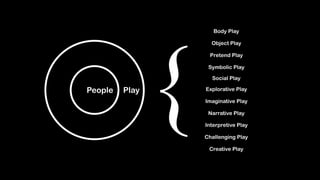
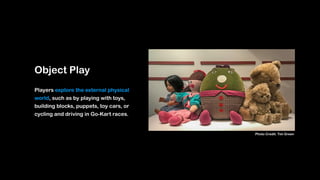
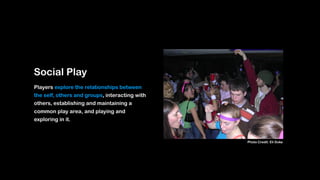
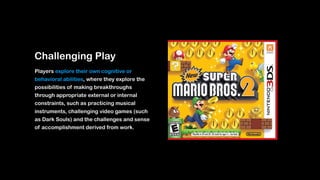
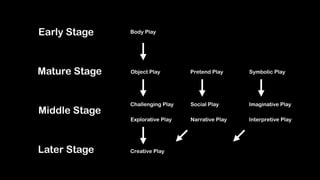
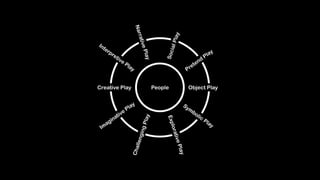
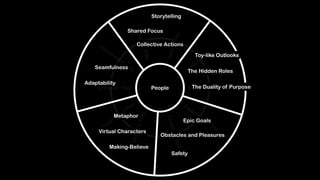
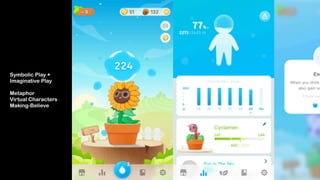
Wei-Fan Chen, CEO of Fourdesire, emphasizes the concept of 'playable design' in app development, highlighting that games must include goals, constraints, and free movement. The document explores various types of play, such as body, object, and social play, illustrating different player interactions and the significance of storytelling and creativity in these experiences. Chen advocates for integrating gamification techniques to enhance engagement and exploration in both digital and real-world contexts.