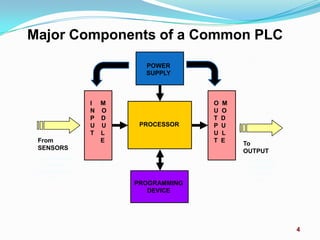
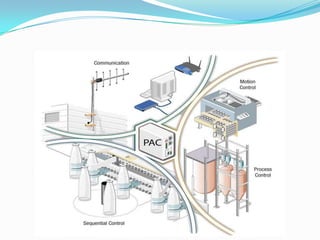
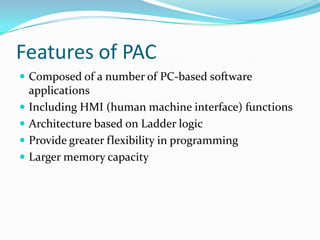
A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a digital computer used to control electromechanical processes in factories. PLCs were introduced in the late 1960s to replace relay-based control systems. The first commercial PLC was developed by Modicon for General Motors. Later, as microprocessors became available, PLCs evolved to be more sophisticated. A PLC has components like a power supply, input/output modules, a processor, and a programming device to control inputs from sensors and outputs to devices. PLCs can operate in harsh industrial environments and use simple ladder logic programming. A Programmable Automation Controller (PAC) is similar but designed for more complex automation with greater flexibility, memory, and control