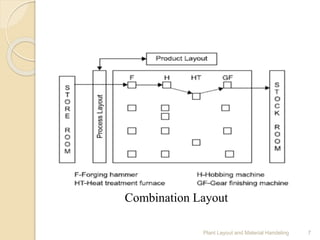
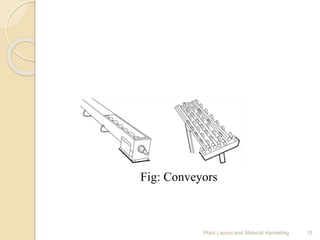
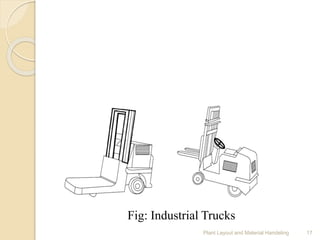
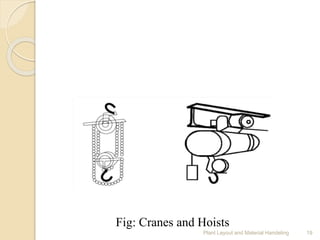
The document discusses plant layout and material handling, detailing different layout types such as process, product, combination, and fixed position layouts. It emphasizes the importance of effective material handling systems, their classification, objectives, and principles, and explains various handling equipment like conveyors, industrial trucks, cranes, hoists, and robots. Key goals include minimizing costs and delays while maximizing safety and efficiency in the manufacturing process.