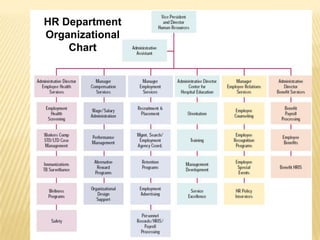
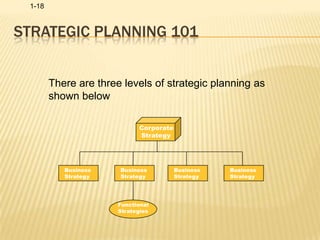
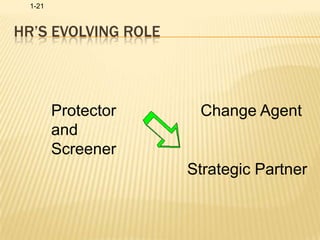
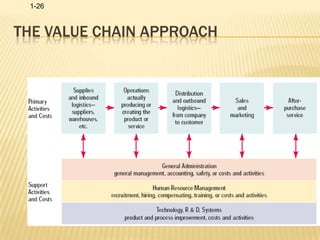
Human resource management involves acquiring, training, evaluating, and compensating employees while ensuring good labor relations, health, safety, and fairness. Key HRM functions include identifying talent, retaining employees, developing a positive culture, training managers, conducting research, and communicating. HRM is important for maintaining good industrial relations, developing organizational commitment, adapting to changes, and coping with political and economic pressures.