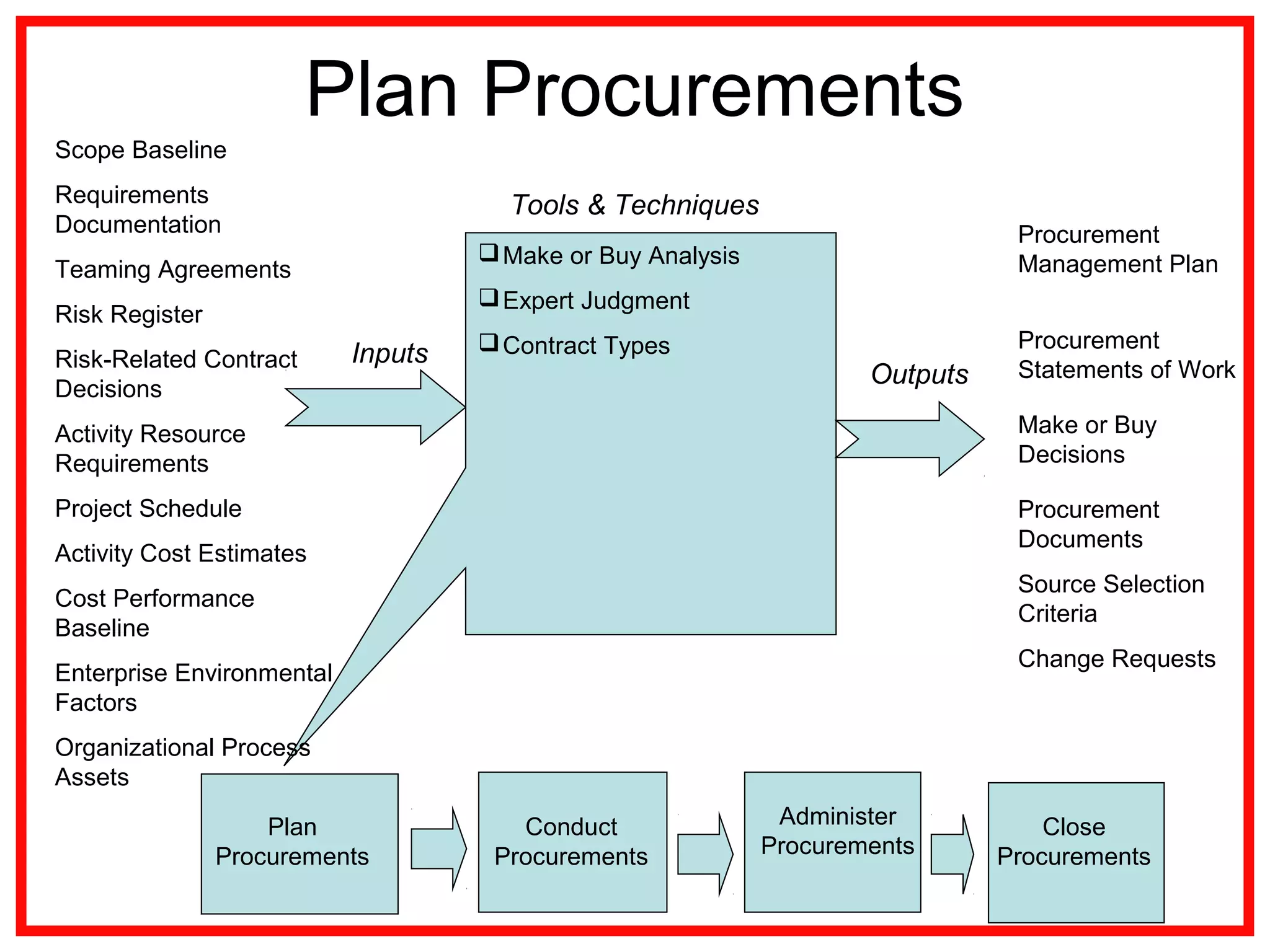
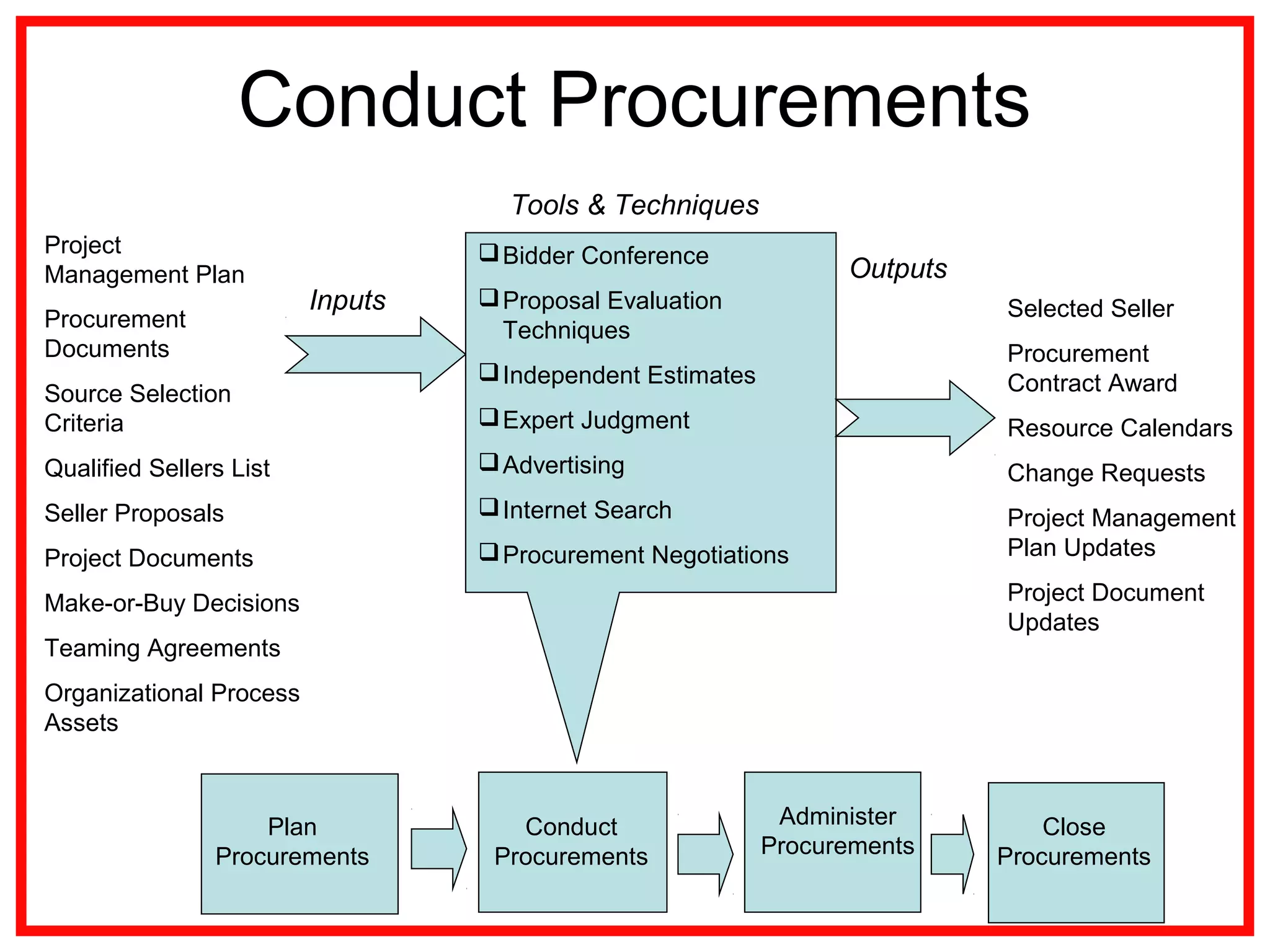
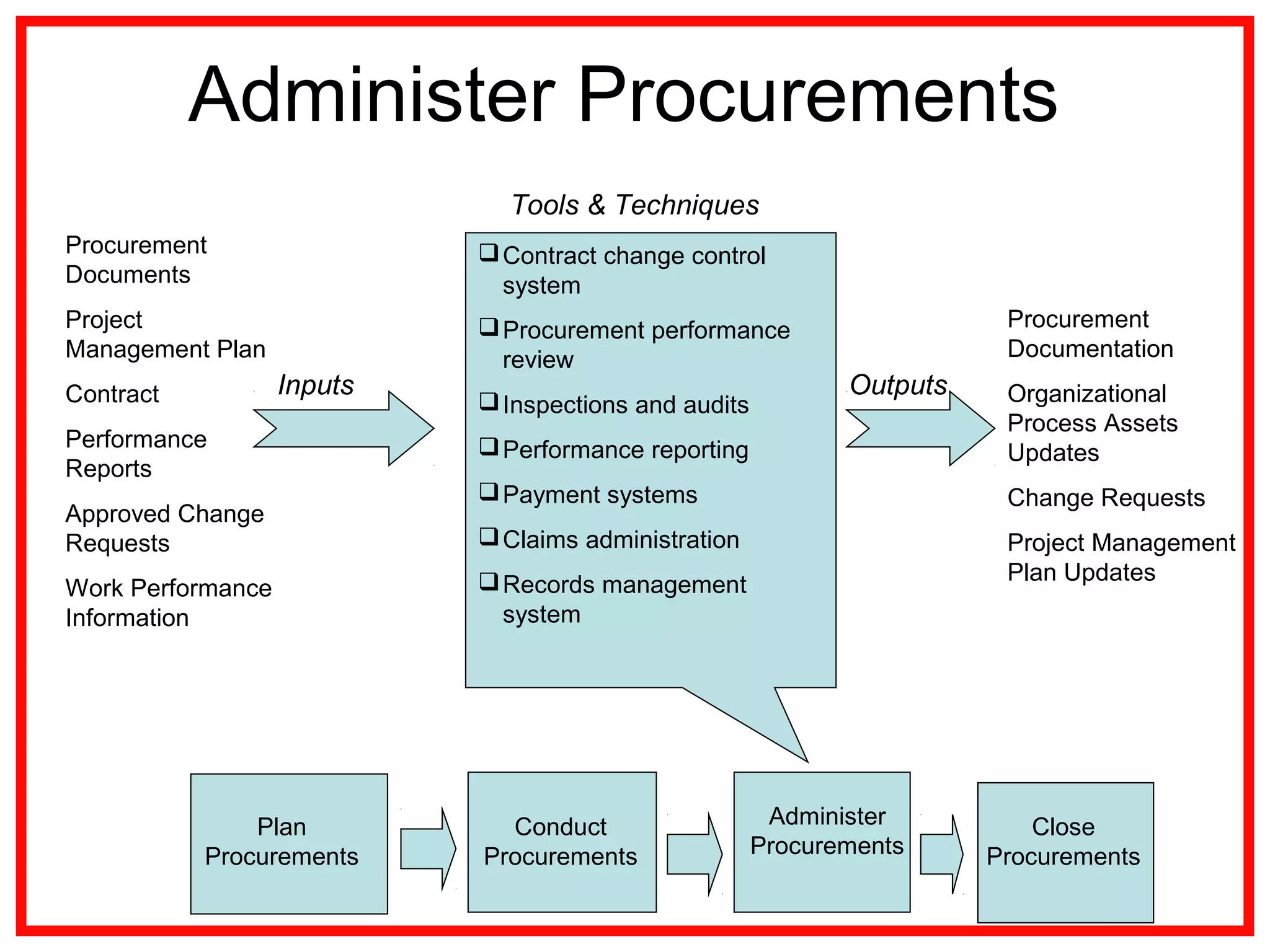
Project procurement management involves processes for acquiring external products, services, or results essential for project work. There are four main procurement processes: planning, conducting, administering, and closing procurements, along with various contract types such as fixed price and cost-reimbursable. Understanding procurement management helps mitigate risks and ensure effective resource acquisition throughout the project lifecycle.