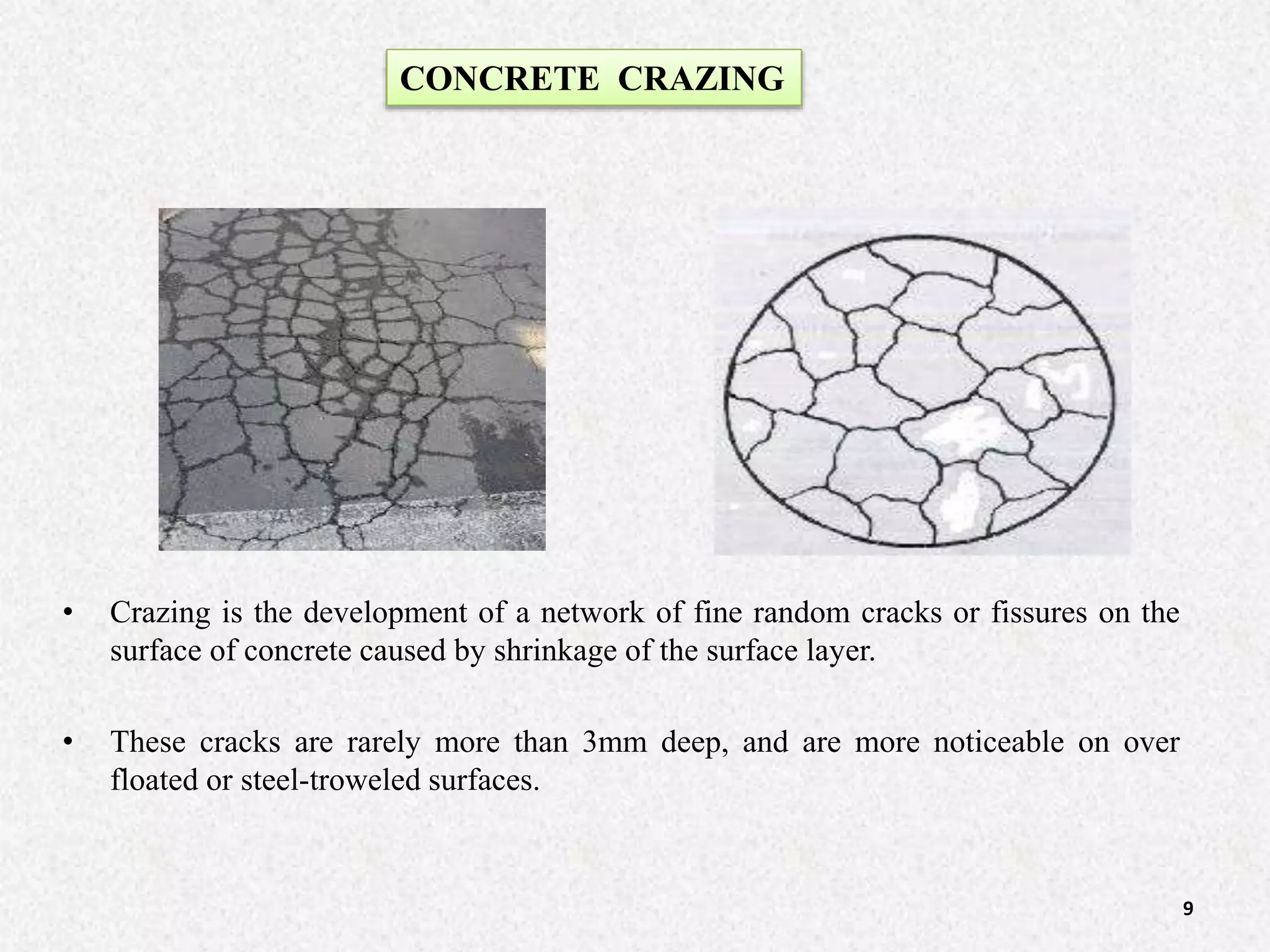
Cracks in concrete can be caused by various factors like plastic shrinkage, drying shrinkage, thermal variations, chemical reactions, errors in design and construction practices, structural overloads, foundation movement, and vegetation. The document classifies cracks as structural or non-structural and describes different types of cracks that can occur before or after concrete hardening. It provides details on the causes and prevention measures for different types of cracks like plastic shrinkage, drying shrinkage, crazing, thermal cracks, cracks due to chemical reactions, and those arising from poor construction practices. The summary focuses on the key information around classification, types, causes and remedies of cracks in concrete structures.