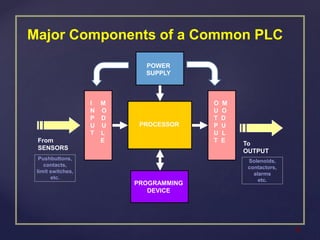
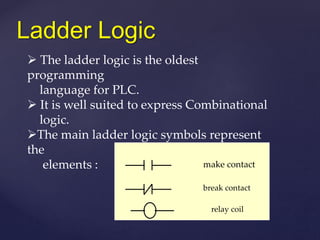
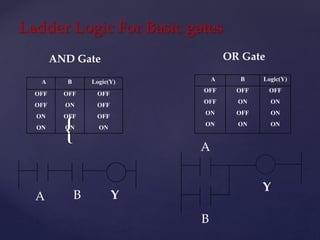
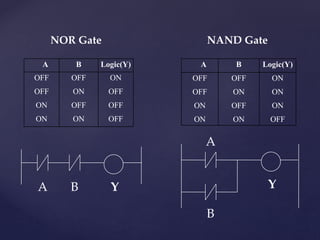
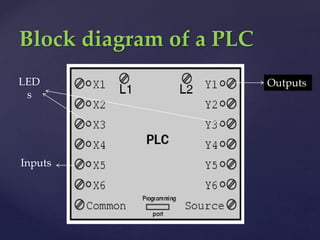
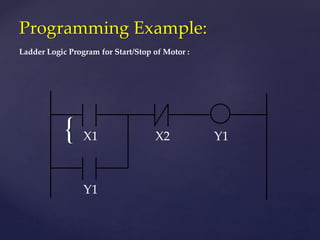
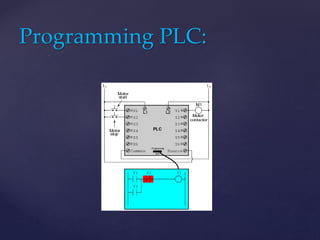
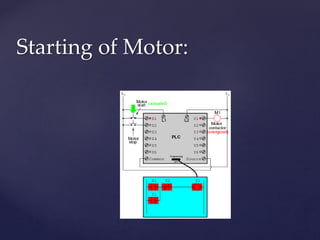
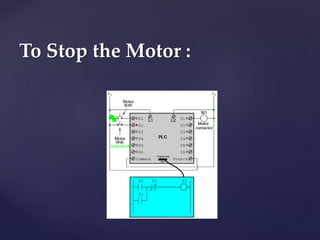
The document provides an overview of Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), detailing their components, operational sequence, programming languages, advantages, and disadvantages. It outlines the history of PLCs, starting from their introduction in the late 1960s, evolving from simple relay replacements to sophisticated systems with the advent of microprocessors. Applications of PLCs span various industries, including robotics, food processing, and automated control systems.