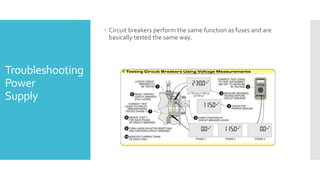
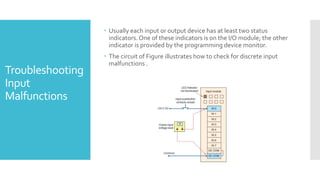
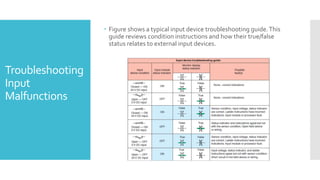
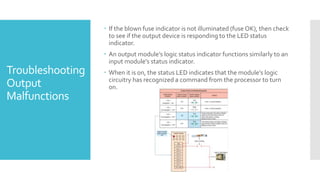
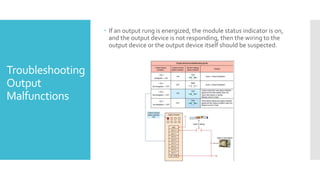
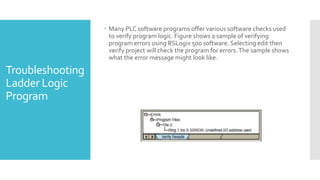
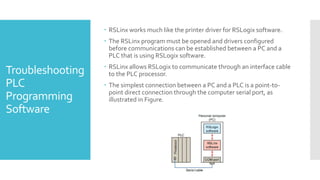
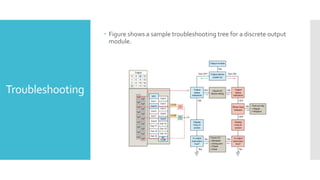
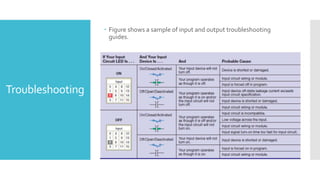
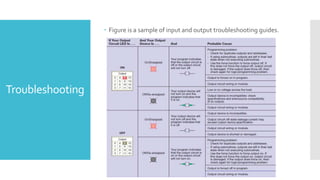
The document provides guidance on troubleshooting Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) systems. It discusses identifying the source of problems, including the power supply, processor module, input/output modules, and ladder logic program. Various troubleshooting steps are outlined for each component, such as checking status indicators, verifying power, and reviewing the program for errors. Communication between the PLC and programming software is also addressed.