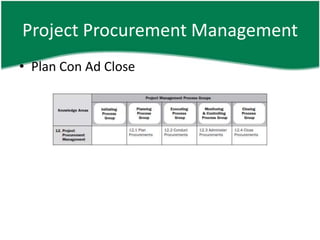
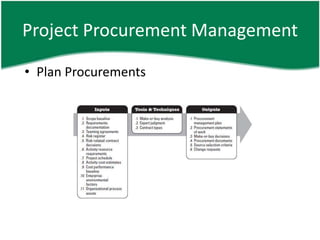
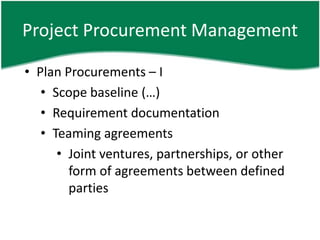
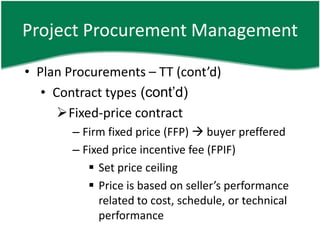
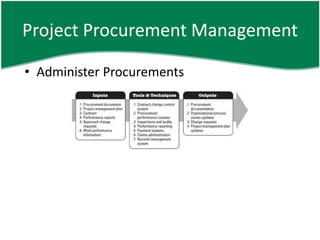
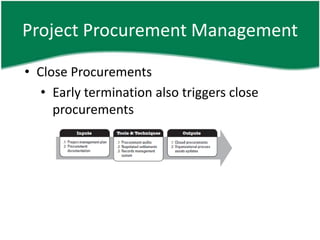
This document provides an overview of a training session on PMP and CAPM exam preparation. It discusses the key topics covered in each of the sessions, including the nine knowledge areas and five process groups. It then goes into detail about project procurement management, explaining the processes of planning procurements, conducting procurements, administering procurements, and closing procurements.