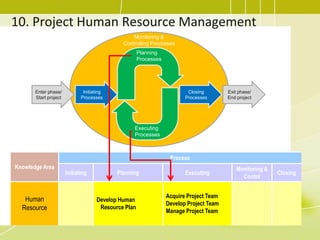
The document discusses project human resource management and outlines several key processes:
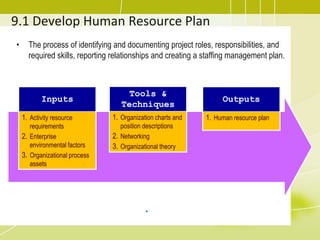
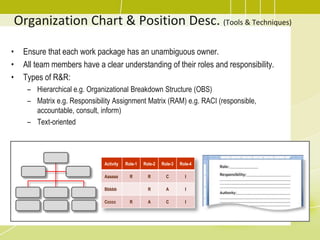
1) Developing a human resource plan to identify project roles, responsibilities, and required skills.
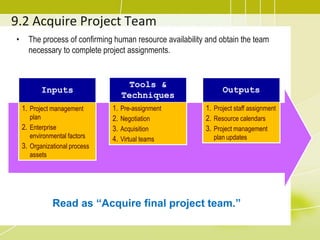
2) Acquiring the project team by confirming availability of resources and obtaining the necessary team members.
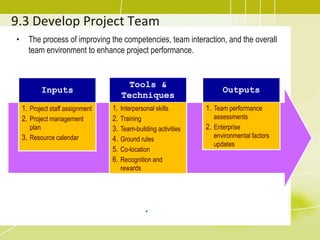
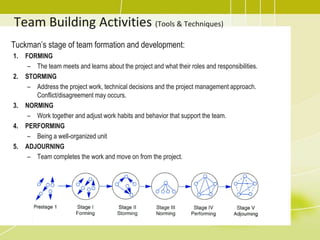
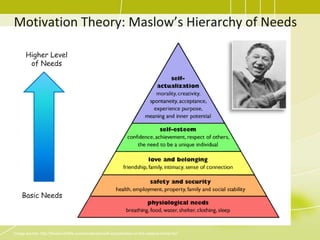
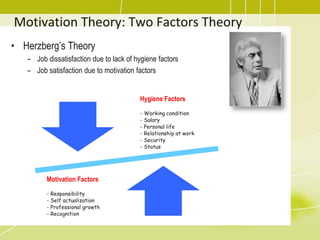
3) Developing the project team through training, team building activities, and establishing guidelines to improve competencies and team interaction.
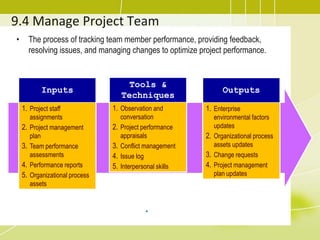
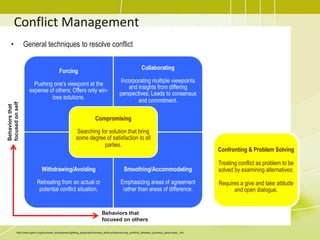
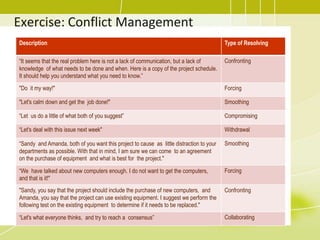
4) Managing the project team by tracking performance, providing feedback, resolving issues, and managing changes.