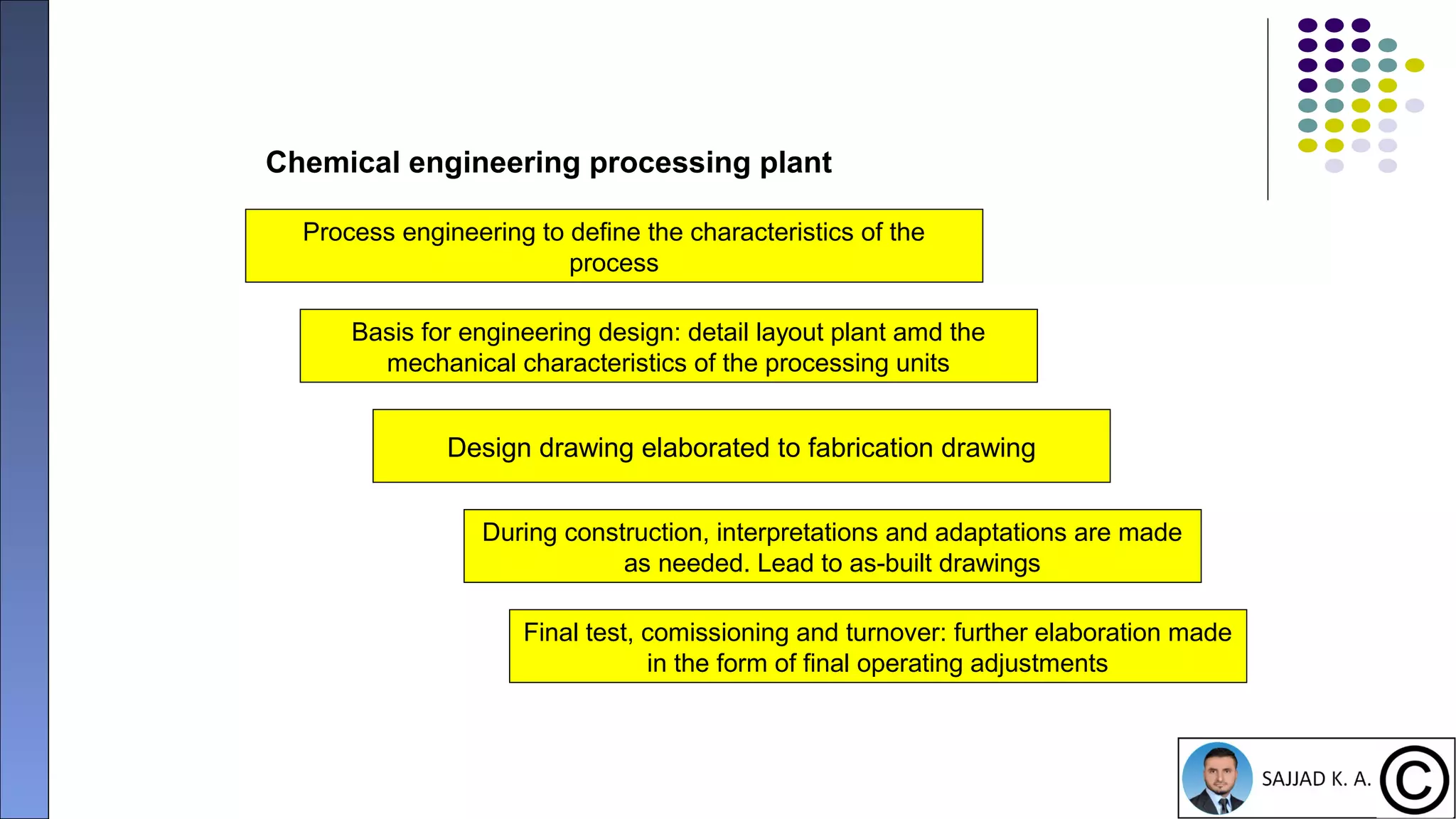
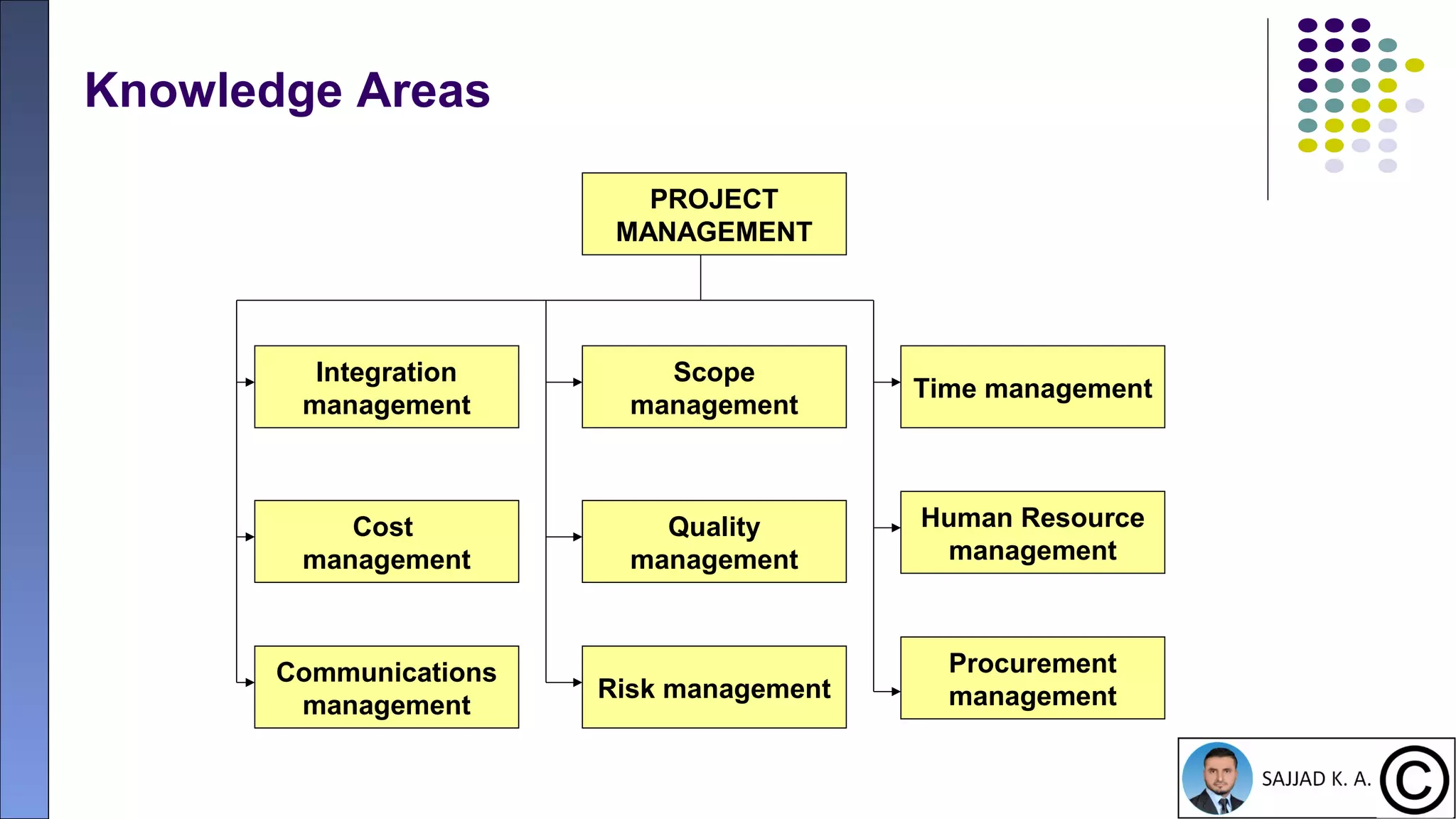
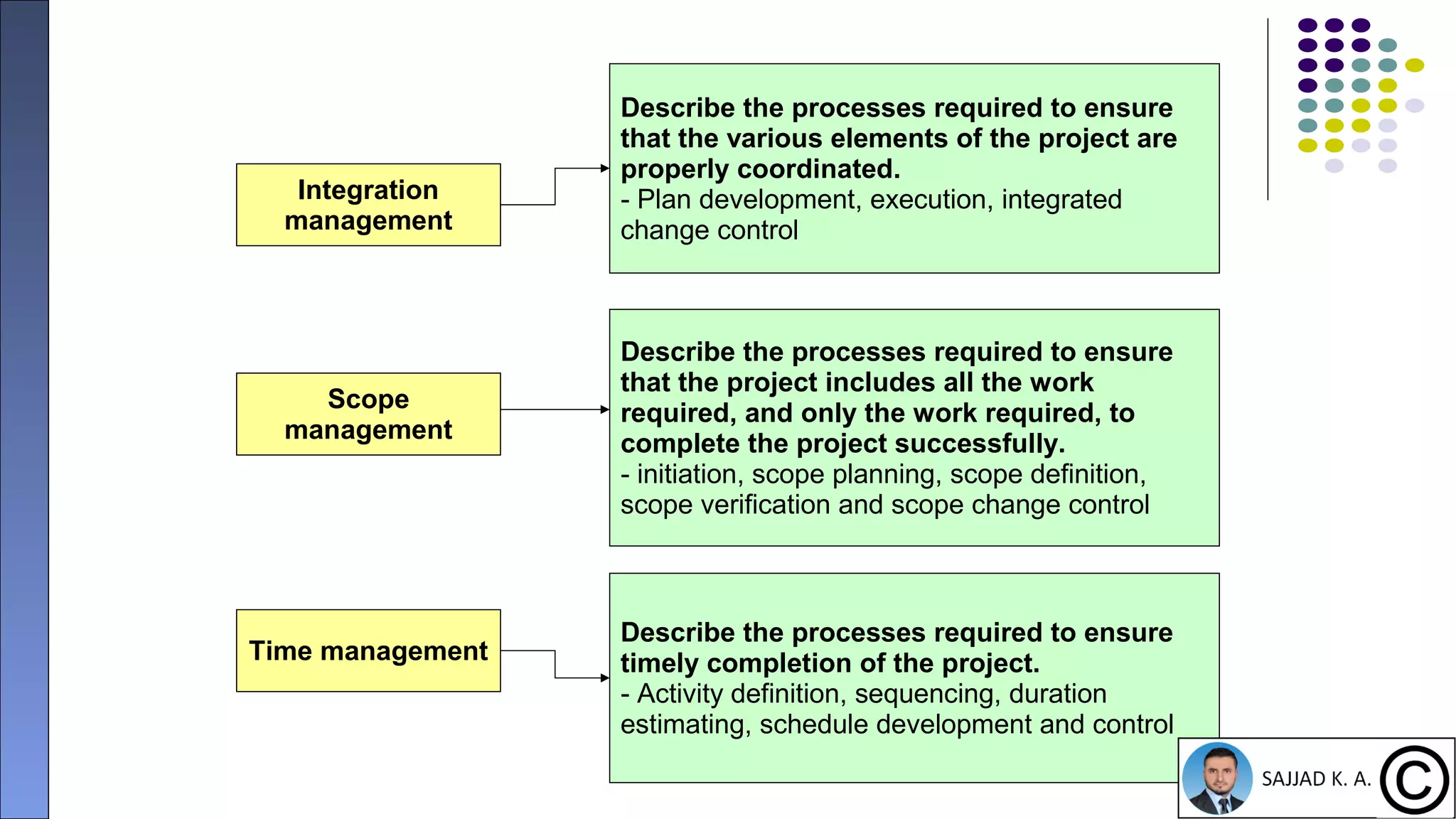
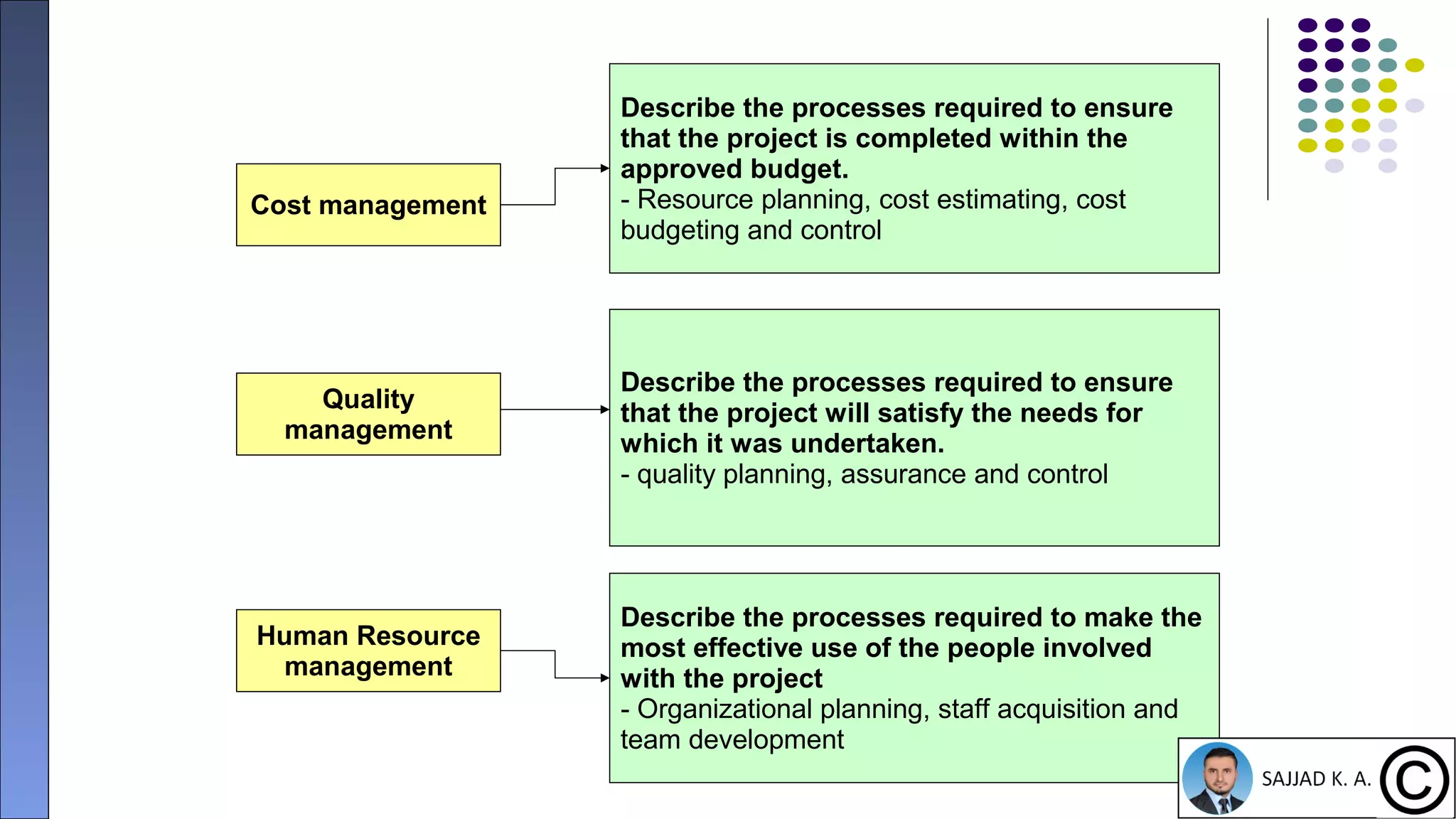
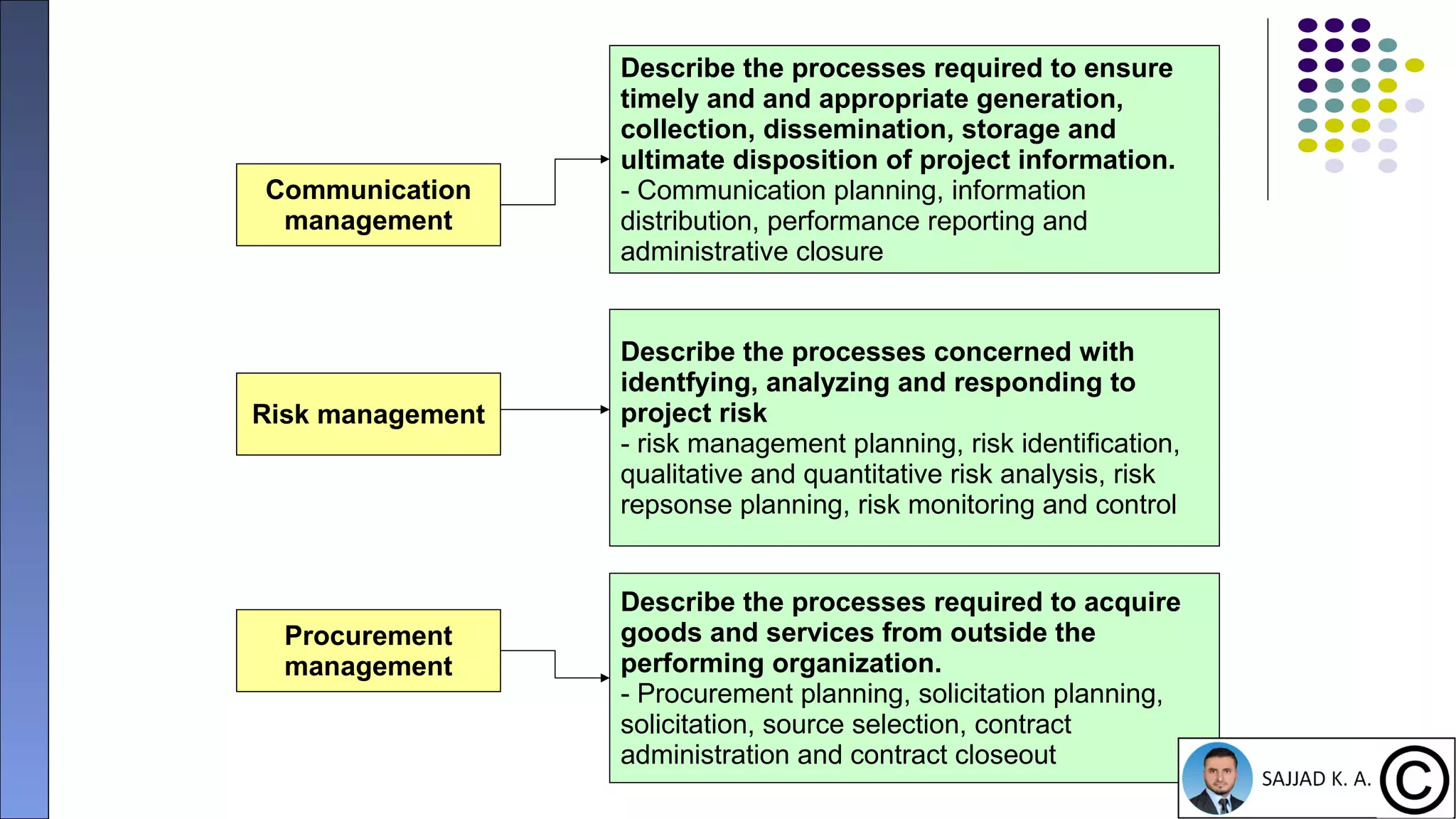
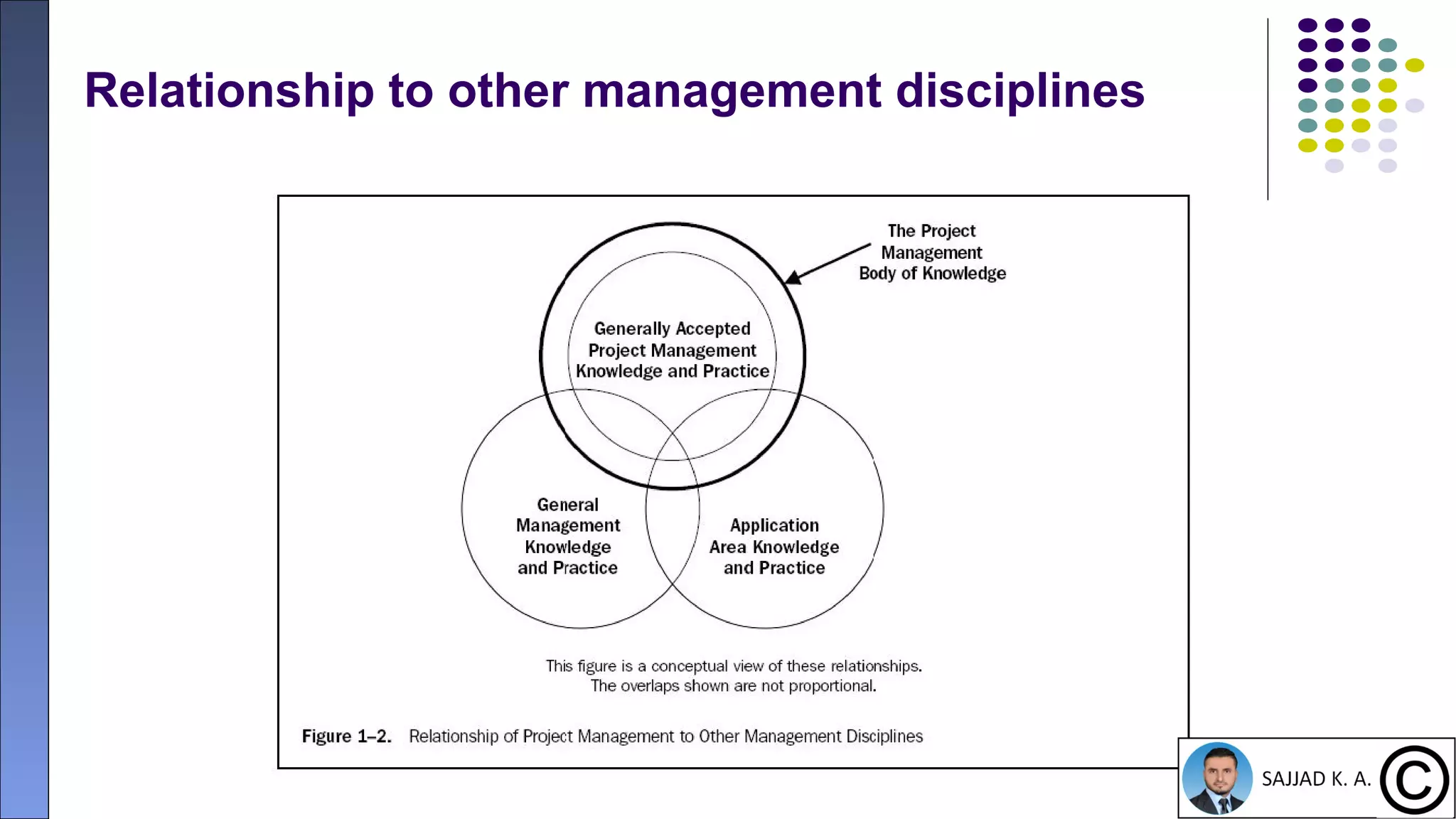
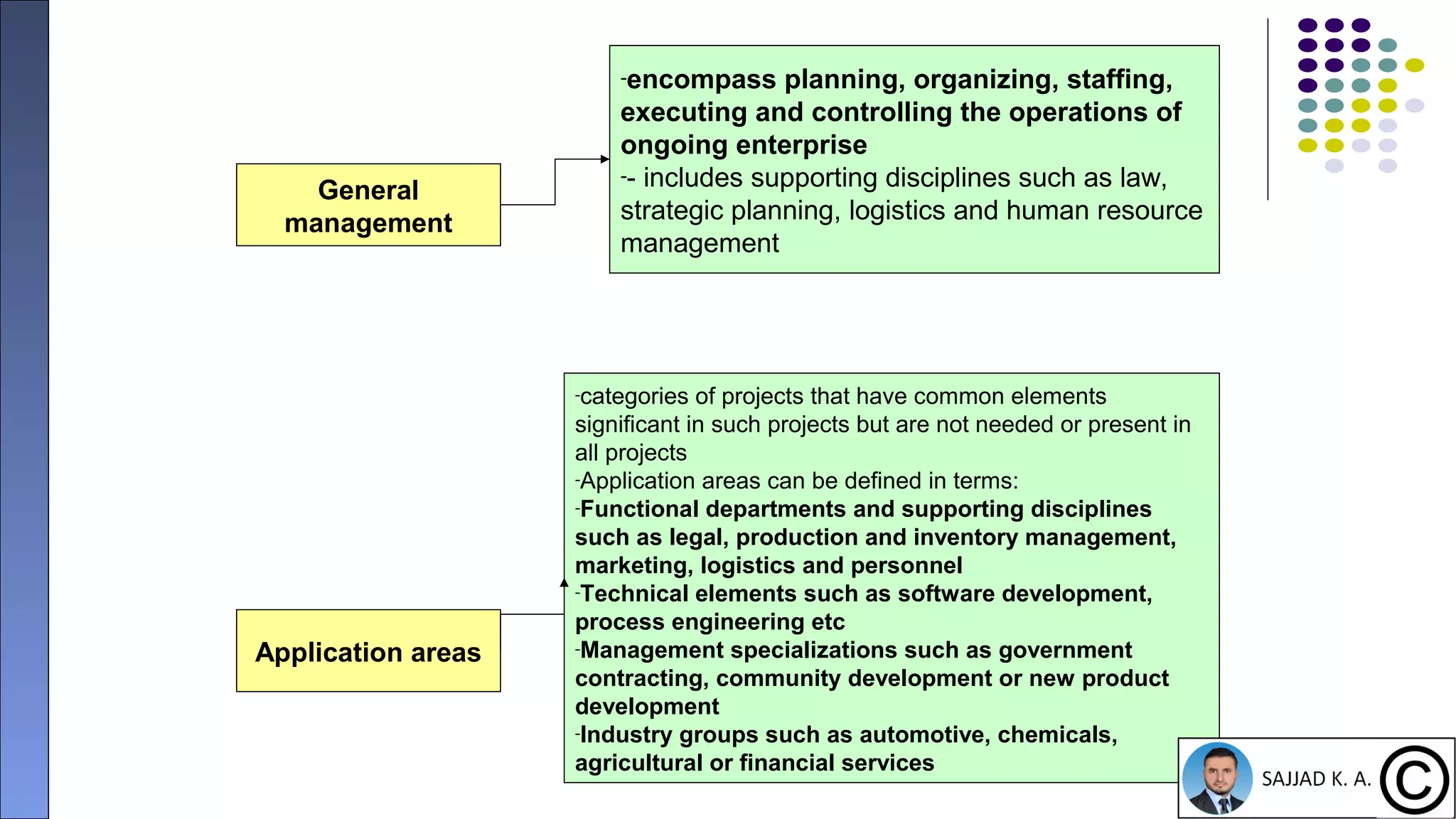
The document provides an introduction to project management, defining projects as temporary endeavors with specific objectives and outlining the importance of managing time, scope, cost, and quality. It discusses various knowledge areas within project management and emphasizes the need for proper coordination and planning. Additionally, it highlights the relationship between project management and other management disciplines, along with common issues leading to project failures.