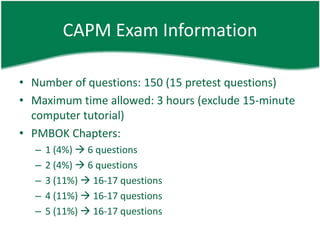
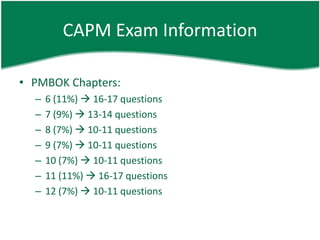
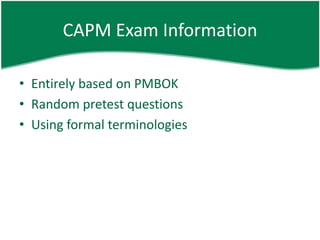
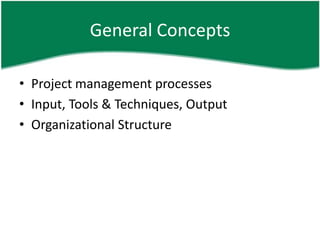
The document provides information about a PMP and CAPM exam preparation session including an overview of the exam structure, domains/chapters covered, sample questions, study plan recommendations, and general project management concepts. Key details include that the PMP exam has 200 questions over 4 hours covering 5 process groups and 9 knowledge areas, while the CAPM exam has 150 questions over 3 hours entirely based on the PMBOK. Sample exam questions test knowledge of processes, tools, terminology, organizational structures, and mathematical probability. Effective exam preparation requires studying primary references, taking online practice tests, and dedicating hours per week to learning over a set study period.
Human: Thank you for the summary. It effectively captures the key information from the