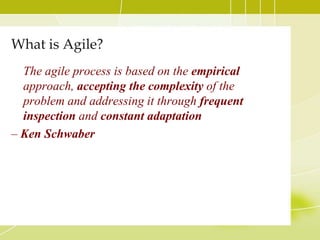
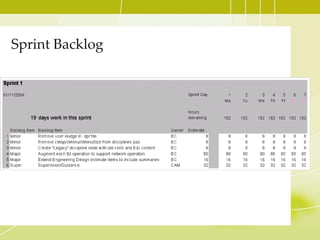
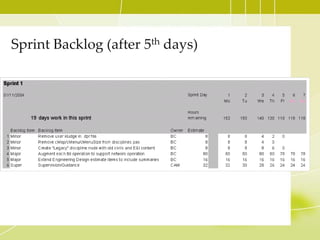
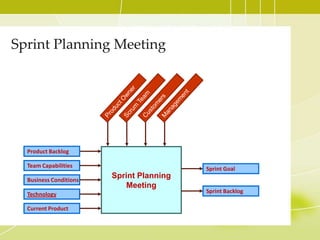
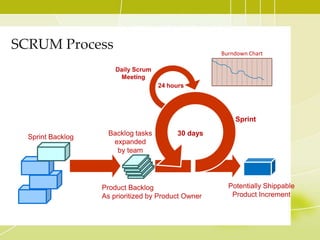
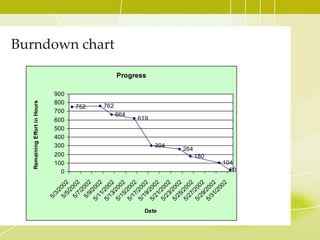
This document provides an overview of Agile methodology and SCRUM. It discusses the principles of Agile, including its emphasis on collaboration, adaptability, and delivering working software frequently. It then describes SCRUM in more detail, covering the roles of Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Team. The key SCRUM artifacts like Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Burn Down Chart are explained. It also outlines the core SCRUM ceremonies of Sprint Planning, Daily Scrum, Sprint Review, and Retrospective. The document concludes by discussing challenges of adopting SCRUM and provides tips for SCRUM Team members.