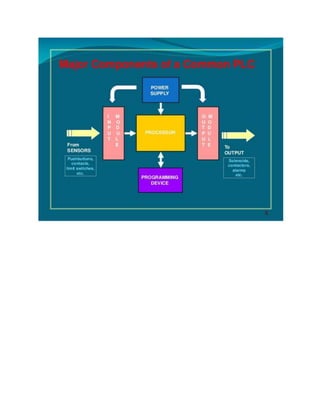
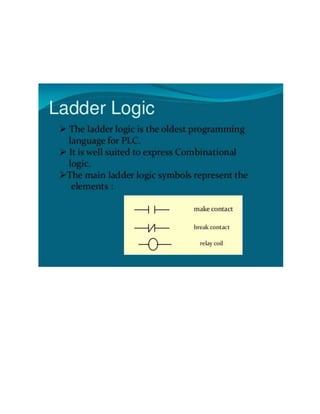
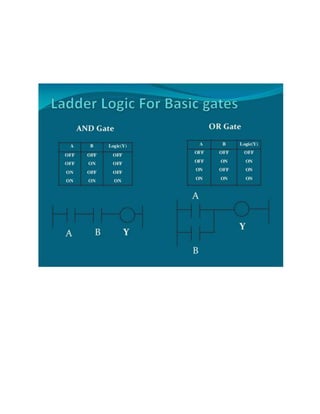
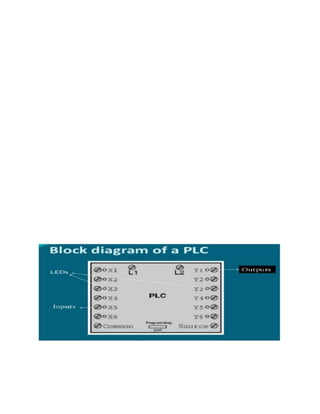
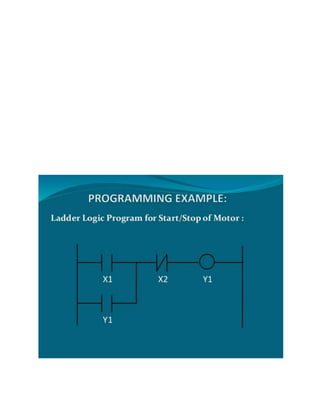
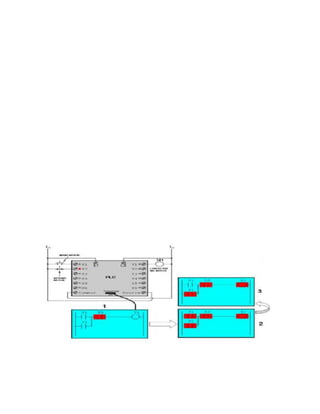
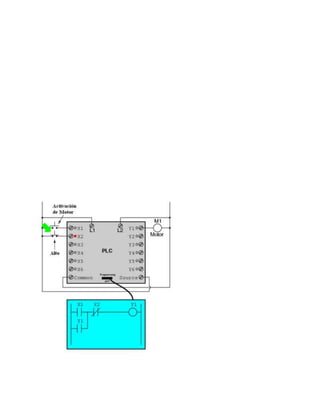
This document provides an overview of programmable logic controllers (PLCs). It discusses what a PLC is, the history and major components of PLCs, programming methods like ladder logic, and examples of how PLCs can be used to start and stop motors. The document also outlines some key advantages of PLCs, such as reliability, flexibility, cost effectiveness, and ease of maintenance, as well as potential disadvantages. Finally, it discusses common applications of PLCs in various industrial automation settings like manufacturing, materials handling, and machine tools.