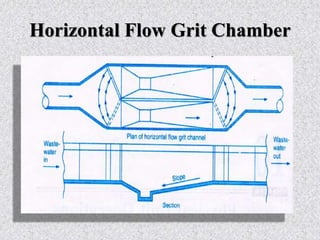
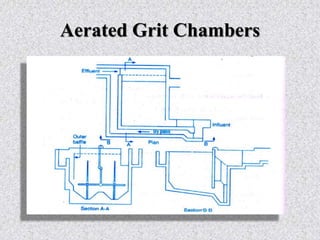
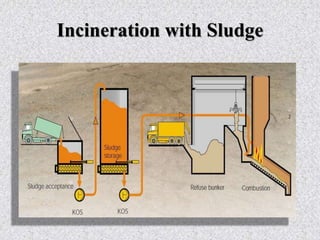
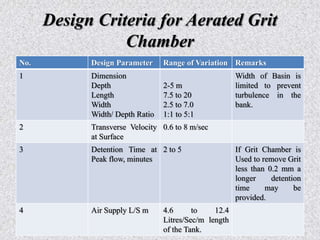
This document provides information about grit removal in wastewater treatment. It discusses that grit such as sand and eggshells can be easily removed from wastewater by reducing the velocity in a grit channel. Grit chambers are used to remove these particles to prevent damage to equipment and clogging. There are two main types of grit chambers - horizontal flow and aerated. The document provides design criteria for both types and works through an example design for a grit chamber for a town with a population of 200,000.