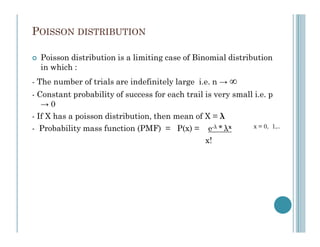
This document presents information about the Poisson distribution. It defines key properties of the Poisson distribution, including that the mean and variance of a Poisson distribution are equal to the parameter λ. It then works through 6 example problems calculating probabilities for various Poisson distributions based on given values of λ. The problems calculate probabilities of certain numbers of events occurring, like errors on a page or accidents on a highway, given the average rate of occurrences.