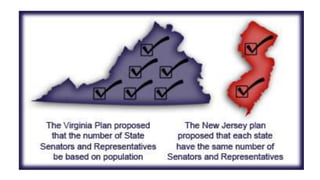
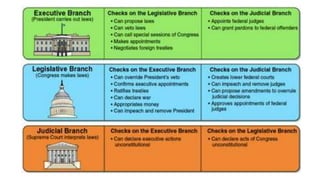
The document summarizes the key events and compromises that led to the creation of the U.S. Constitution. It explains that the Constitutional Convention was called to revise the Articles of Confederation but resulted in an entirely new framework of government. Major points of contention, like state representation and slavery, were addressed through compromises. This established a system of checks and balances across three branches of government at both the federal and state levels.