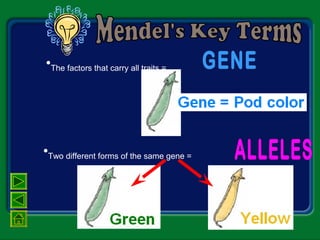
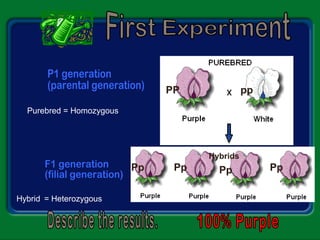
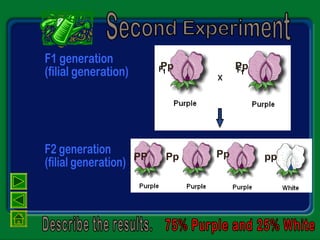
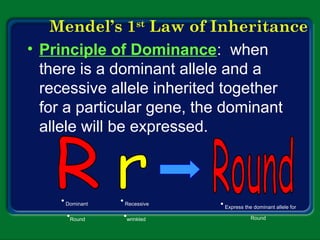
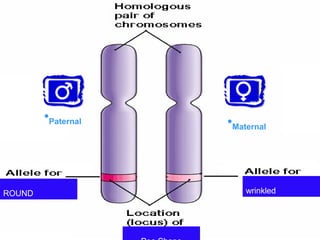
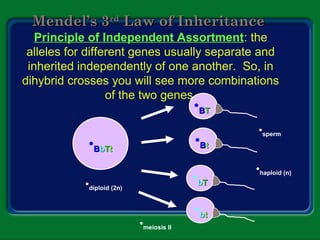
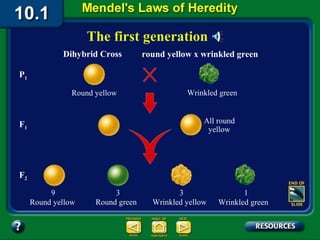
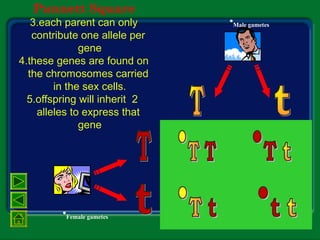
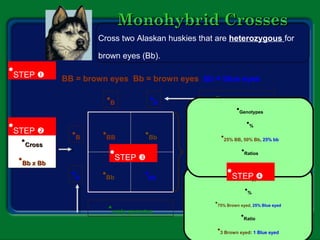
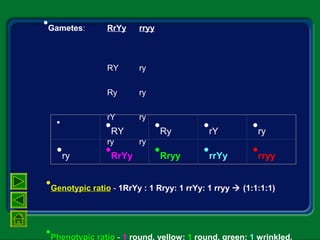
Mendel studied inherited traits in pea plants through controlled breeding experiments in the mid-1800s. He discovered that traits are passed from parents to offspring through discrete factors that he called genes. His experiments demonstrated that genes come in different versions called alleles that are separated during gamete formation and transmitted independently of one another based on simple mathematical probabilities seen in his Punnett square diagrams. Mendel was thus able to deduce the basic principles of heredity and inheritance that became the foundation of modern genetics.