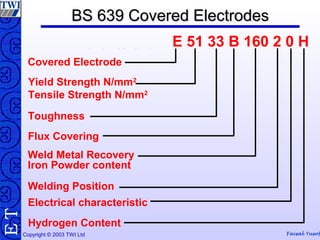
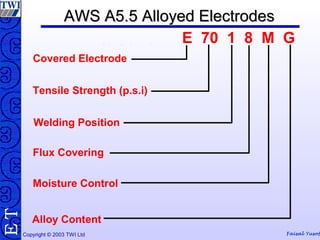
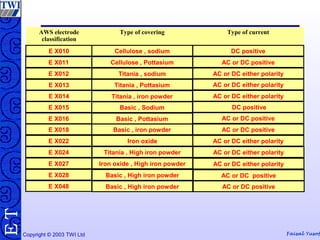
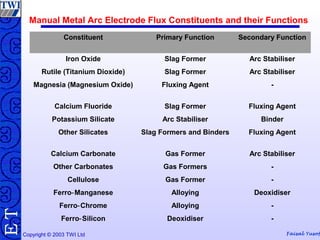
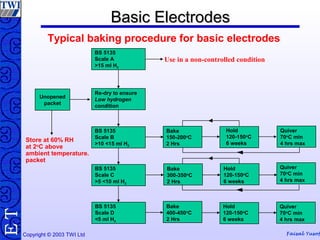
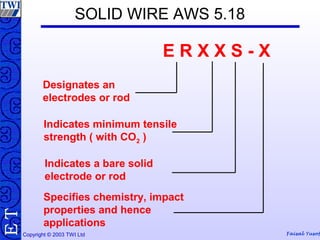
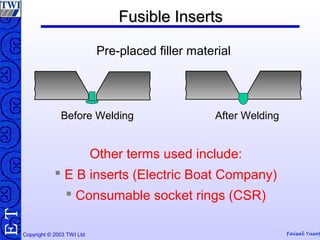
This document discusses welding consumables used in various welding processes. It describes the types of consumables which may include filler wires, covered electrodes, shielding gases, and fluxes. For each consumable type, details are provided on their composition, characteristics, functions of constituents, and relevant standards. Proper handling and storage of consumables is emphasized as critical. Specific consumables for processes like MMAW, GMAW, GTAW, and SAW are examined in more depth.