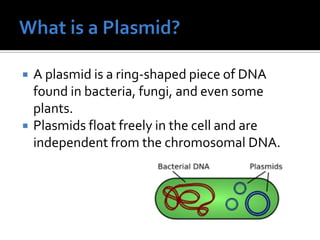
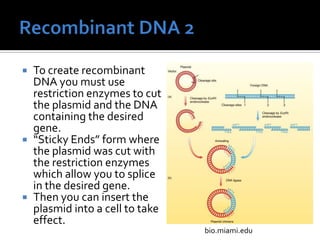
A plasmid is a ring-shaped piece of DNA that can transfer genes between bacteria. It contains non-essential genes for traits like antibiotic resistance. Researchers can create recombinant DNA by splicing genes into plasmids, then inserting these plasmids into cells to produce large quantities of proteins for research. For example, scientists generated heart muscle cells by adding seven genes to plasmids and introducing them into stem cells.