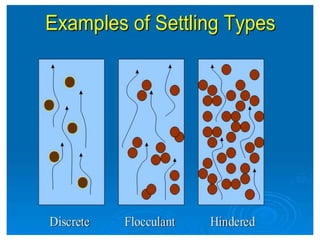
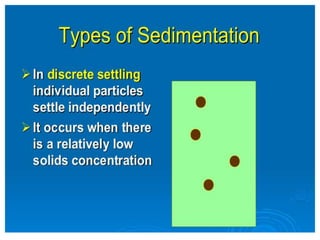
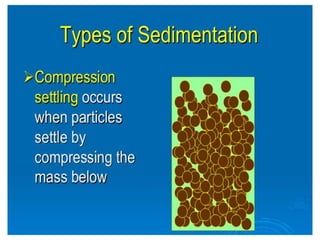
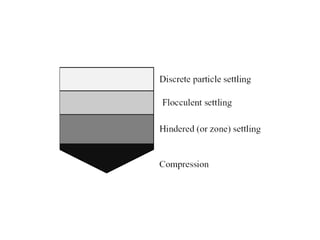
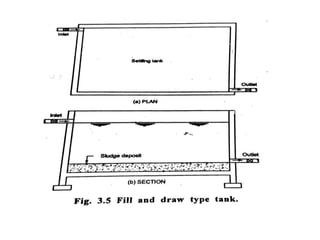
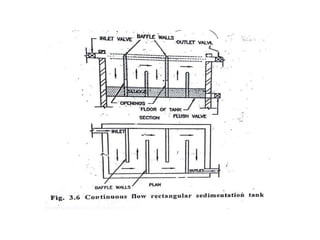
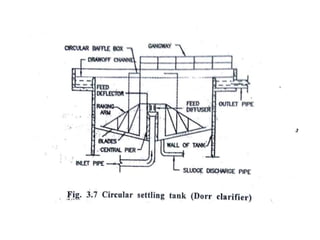
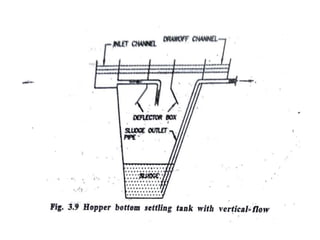
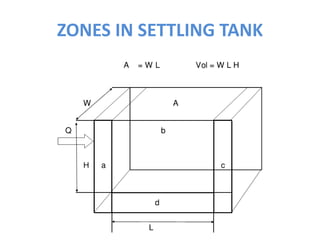
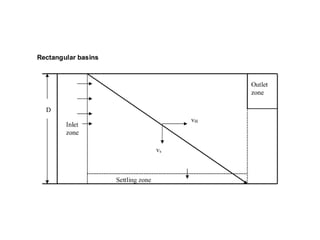
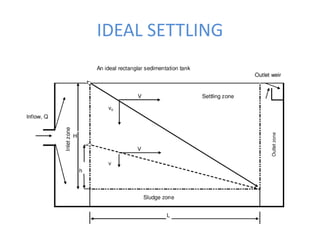
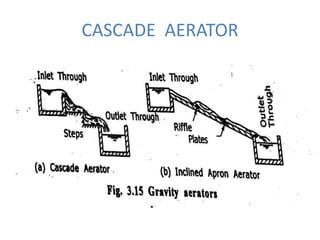
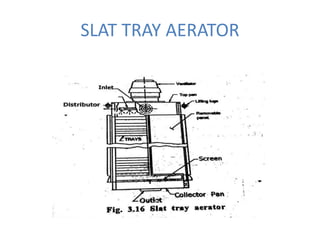
This document discusses two types of sedimentation processes: plain sedimentation and sedimentation with coagulation. Plain sedimentation involves separating impurities from water through natural gravitational forces alone, without chemical additives. This process lightens the load on subsequent treatment steps and reduces costs. Sedimentation occurs as particles heavier than water settle out due to gravity. Sedimentation tanks come in various shapes and sizes, and different zones exist within the tanks. Aeration is discussed as well, including its purposes and different aerator types like cascade, spray, and air diffusers. Design criteria and an example calculation for sedimentation tank sizing is also provided.