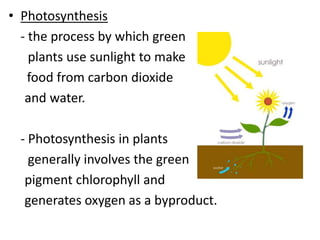
Plants are many-celled organisms that use photosynthesis to produce food from sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. They contain chlorophyll and have adapted to nearly every environment on Earth. Plant cells contain organelles like the nucleus and chloroplasts, as well as a cell wall and central vacuole. Plants are categorized as vascular or nonvascular, with vascular plants having transport structures like xylem and phloem to move water and nutrients. Nonvascular plants like mosses anchor via rhizoids instead of roots. Flowers contain reproductive parts like petals, sepals, stamens, and pistils that produce pollen and ovules.