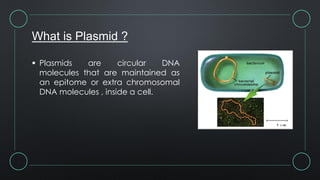
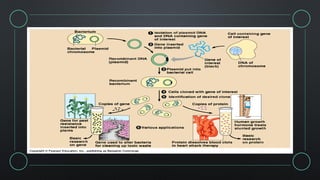
Plasmids are circular DNA molecules that serve as delivery vectors in genetic engineering, allowing for the introduction of foreign genes into host cells. They can be categorized into various cloning vectors and types, including conjugative and non-conjugative plasmids, each serving distinct functions in research and biotechnology. Despite challenges in protein purification and quantity prior to genetic engineering, plasmids enable the mass production of proteins, facilitating advancements in fields such as regenerative medicine and drug testing.