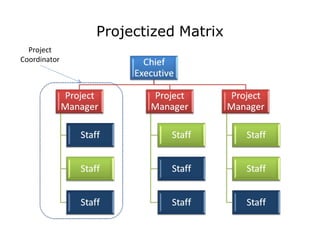
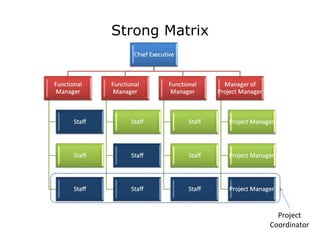
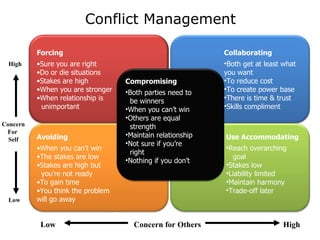
The document discusses several aspects of project management including project integration management, scope management, time management, cost management, quality management, human resource management, communications management, risk management, and procurement management. It then focuses on organizational influences on project management and the roles of different project coordinators depending on the organizational structure. The rest of the document discusses human resource planning, developing and managing the project team, communication planning and methods, performance reporting, and stakeholder management.