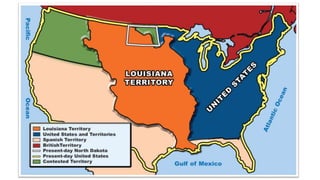
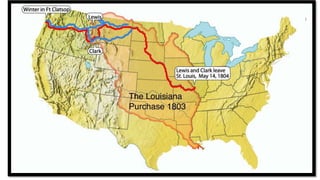
Thomas Jefferson was elected the third US President in 1800. During his two terms, he oversaw the Louisiana Purchase which doubled the size of the US, established judicial review in the Marbury v. Madison Supreme Court case, and issued the Embargo Act in an attempt to punish Britain and France for trade issues but which damaged the US economy instead. An expedition led by Meriwether Lewis and William Clark also explored the new western lands.