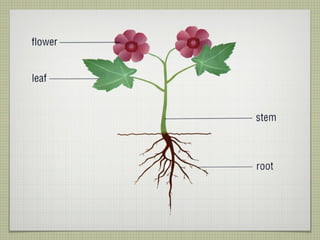
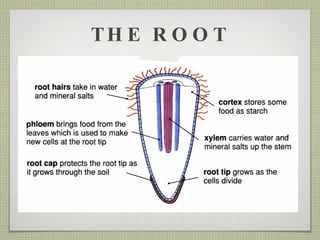
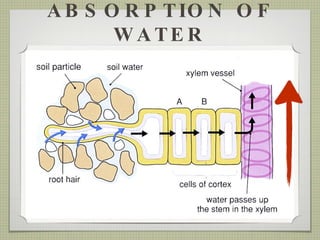
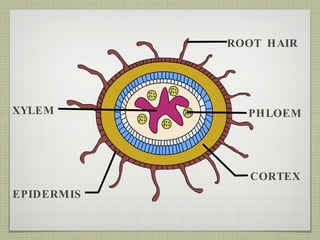
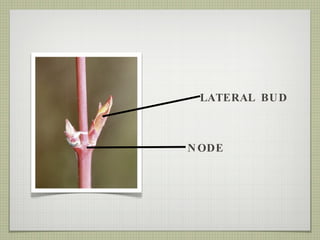
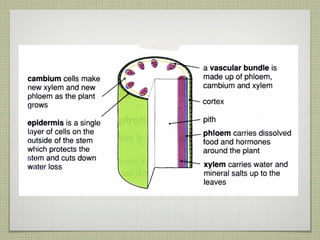
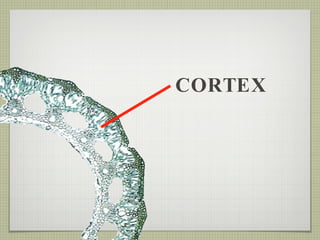
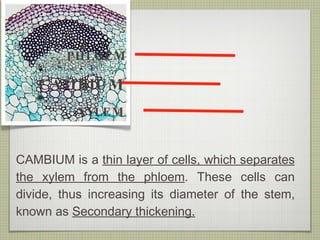
The document discusses the structures and functions of plant roots, stems, and leaves. It explains that plants have either taproots or fibrous roots, and that roots absorb water and minerals. The stem transports water and nutrients throughout the plant and has nodes, buds, and vascular bundles. Leaves undergo photosynthesis to produce sugars for the plant.