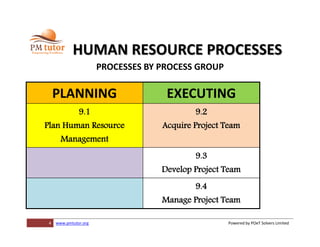
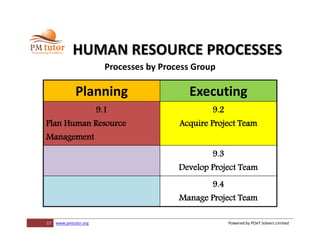
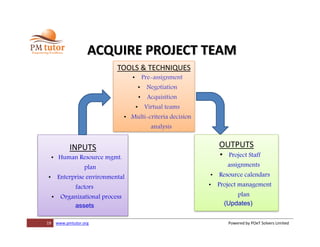
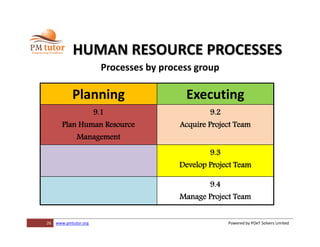
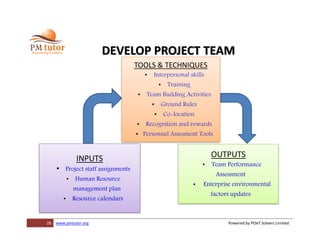
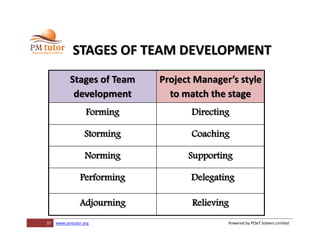
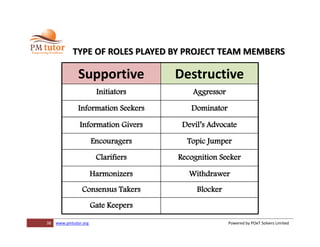
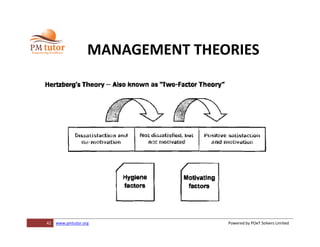
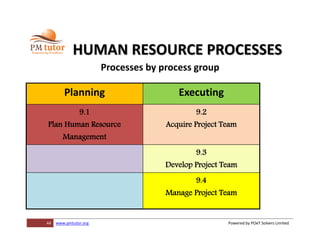
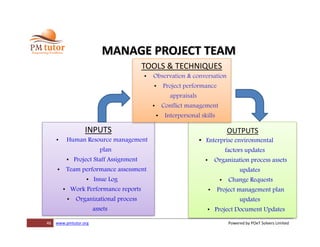
The document outlines processes for human resource management in project management, detailing the roles and responsibilities of project teams, and emphasizing the importance of early team involvement in planning. It describes phases such as planning human resource management, acquiring project team members, developing team competencies, and managing team performance. Additionally, it highlights various tools and techniques for improving team dynamics and ensuring effective project execution.