This document provides an overview of project cost management based on the PMBOK Guide. It discusses the key processes involved, including plan cost management, estimate costs, determine budget, and control costs. For each process, it outlines the typical inputs, tools and techniques, and outputs. It also discusses important concepts like the cost management plan, cost baselines, earned value management, variance analysis, and estimating techniques. The overall purpose is to plan, estimate, budget, and control costs throughout the project life cycle.









![RISK AND COST ESTIMATING
Risk Register
Opportunity and Threat
Contingency reserve - [known-unknown risks]
Management reserve - [unknown-unknown risks] which affect time as well.
Scope Baseline in Cost Estimating
Scope Baseline includes :
Project Scope statement: Reflects funding constraints
WBS: shows relationships among the deliverables
WBS dictionary: identification of the deliverables and description of the work in each component](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmp-costmanagementarea-210215192816/85/PMP-Cost-Management-area-13-320.jpg)














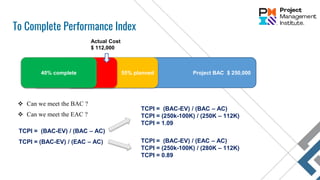
![Project BAC $ 250,000
55% planned
EAC : CPI and SPI factors considered
40% complete
Actual Cost
$ 112,000
EAC = AC + [(BAC-EV) / (CPI * SPI)]
EAC = 112K + [(250K-100K) / (0.89 * 0.73)
EAC = 342,769 $
Estimate at Completion (EAC)
Same efficiency rate for time and cost
EAC = BAC / CPI
EAC = 250K / 0.89
EAC = 280K](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pmp-costmanagementarea-210215192816/85/PMP-Cost-Management-area-32-320.jpg)