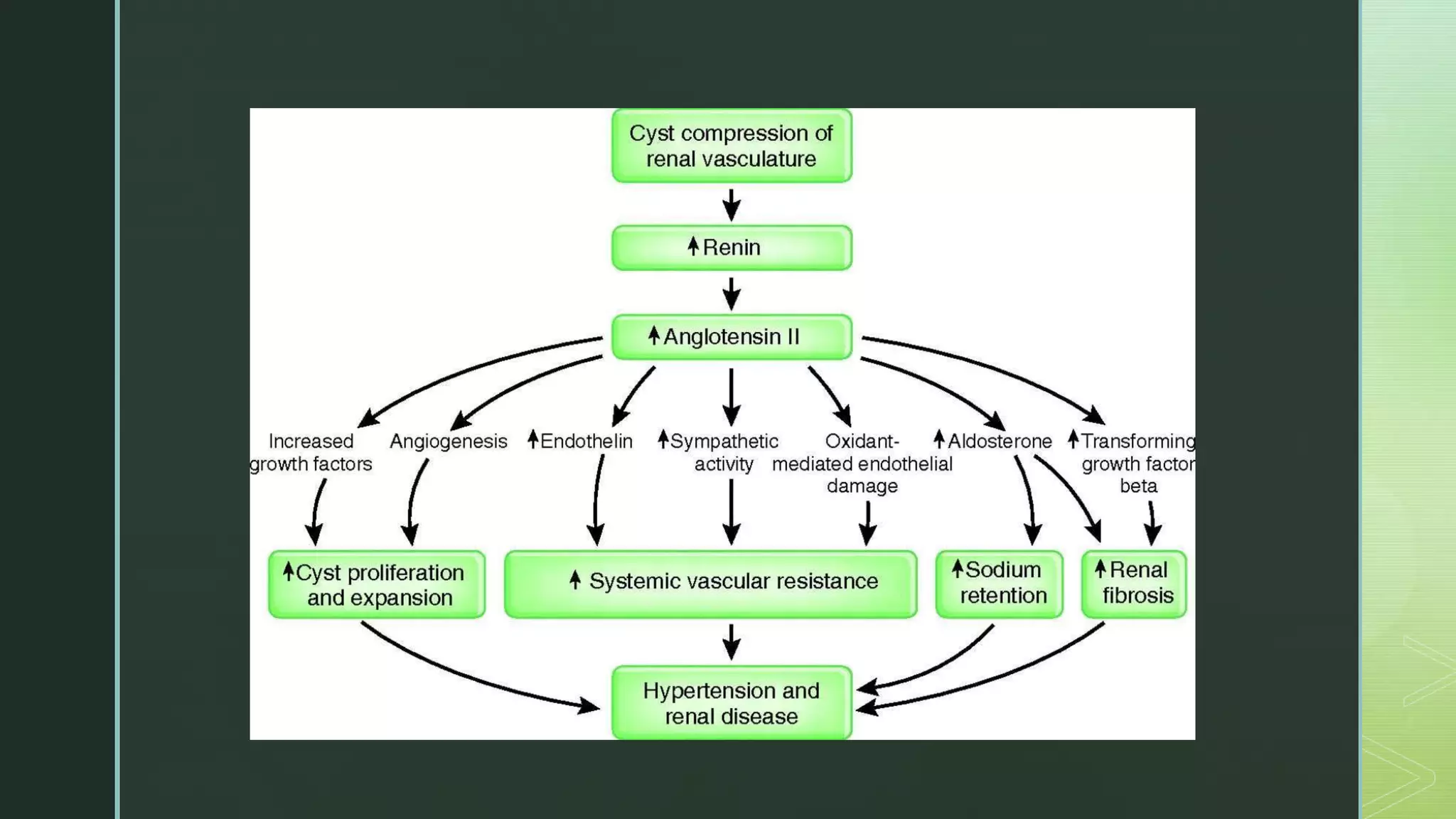
▶ Hypertension 60-100% [Cardiovascular complications are the major
cause of mortality in patients with ADPKD]
▶ Infection [second most common cause of death for patients with
ADPKD]
▶ Gross hematuria 50%
▶ Nephrolithiasis 20-25%
▶ Renal failure 50% by age 60 (PKD1) and 85% in lifetime
▶ Polycystic liver disease
▶ Cerebral aneurysms [occur in 4-10% of patients]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-230308175022-2804ec52/75/Presentation-1-pptx-12-2048.jpg)






![z
Investigations
▶ Serum electrolytes, including calcium and phosphate
▶ Complete blood cell count [An increased hematocrit may result
from increased erythropoietin secretion from cysts]
▶ Urinalysis
▶ Urine culture
▶ Uric acid determination
▶ parathyroid hormone assay](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-230308175022-2804ec52/75/Presentation-1-pptx-21-2048.jpg)
![▶ Complete blood cell count :
An increased hematocrit may result from increased
erythropoietin secretion from cysts.
▶ Urinalysis:
Decrease in urine-concentrating ability,
Microalbuminuria occurs in 35% of patients,
Nephrotic-range proteinuria is uncommon]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-230308175022-2804ec52/75/Presentation-1-pptx-22-2048.jpg)
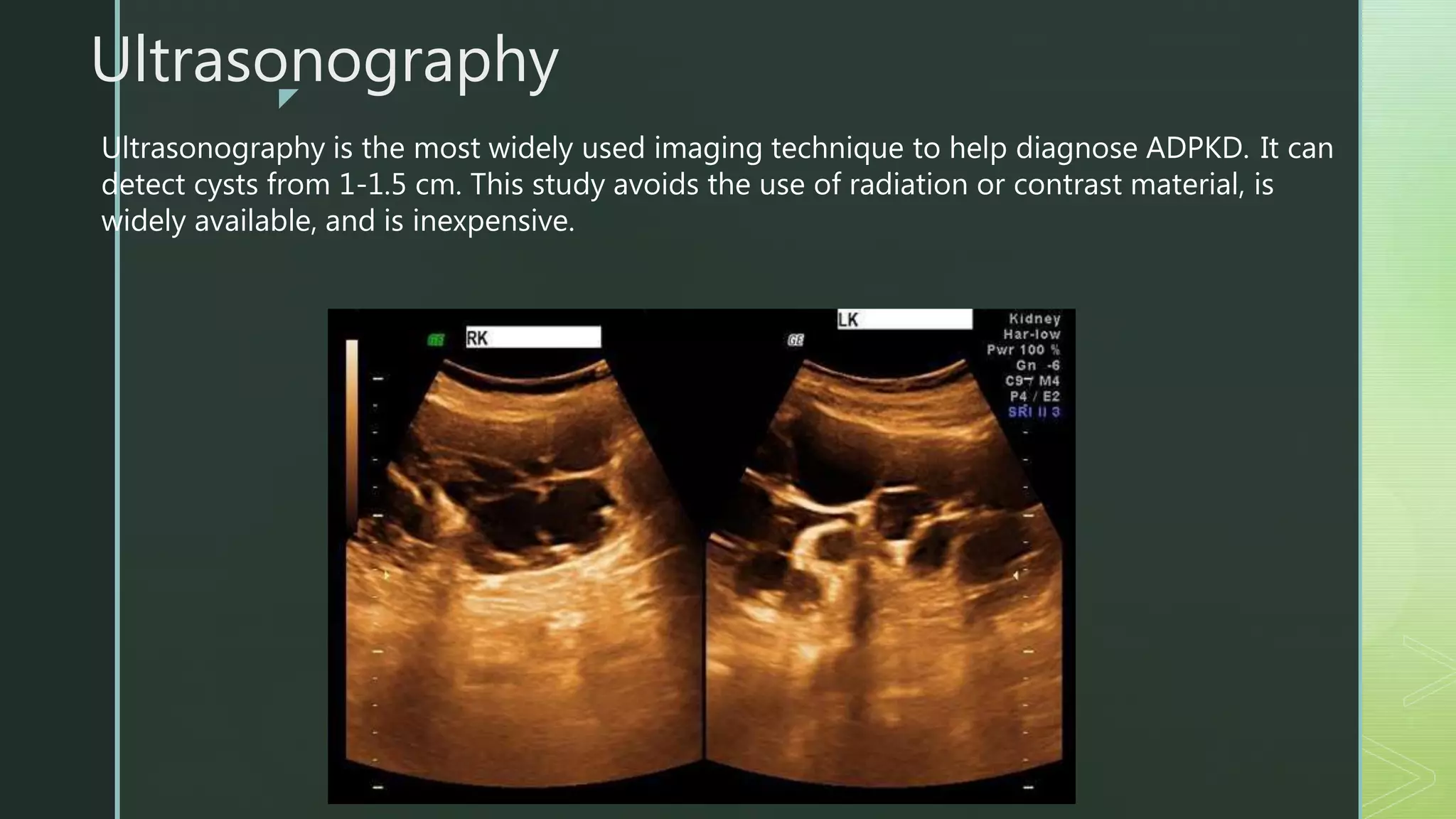
![z
Imaging
▶ Ultrasonography [is the procedure of choice]
▶ Computed tomography (CT) scan
▶ Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Genetic testing
▶ Genetic testing by linkage analyses and mutational analyses](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/presentation1-230308175022-2804ec52/75/Presentation-1-pptx-23-2048.jpg)