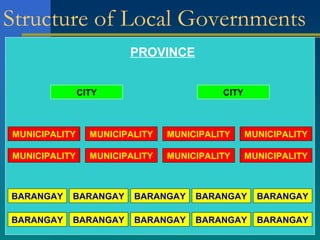
The Local Government Code of 1991 establishes the framework for local governance in the Philippines, emphasizing principles like local autonomy, decentralization, and accountability. It outlines the structures and requirements for various local government units (LGUs), including provinces, cities, municipalities, and barangays, including criteria for their creation and governance. Additionally, it grants LGUs certain powers and responsibilities, while also providing for national supervision and financial provisions.