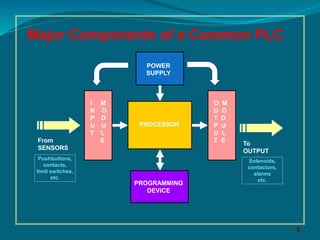
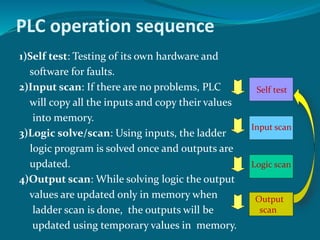
The document provides an overview of programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It discusses that PLCs were introduced in the late 1960s as replacements for relay-based controls. The major components of a PLC are the processor, power supply, input/output modules, and a programming device. PLCs operate by performing a self-test, scanning inputs, solving ladder logic to update outputs in memory, and then scanning outputs to devices. Common PLC programming languages include ladder logic, functional block diagrams, sequential function charts, and Boolean mnemonics.