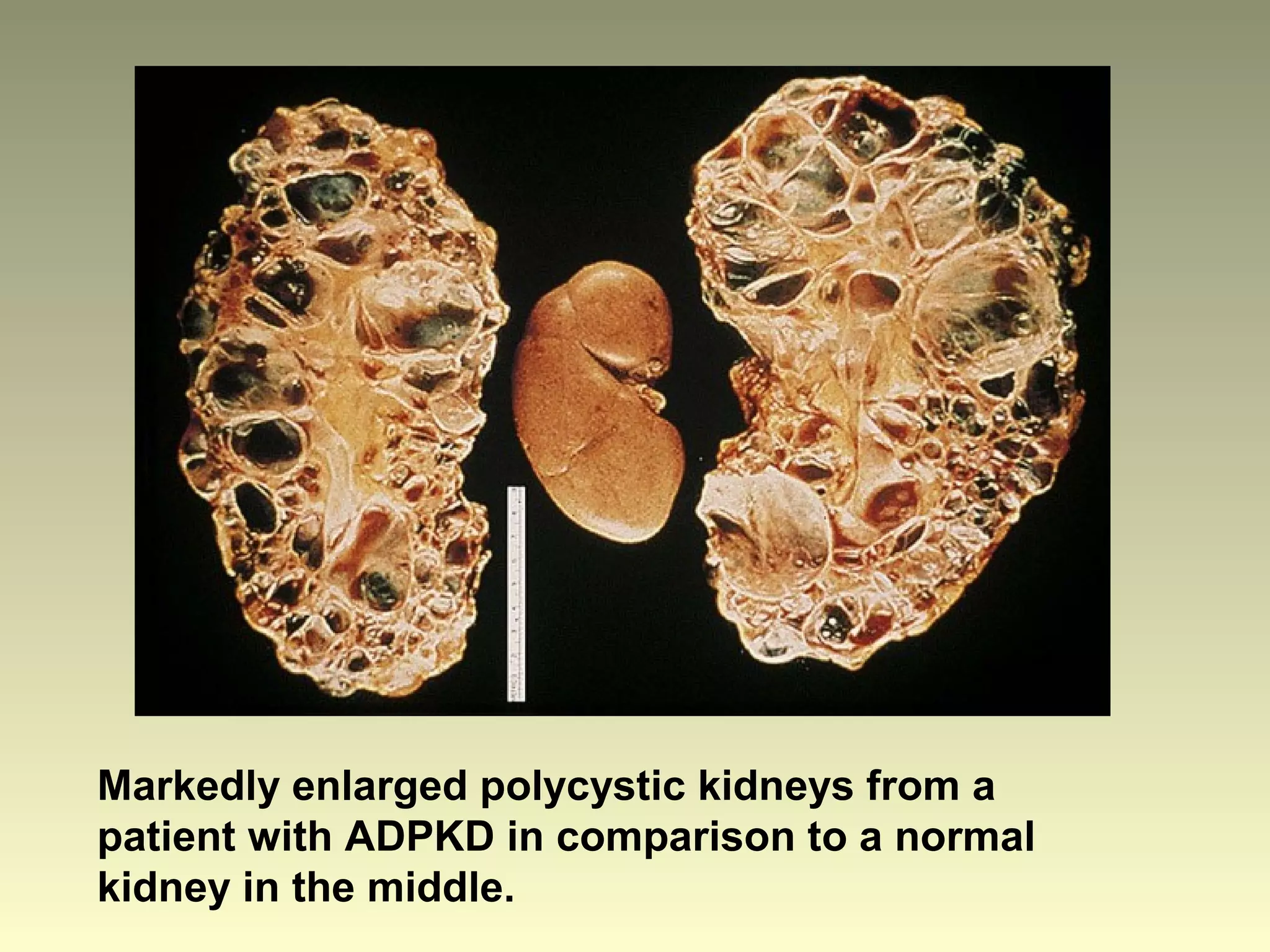
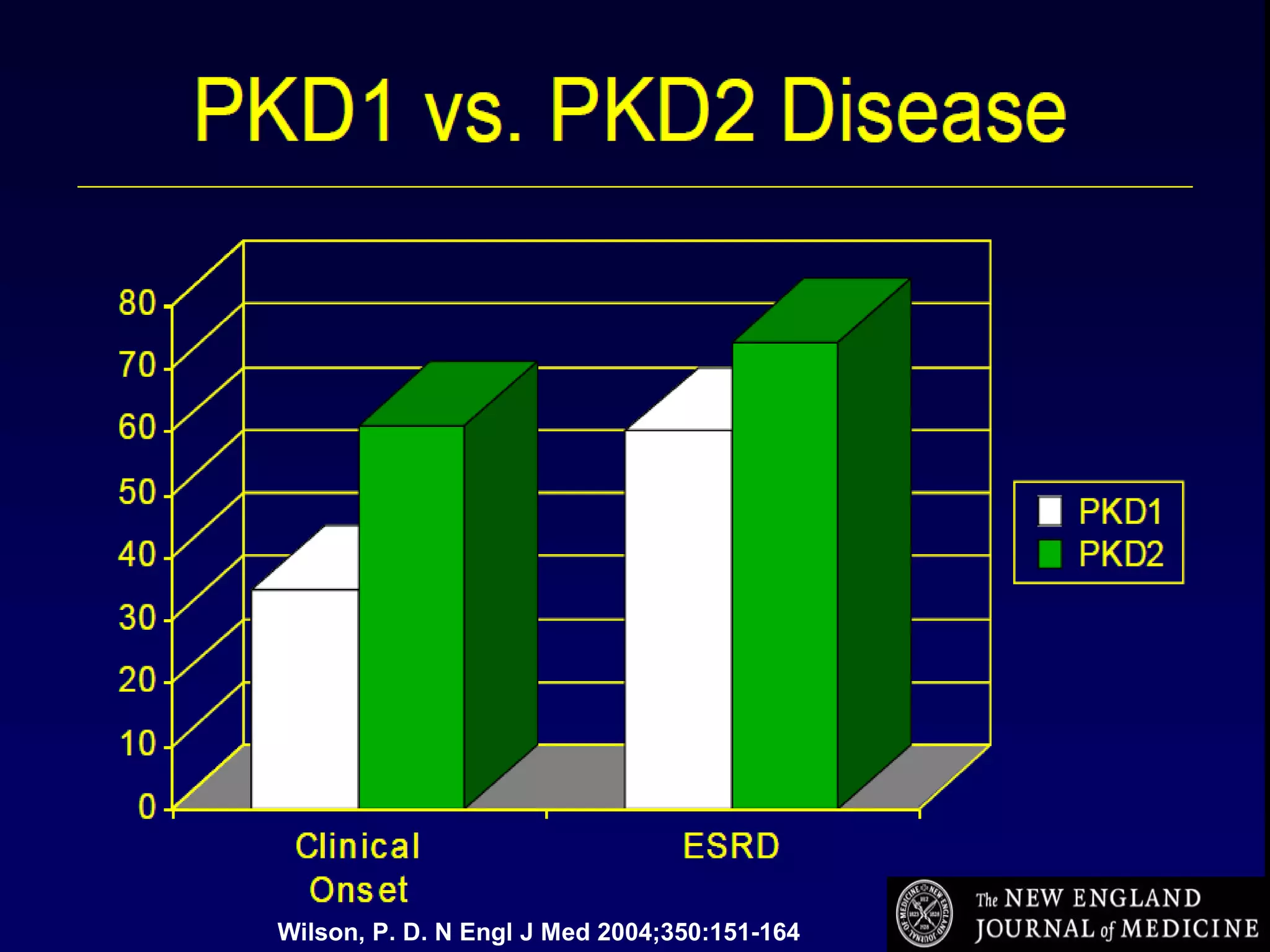
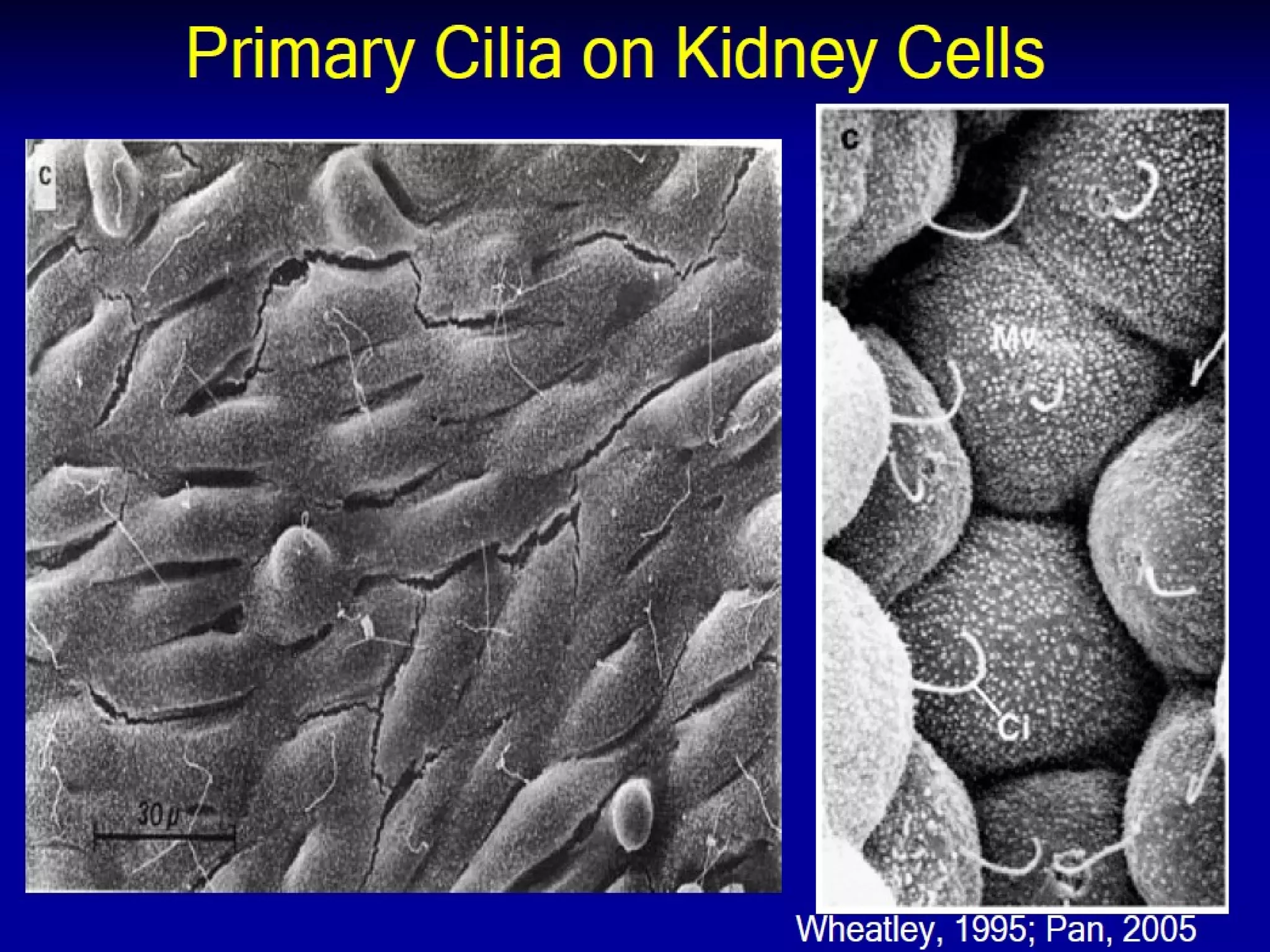
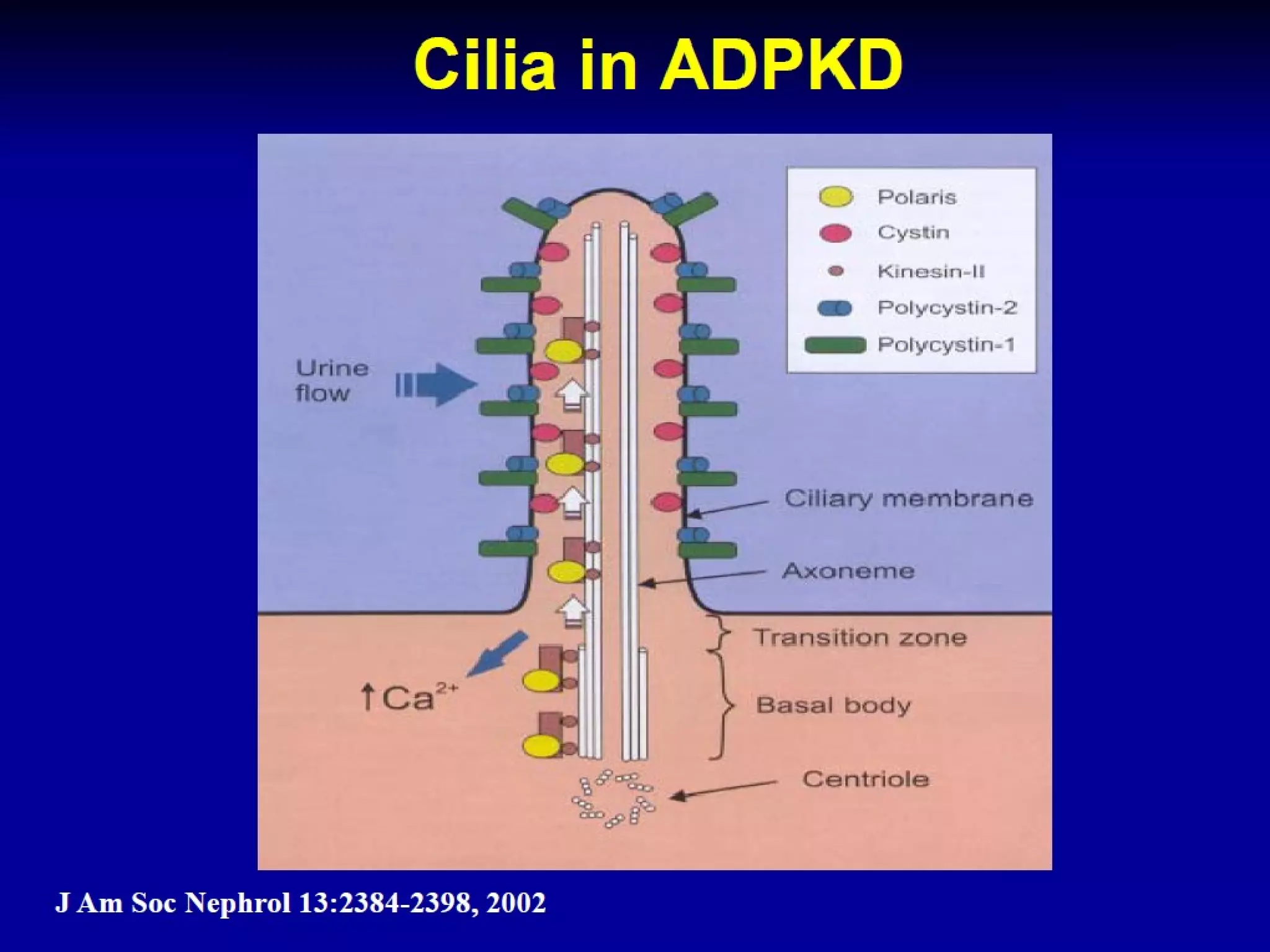
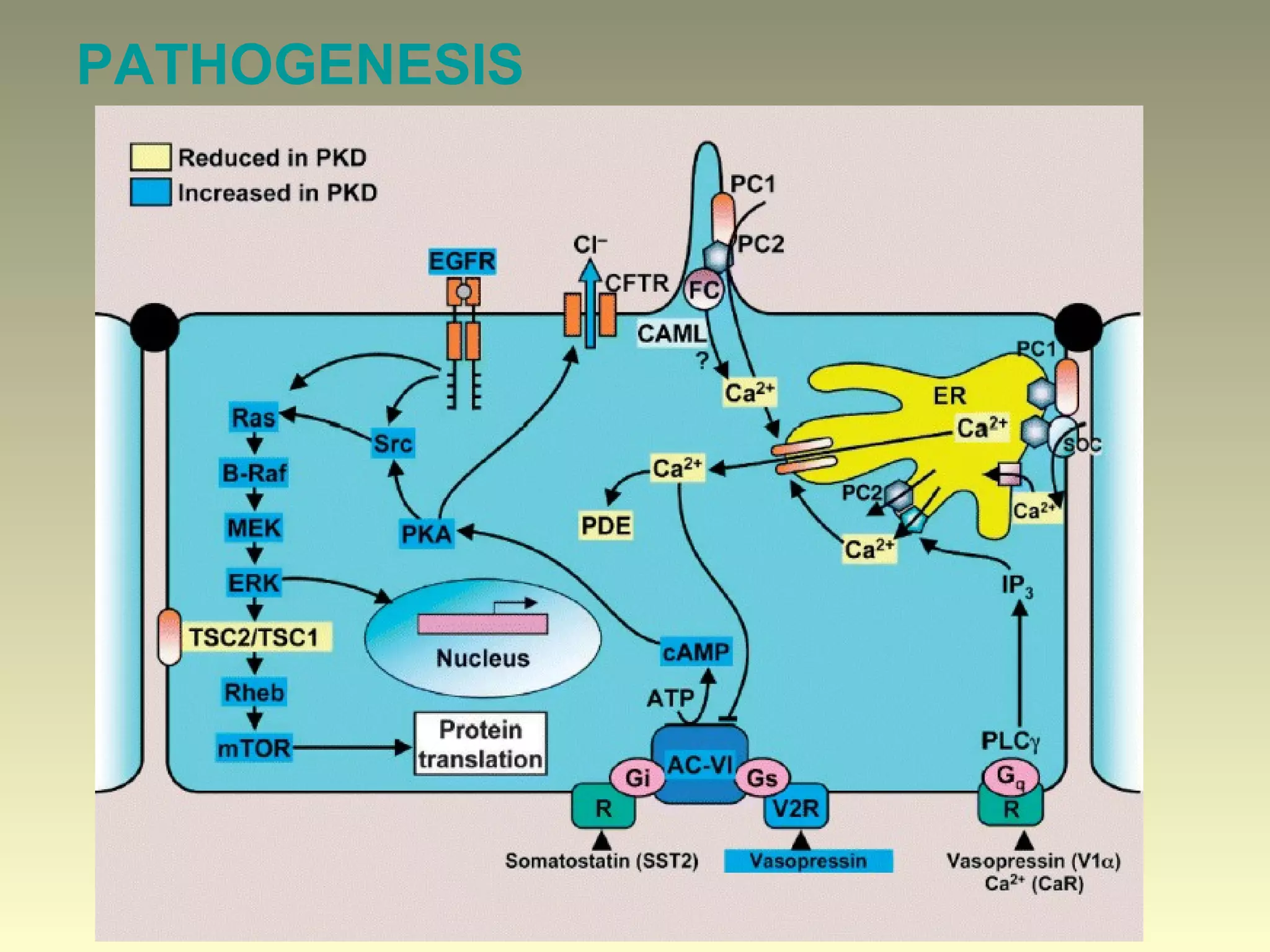
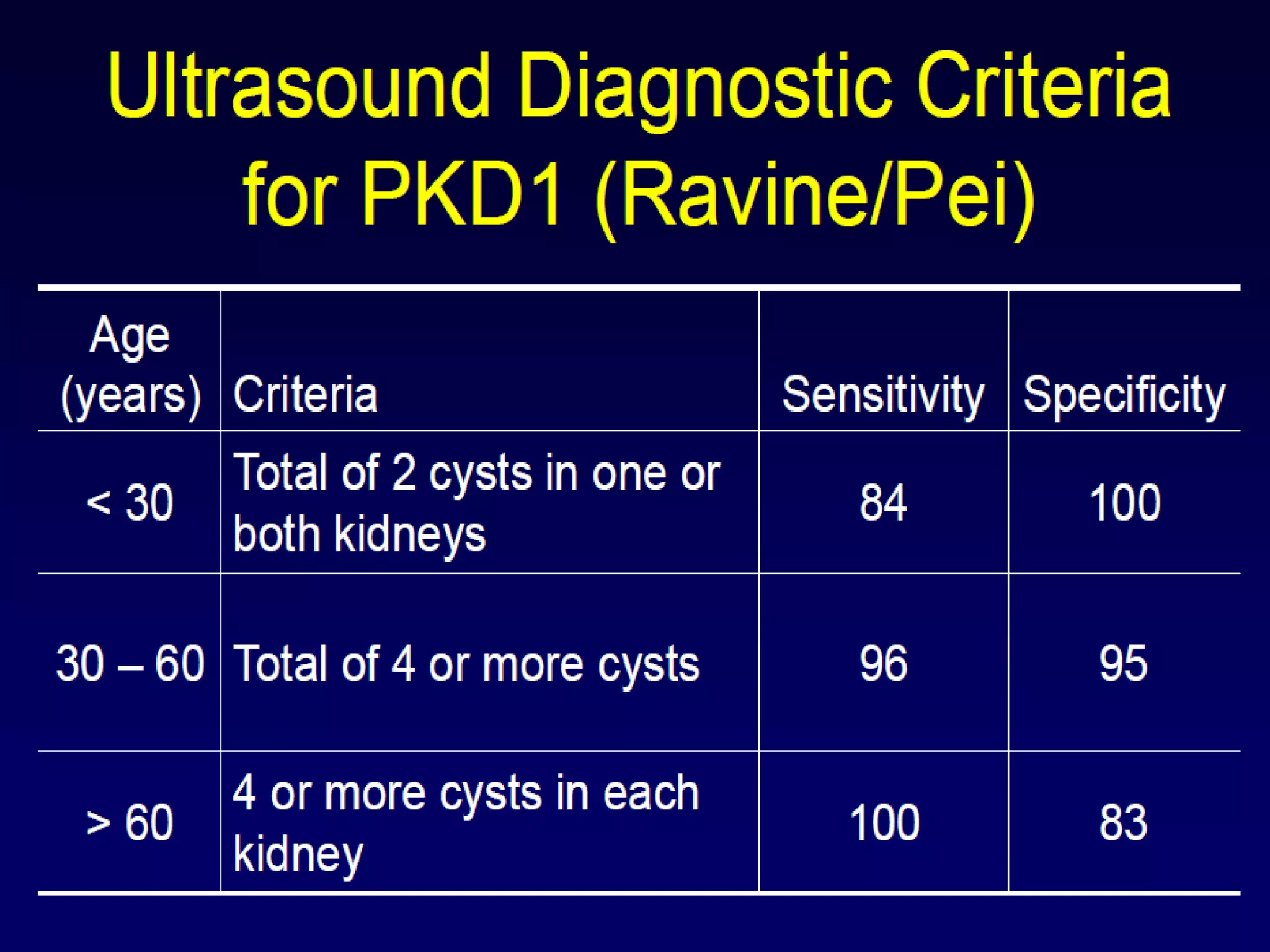
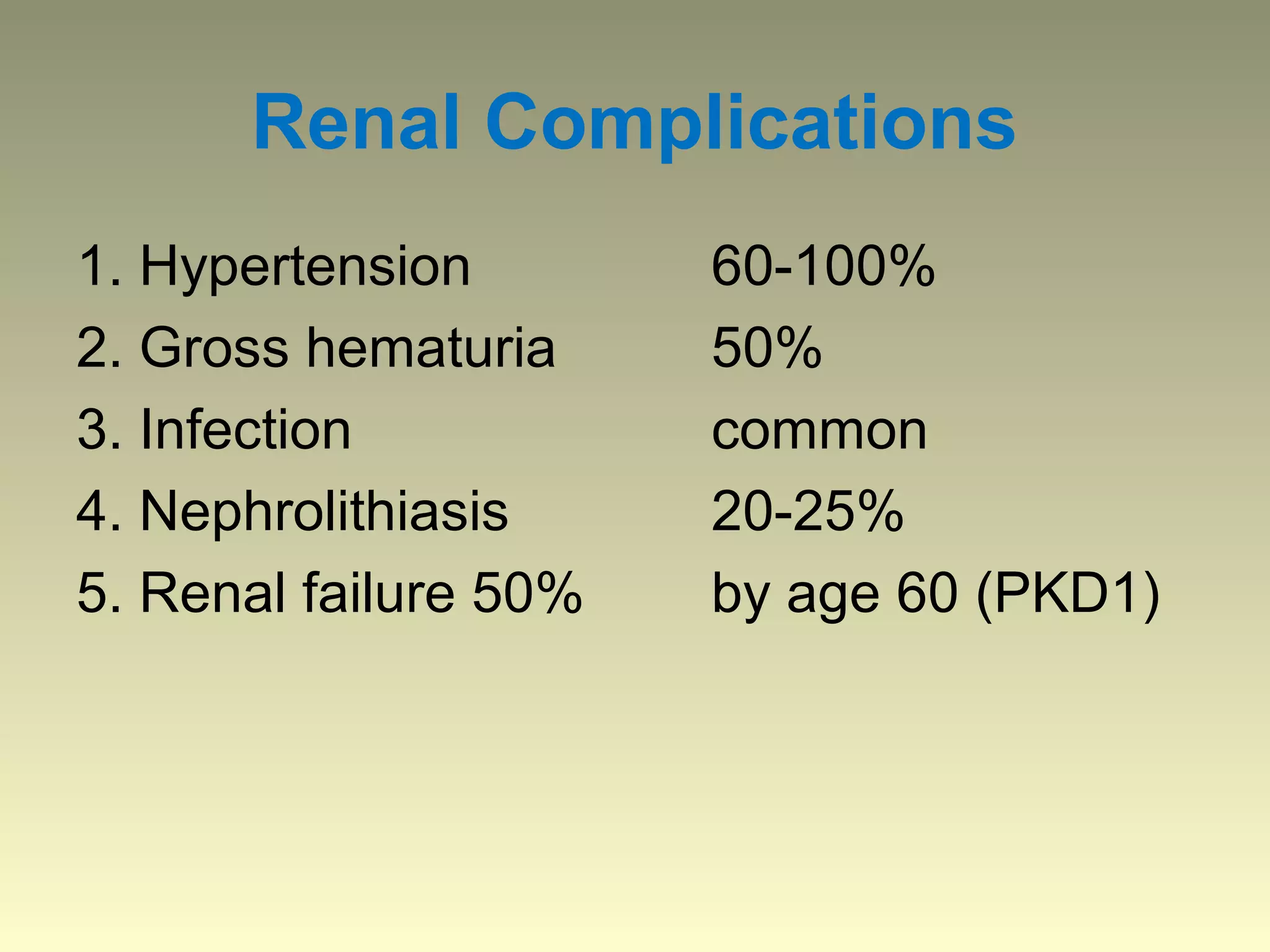
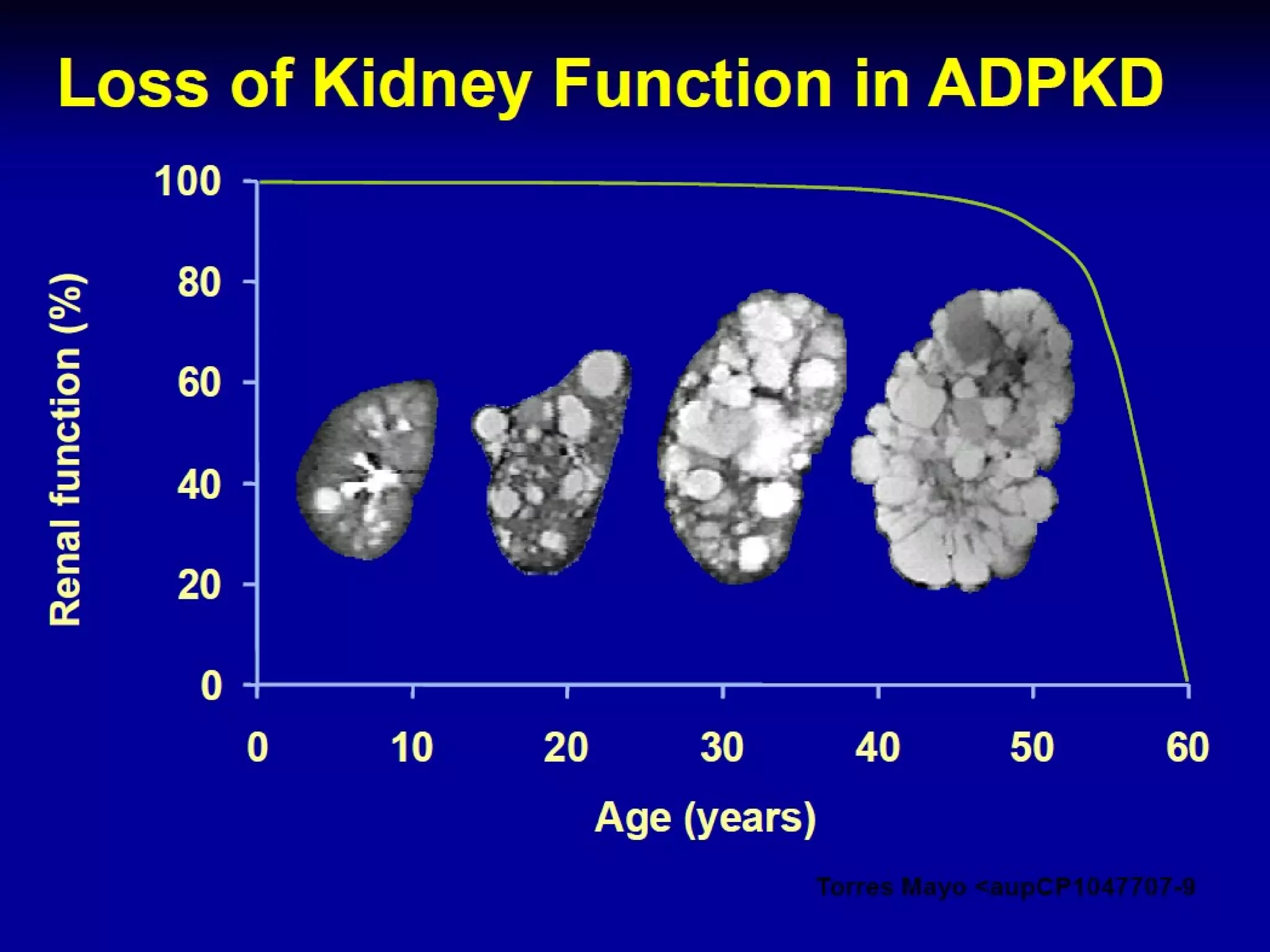
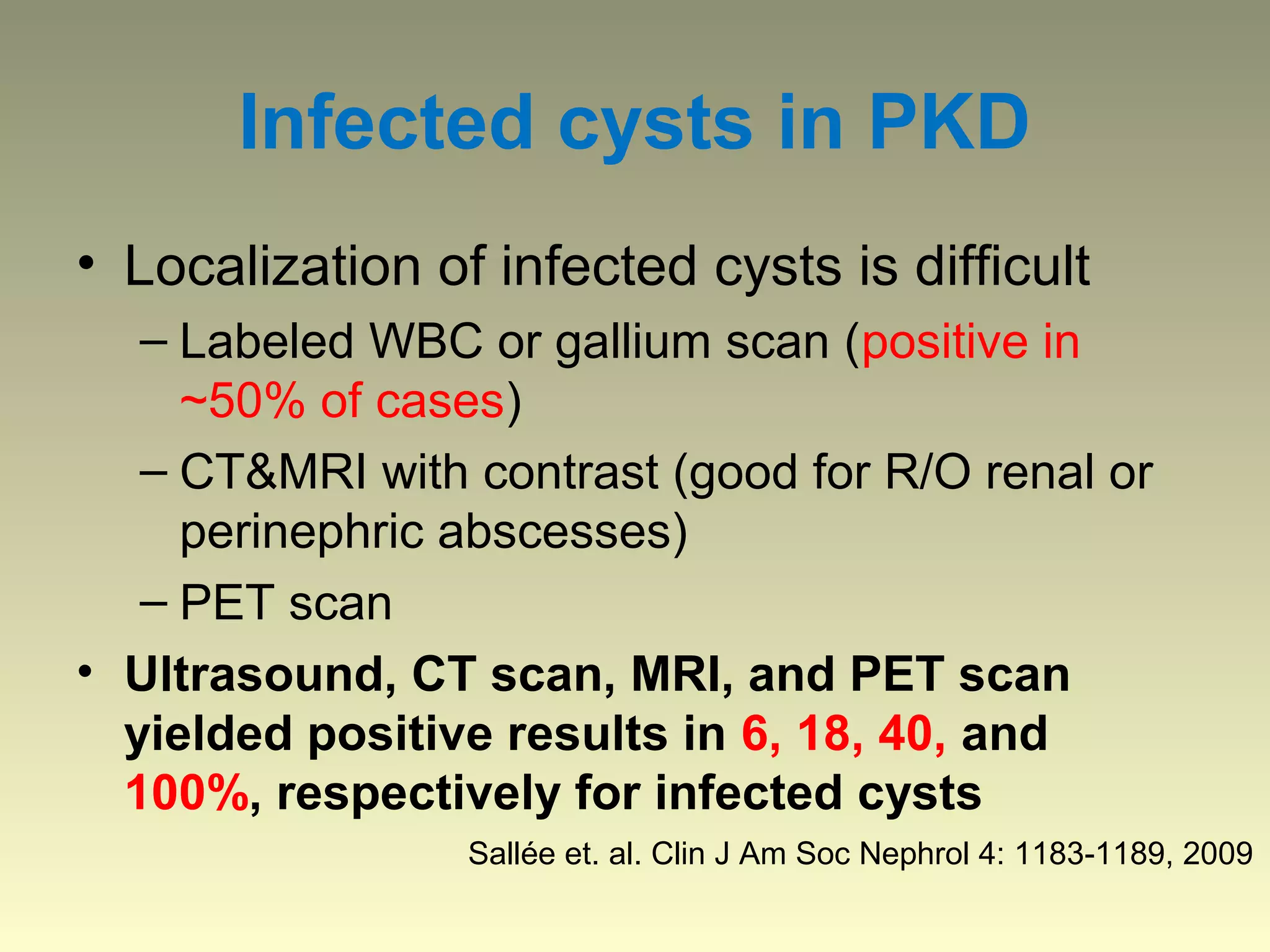
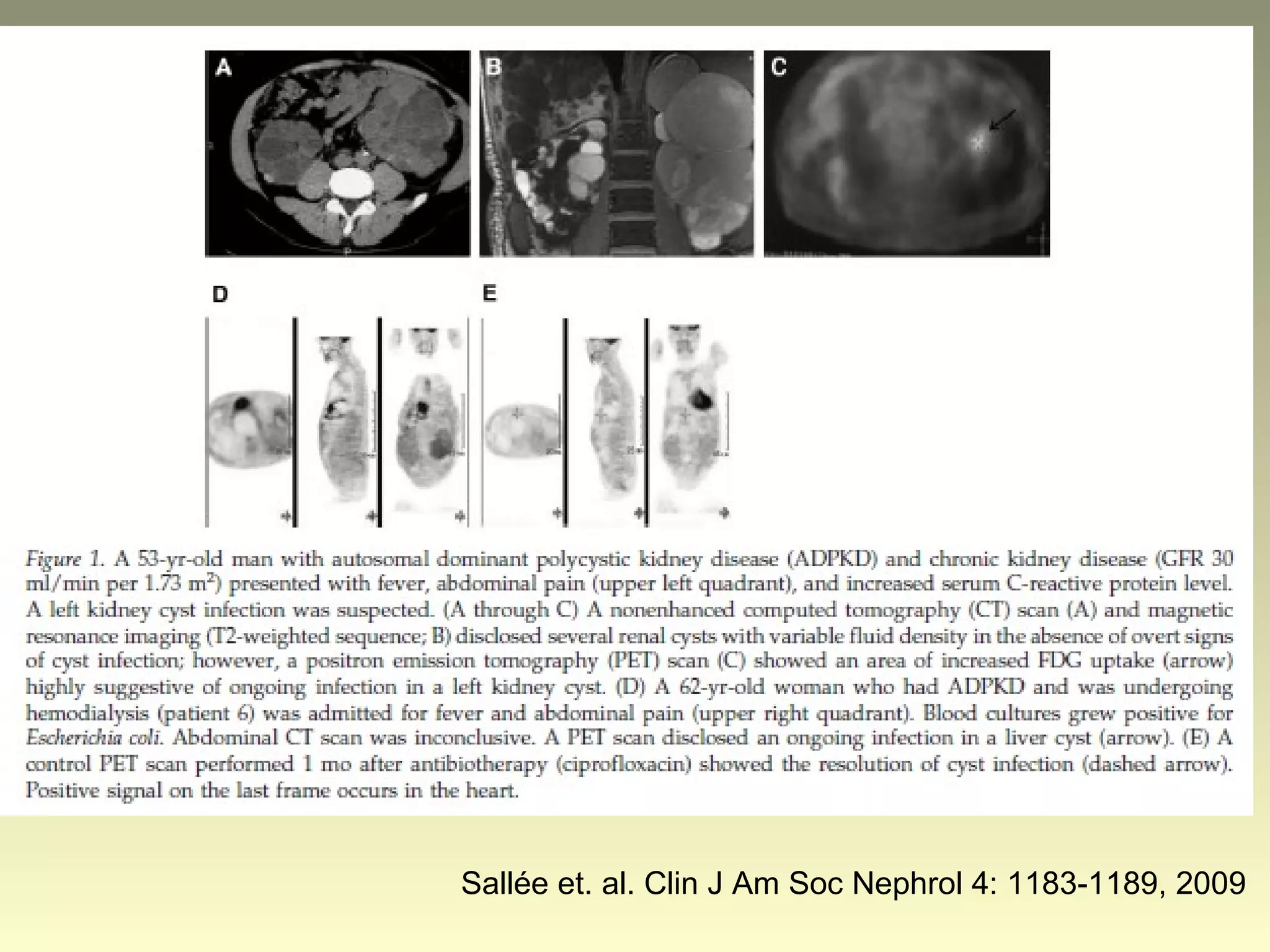
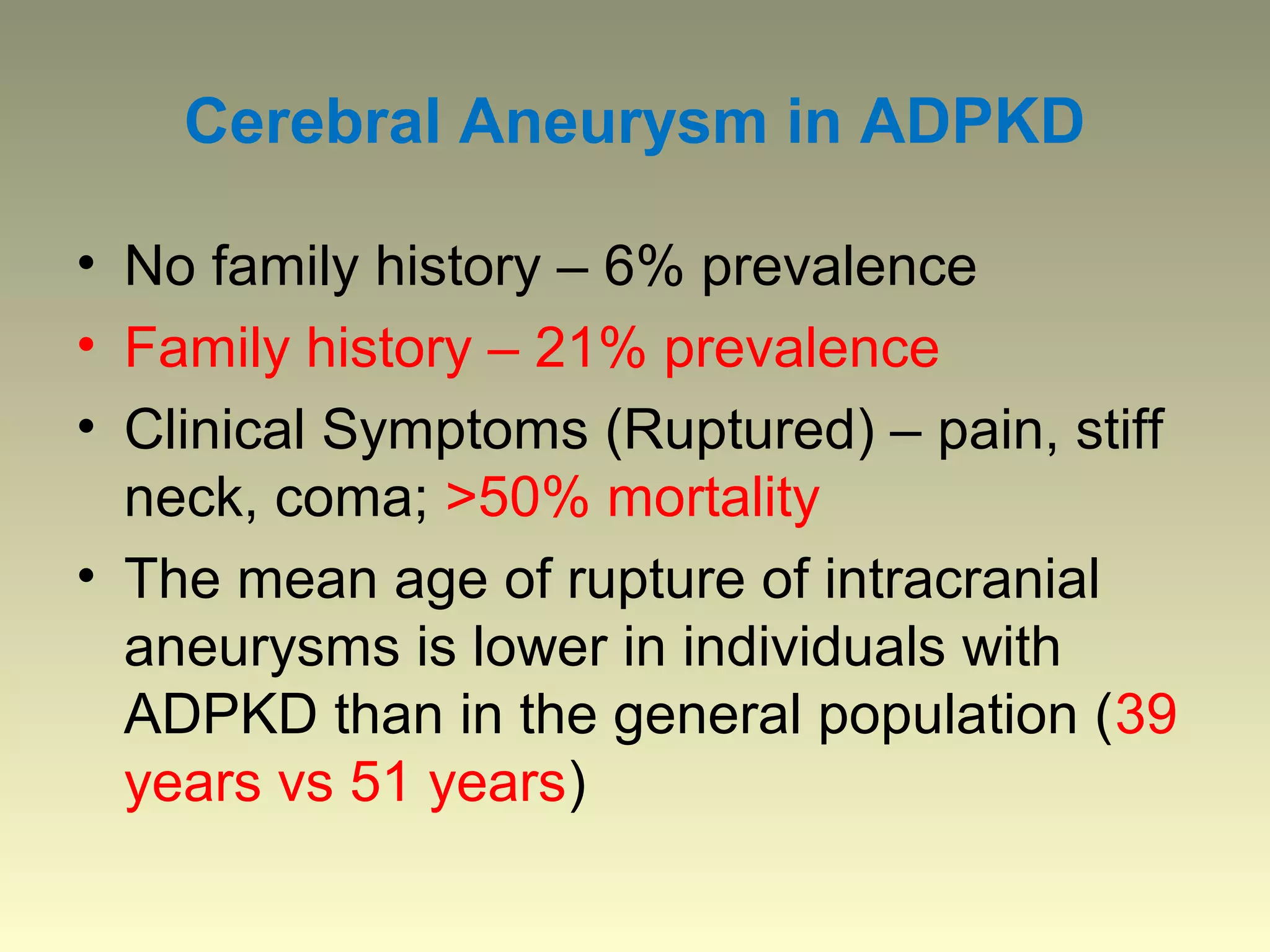
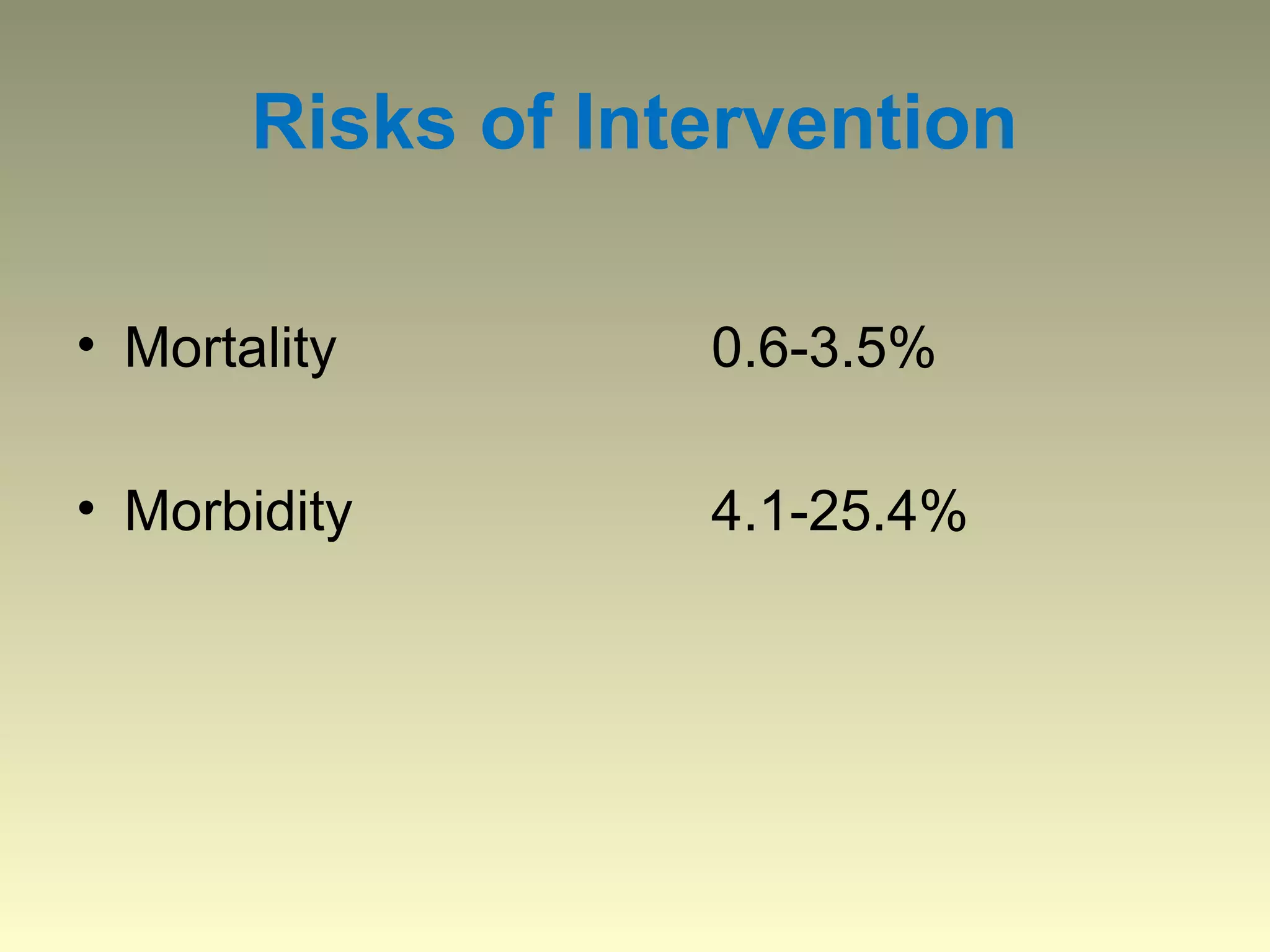
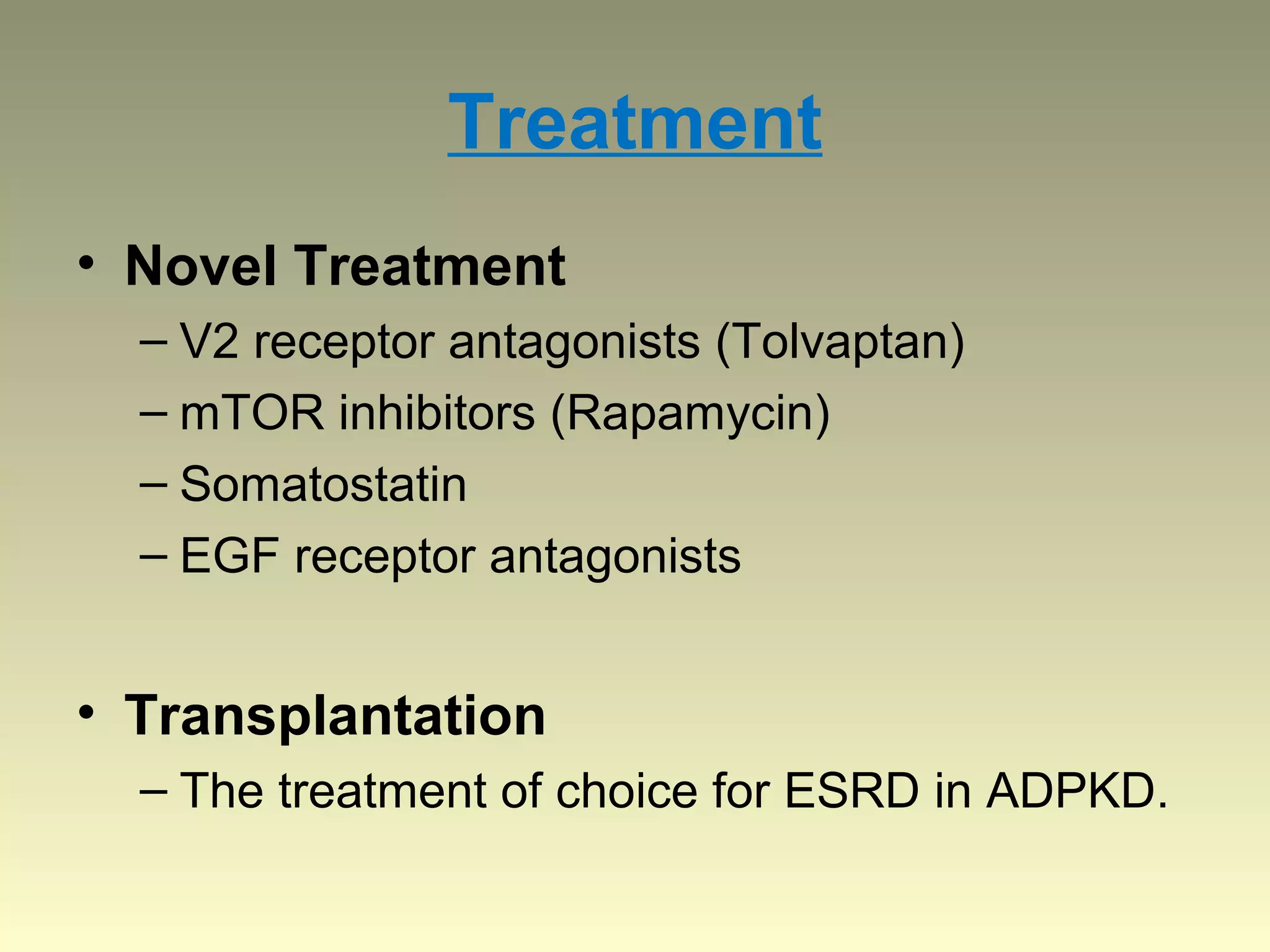
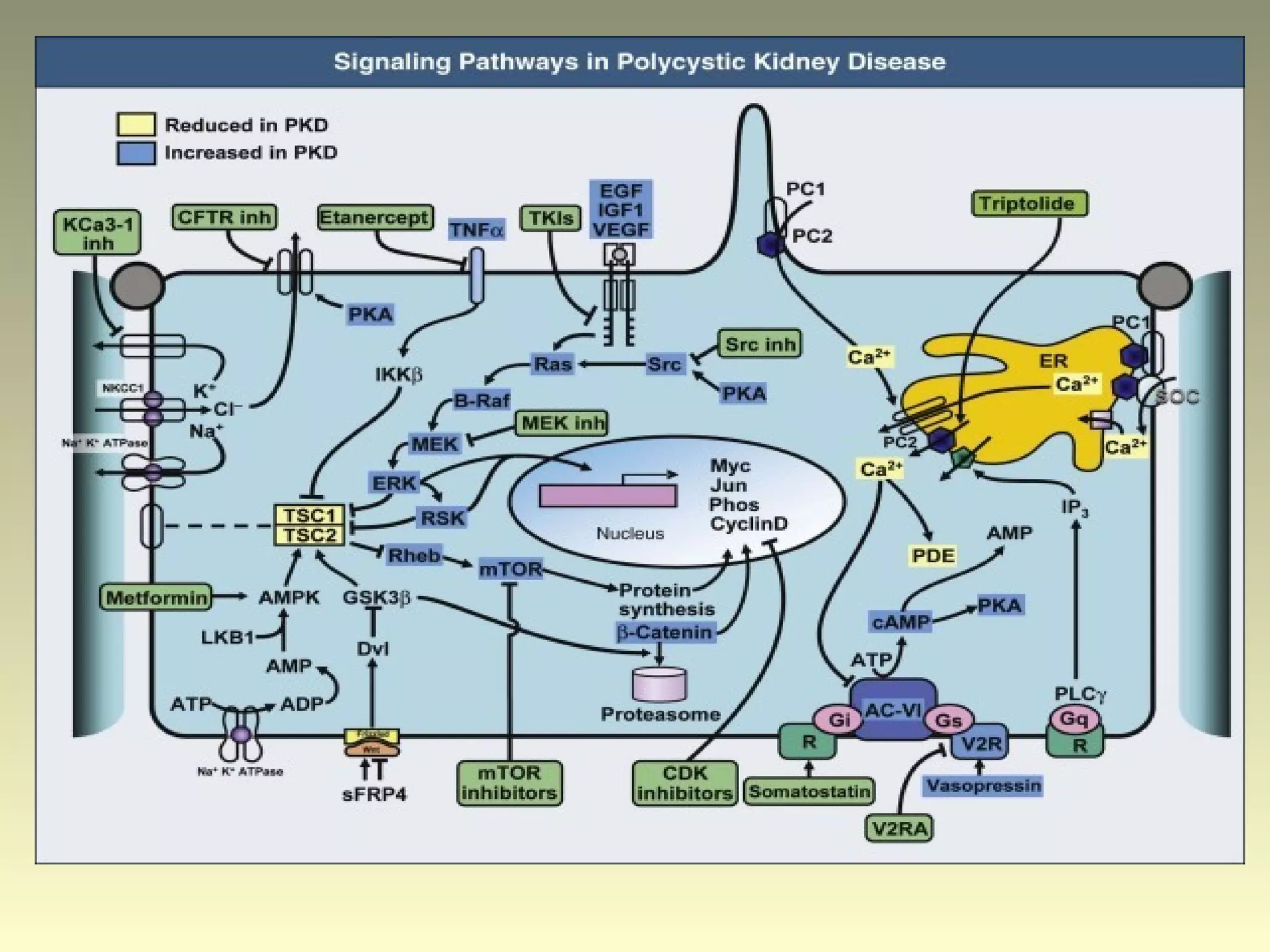
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) is a genetic disorder characterized by multiple bilateral renal cysts that can lead to kidney failure, with mutations in two genes causing cyst formation through disordered polycystin function; it commonly causes hypertension, pain, infection, and kidney failure and can involve the liver and other organs; management focuses on slowing progression through blood pressure control, pain management, and potentially targeting the renin-angiotensin system or mTOR pathway.