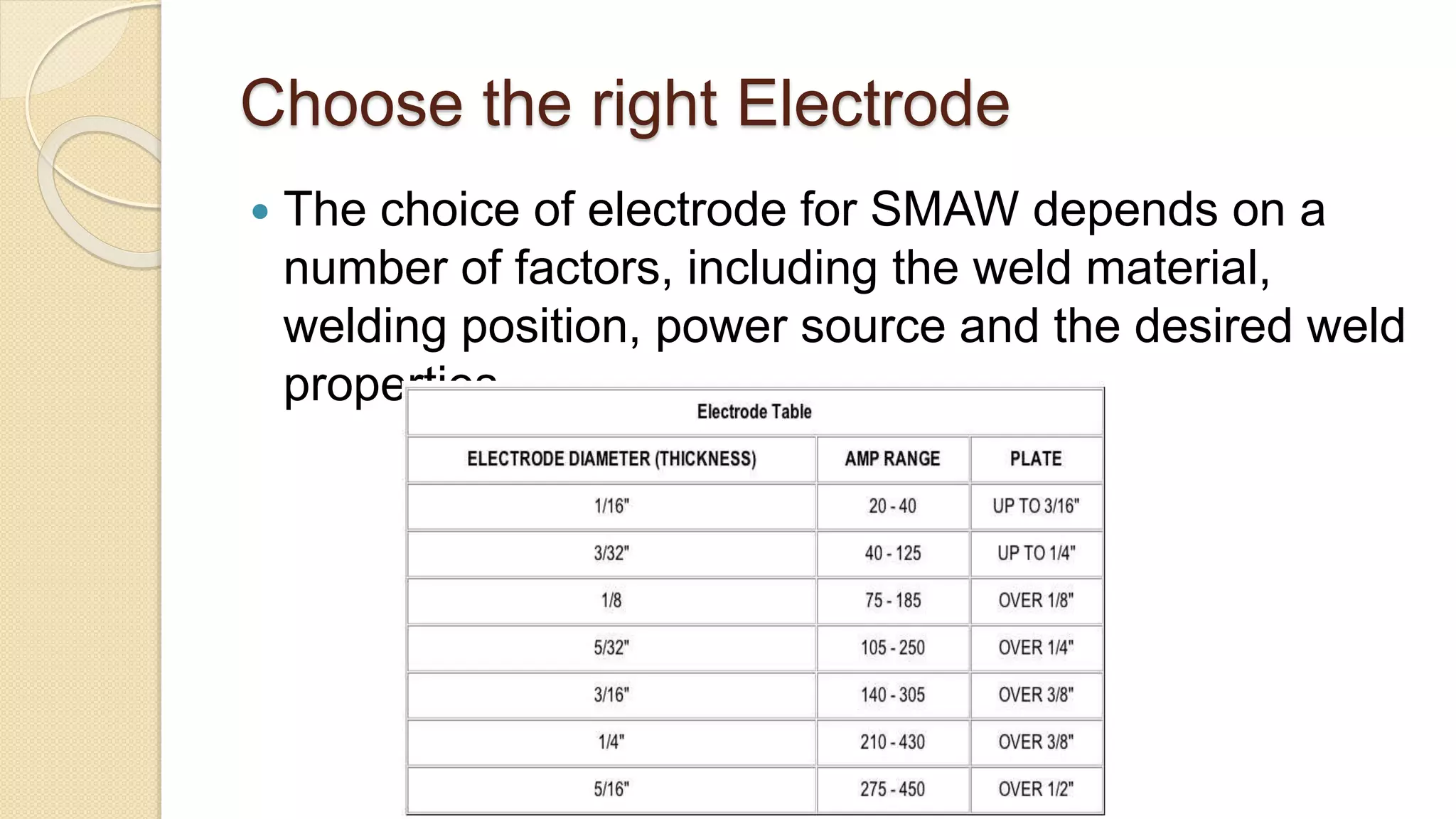
This document provides planning information for shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) operations. It discusses selecting the appropriate welding equipment, including power source, electrode, and safety gear. It outlines the steps for preparing the base materials, choosing the correct electrode, setting the current and voltage, and complying with safety requirements. The document describes how to properly start and complete the weld, clean and inspect the finished weld, and the purpose and contents of welding procedure specifications and procedure qualification records for quality control and process documentation.