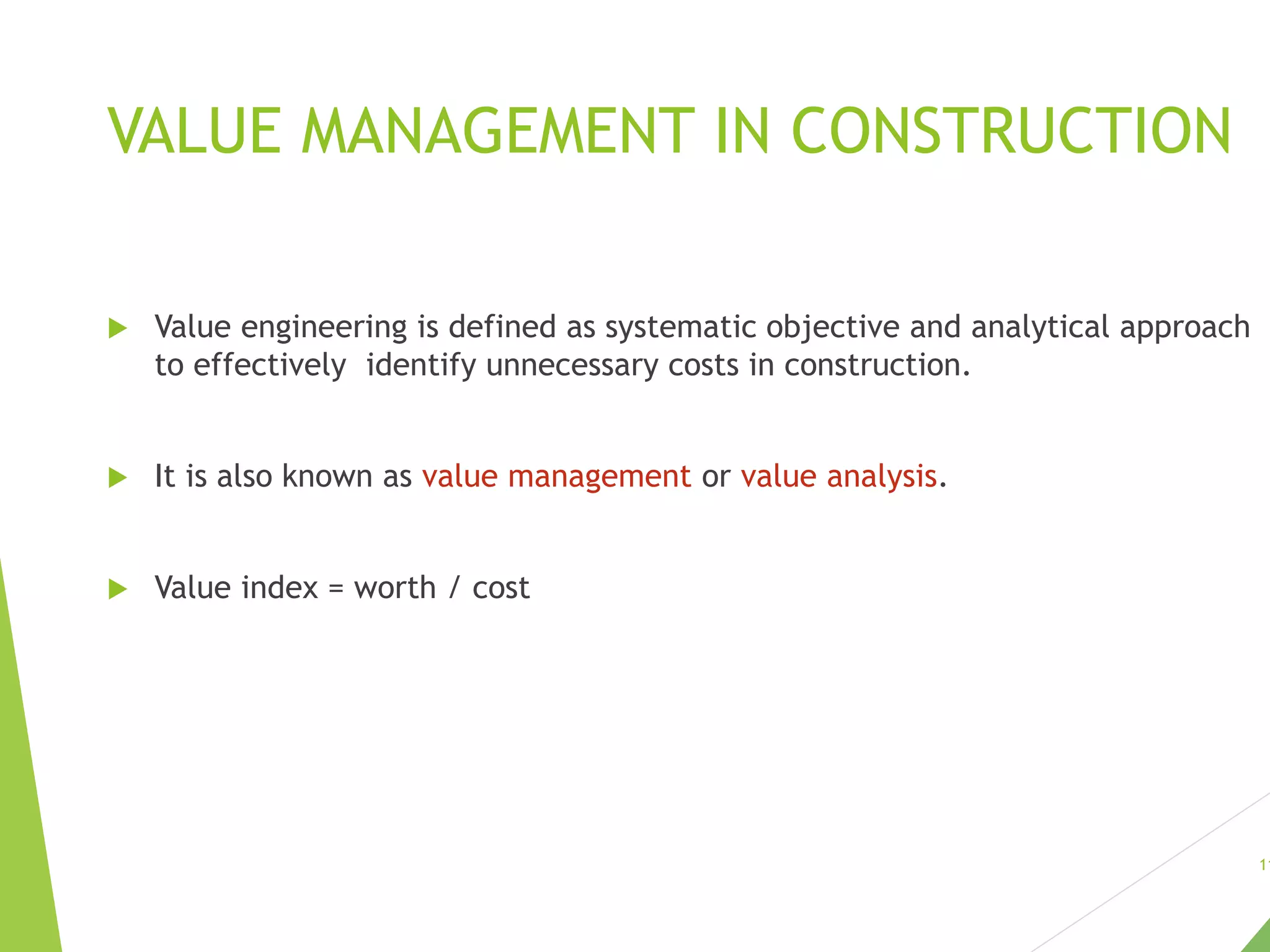
This document discusses project cost management. It describes how project cost management deals with controlling the costs of resources needed to complete project activities. The main steps in project cost management are: 1) resource planning schedules, 2) cost planning, 3) cost budgeting, and 4) cost control. Resource planning schedules show quantity requirements of resources on a weekly or monthly basis. Cost planning aims to ascertain costs before design decisions. Cost budgeting allocates overall cost estimates to individual work items. Cost control ensures final costs do not exceed planned costs by observing, comparing, and computing variances of actual versus standard costs.