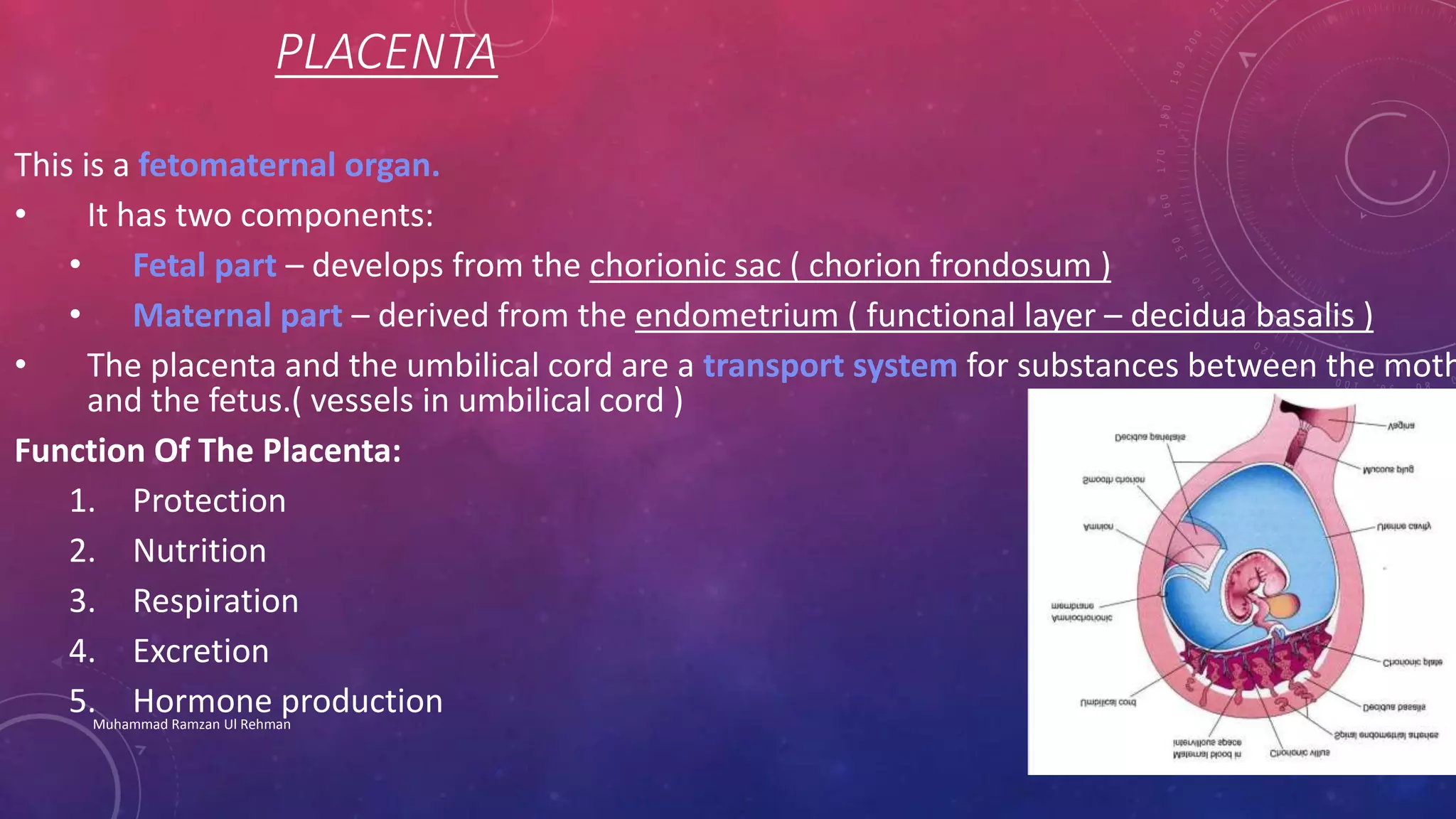
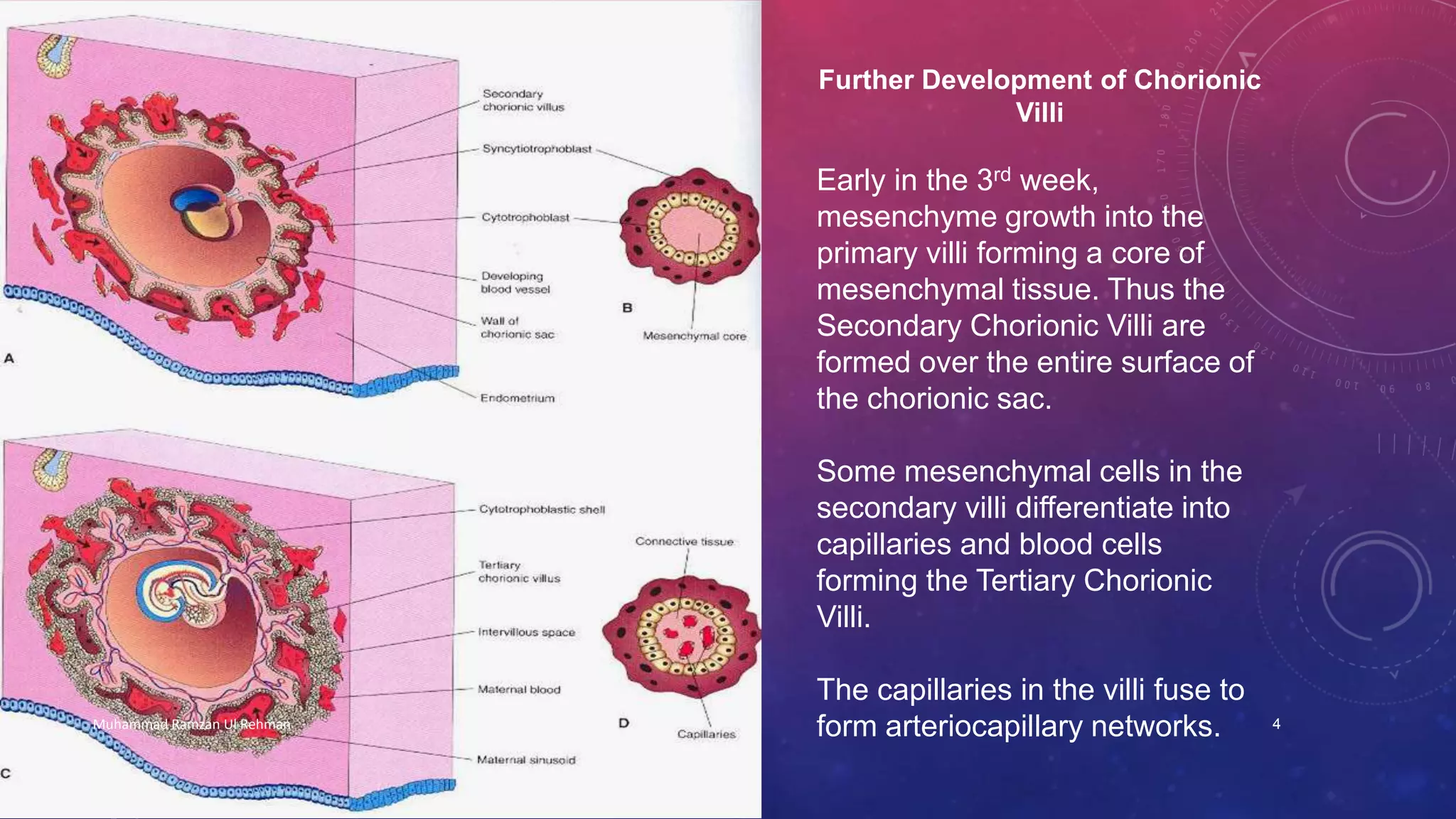
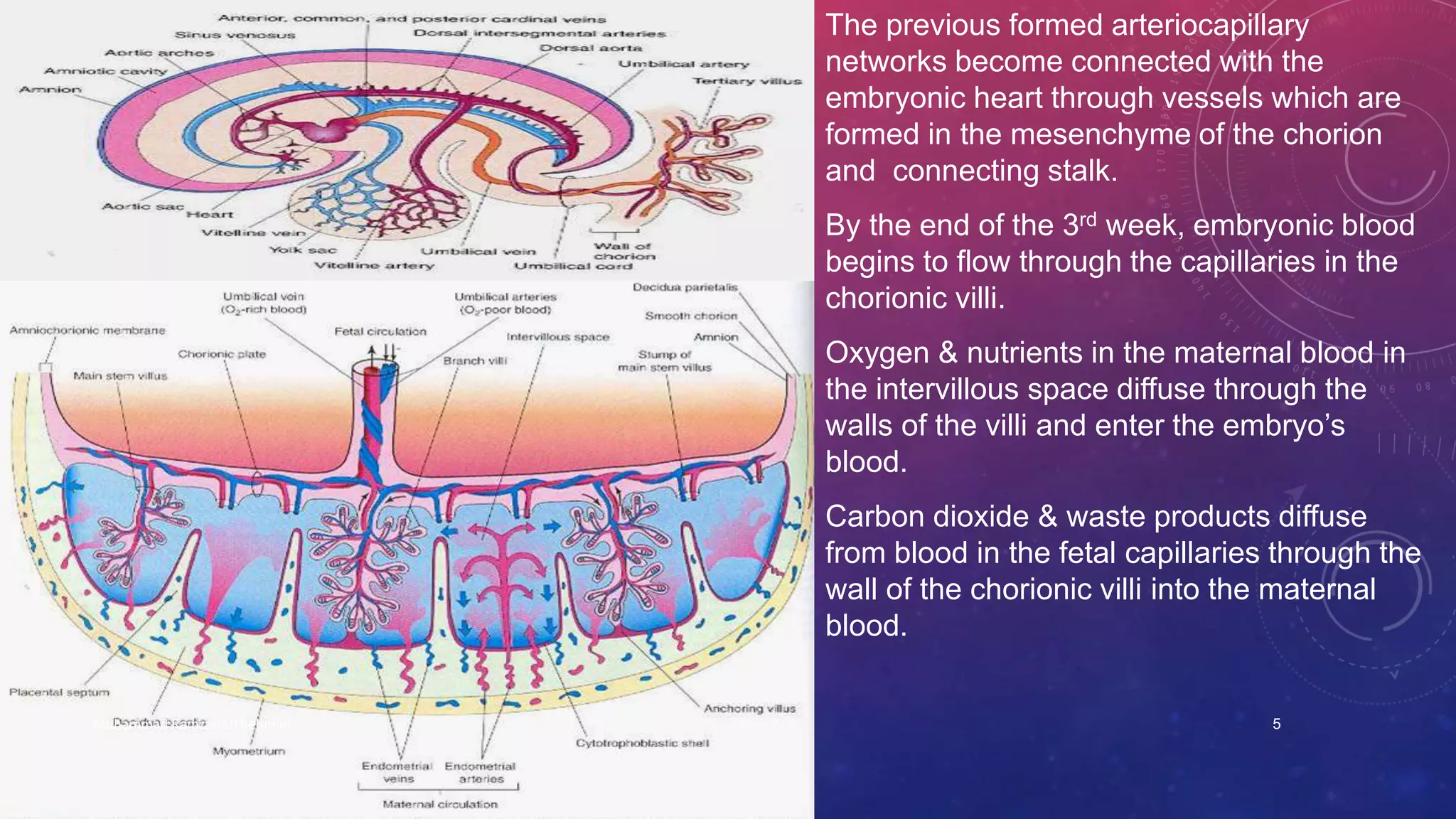
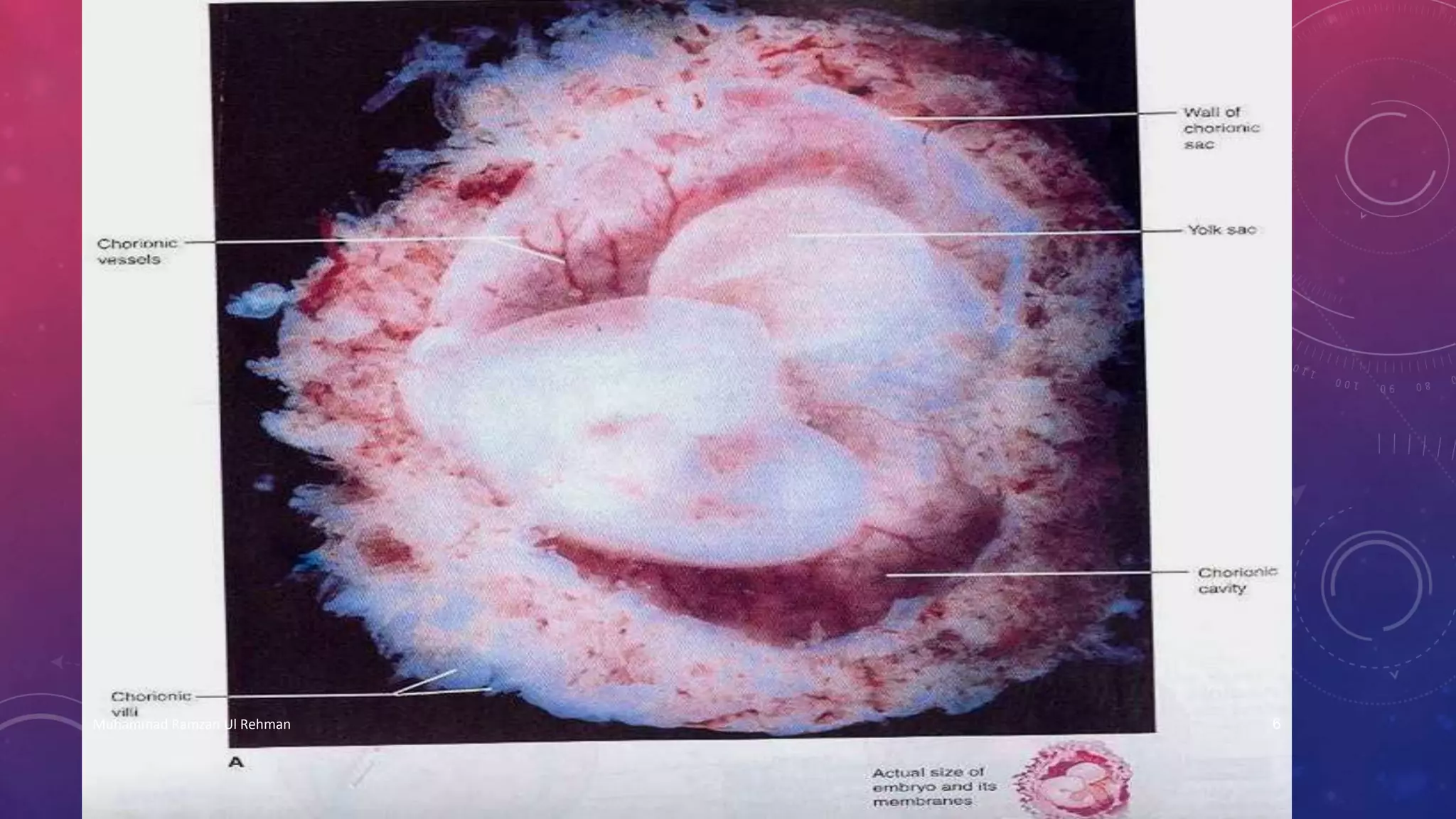
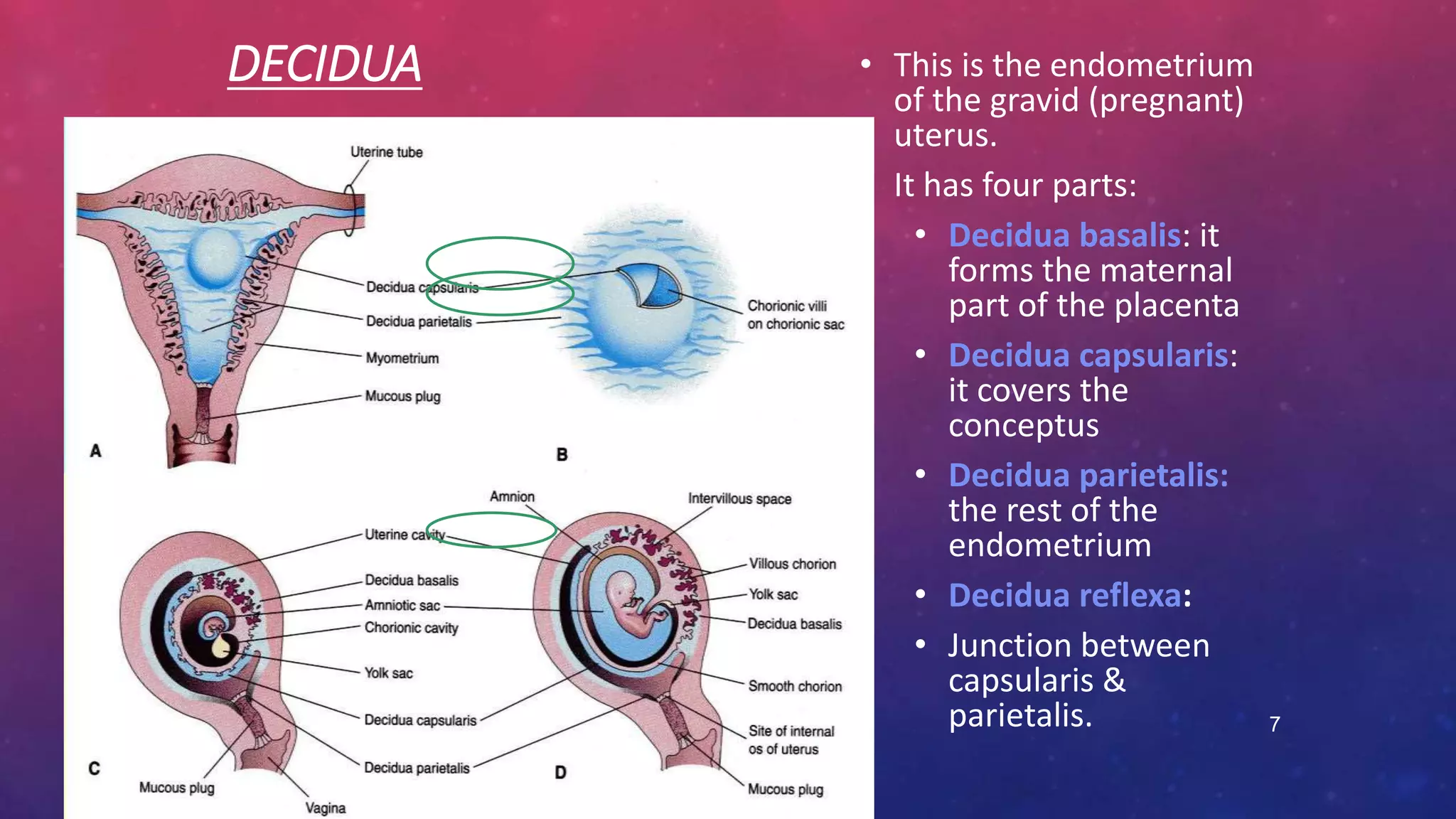
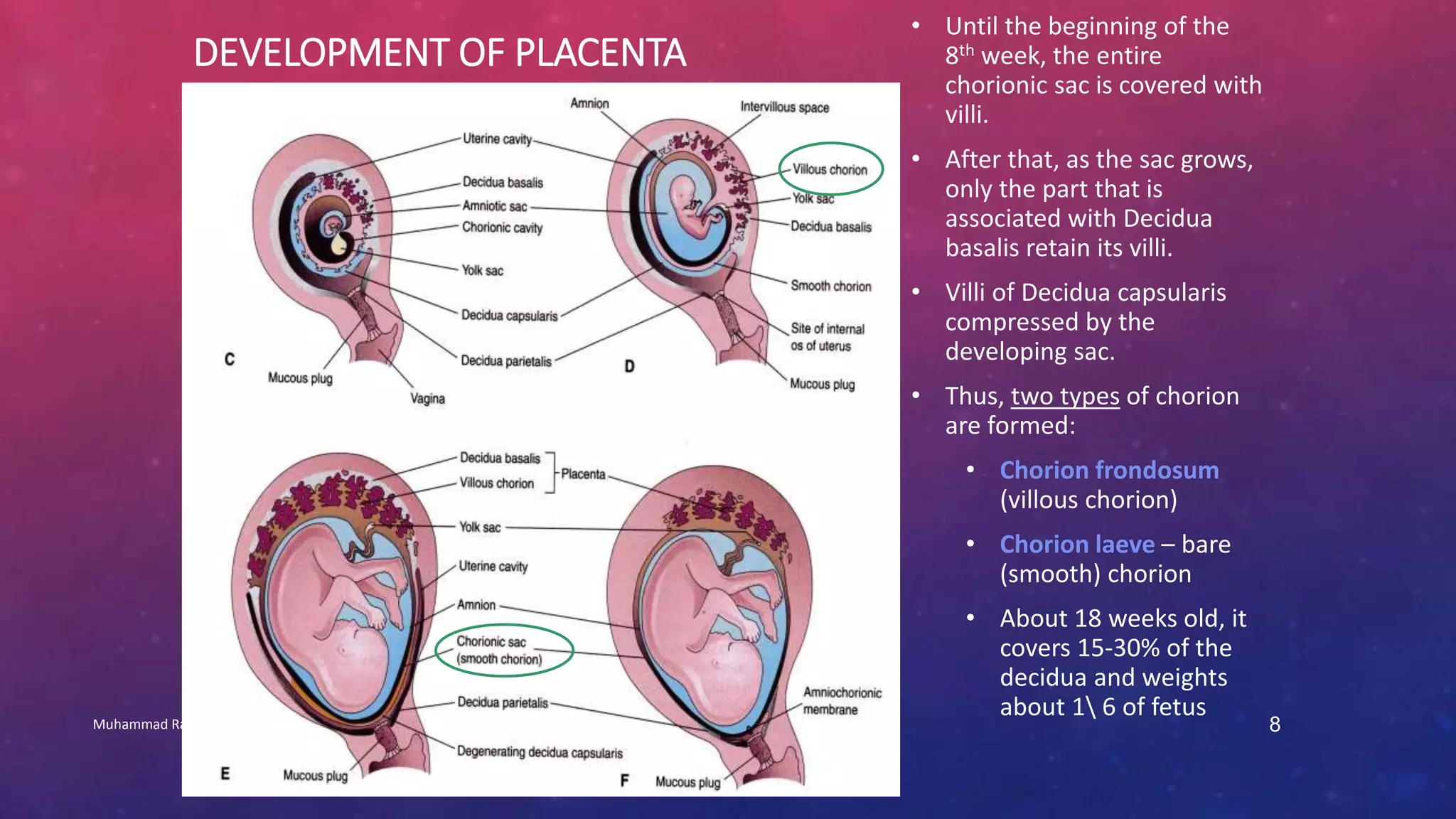
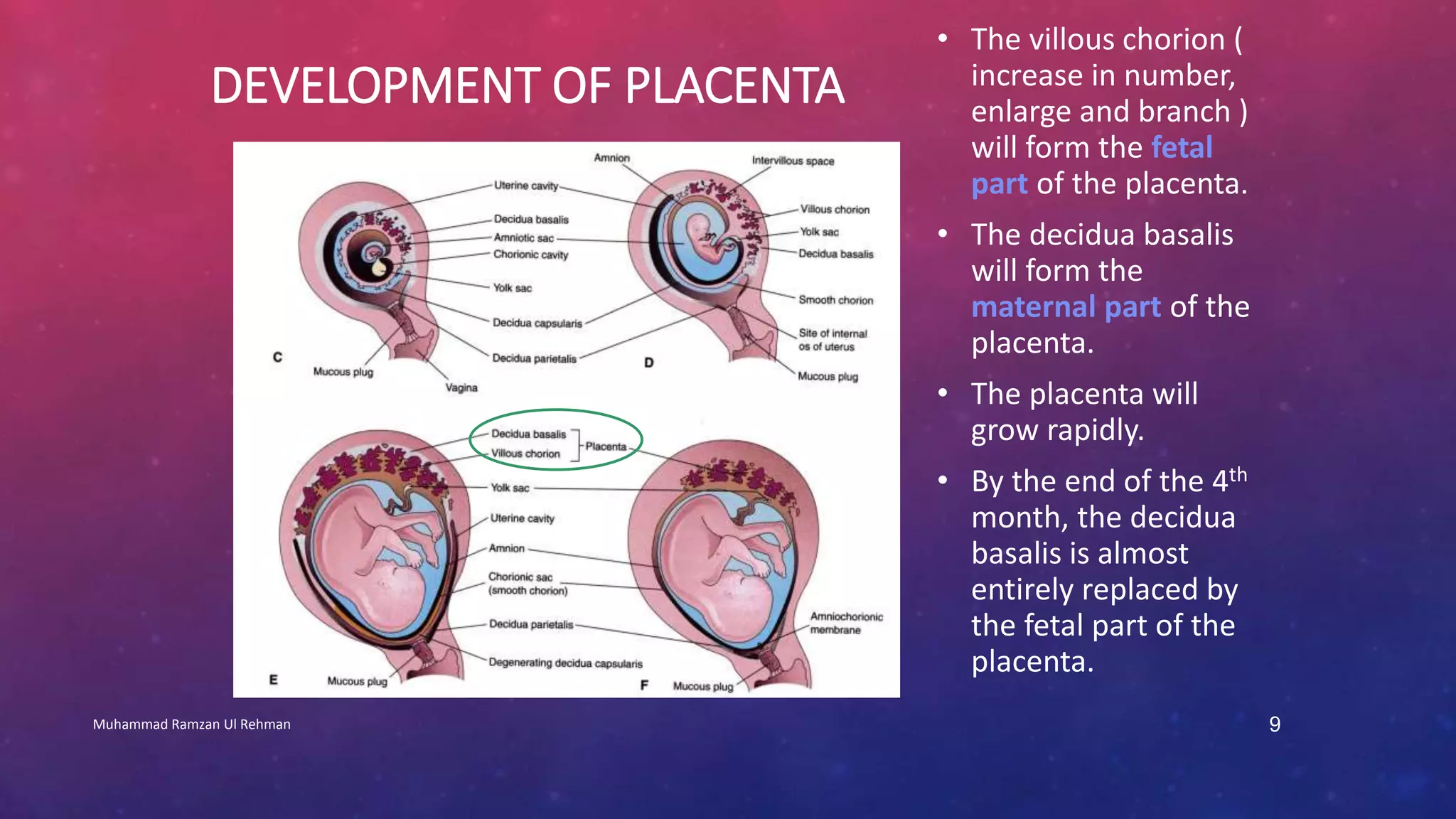
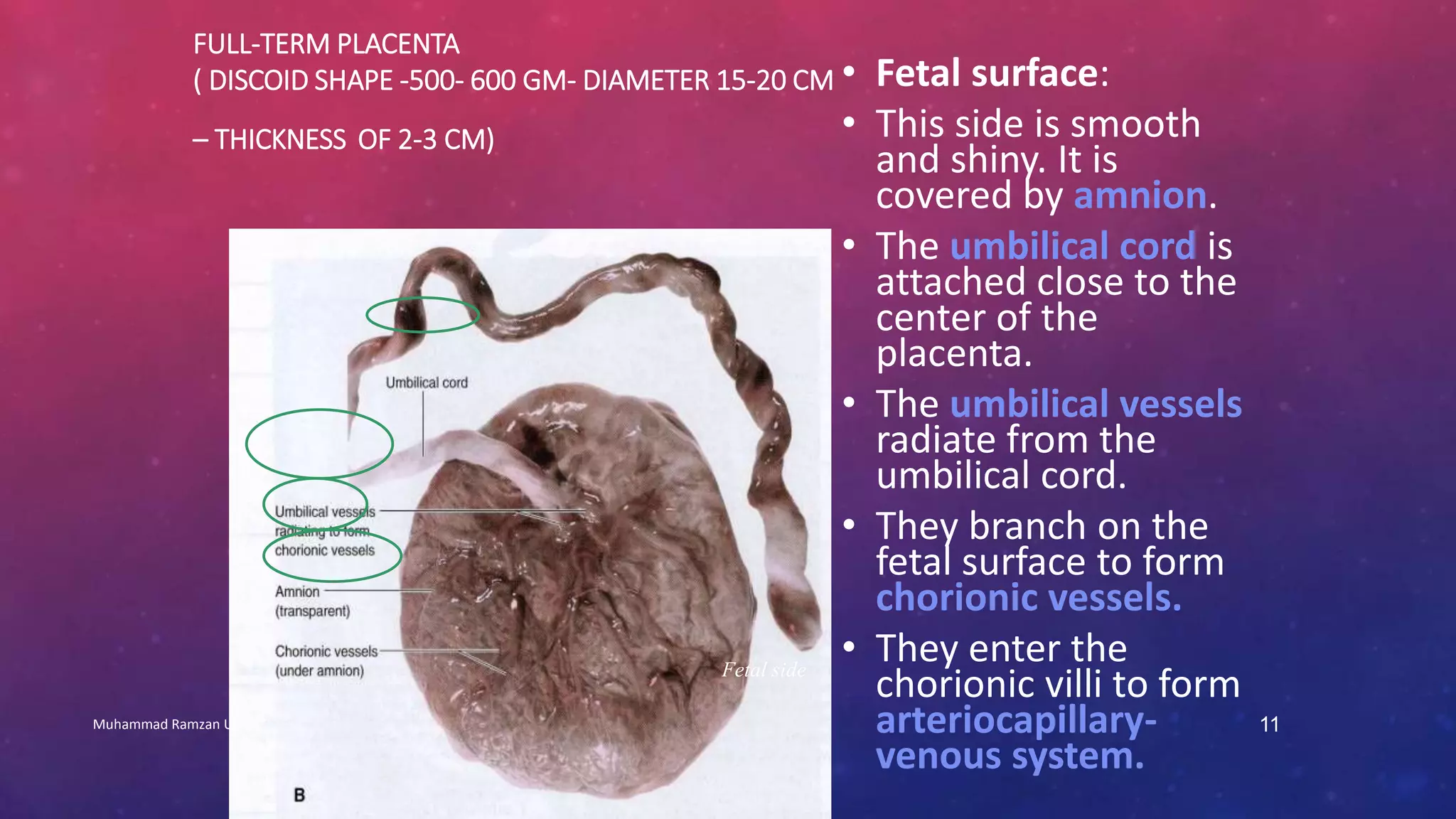
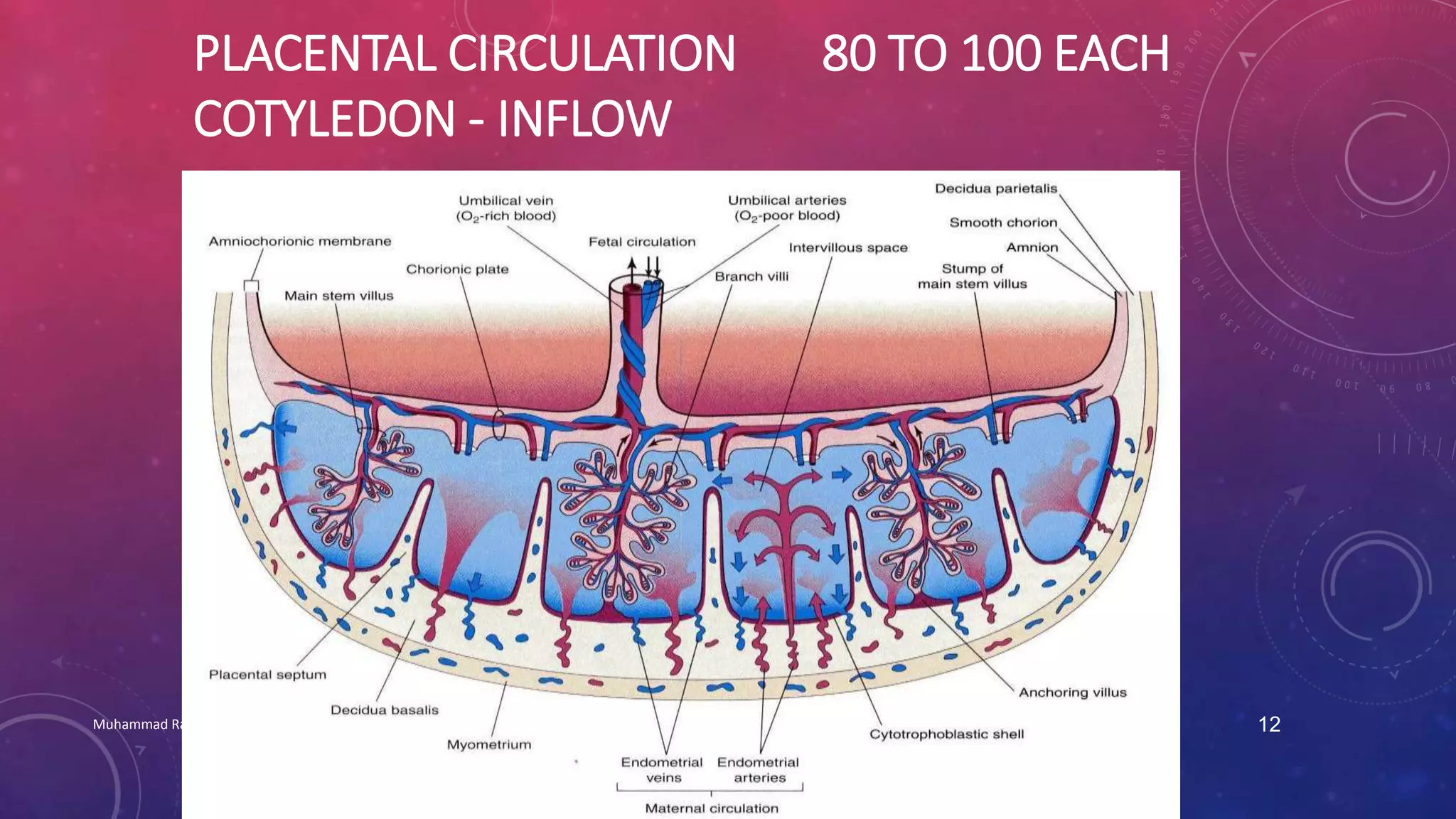
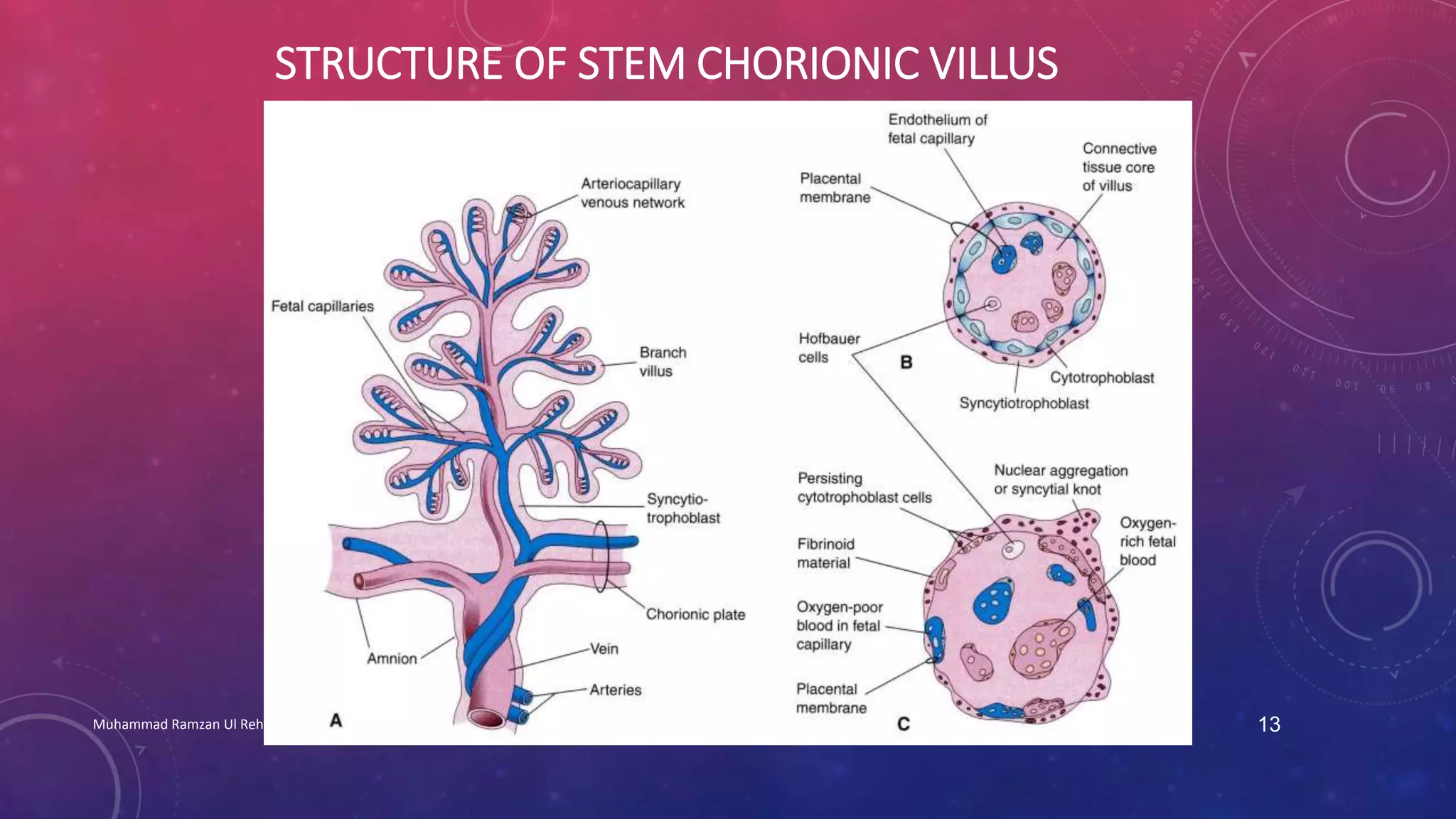
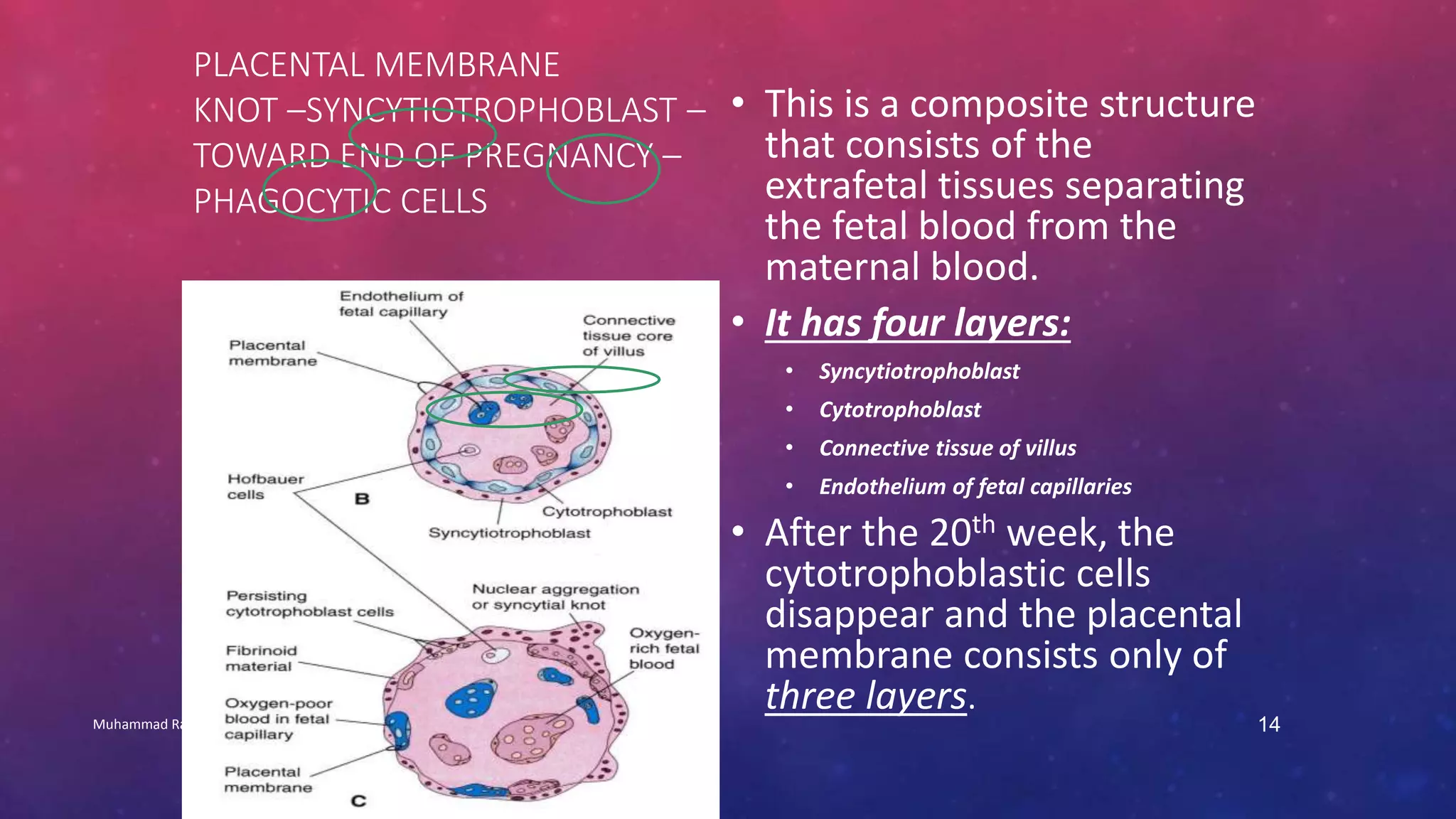
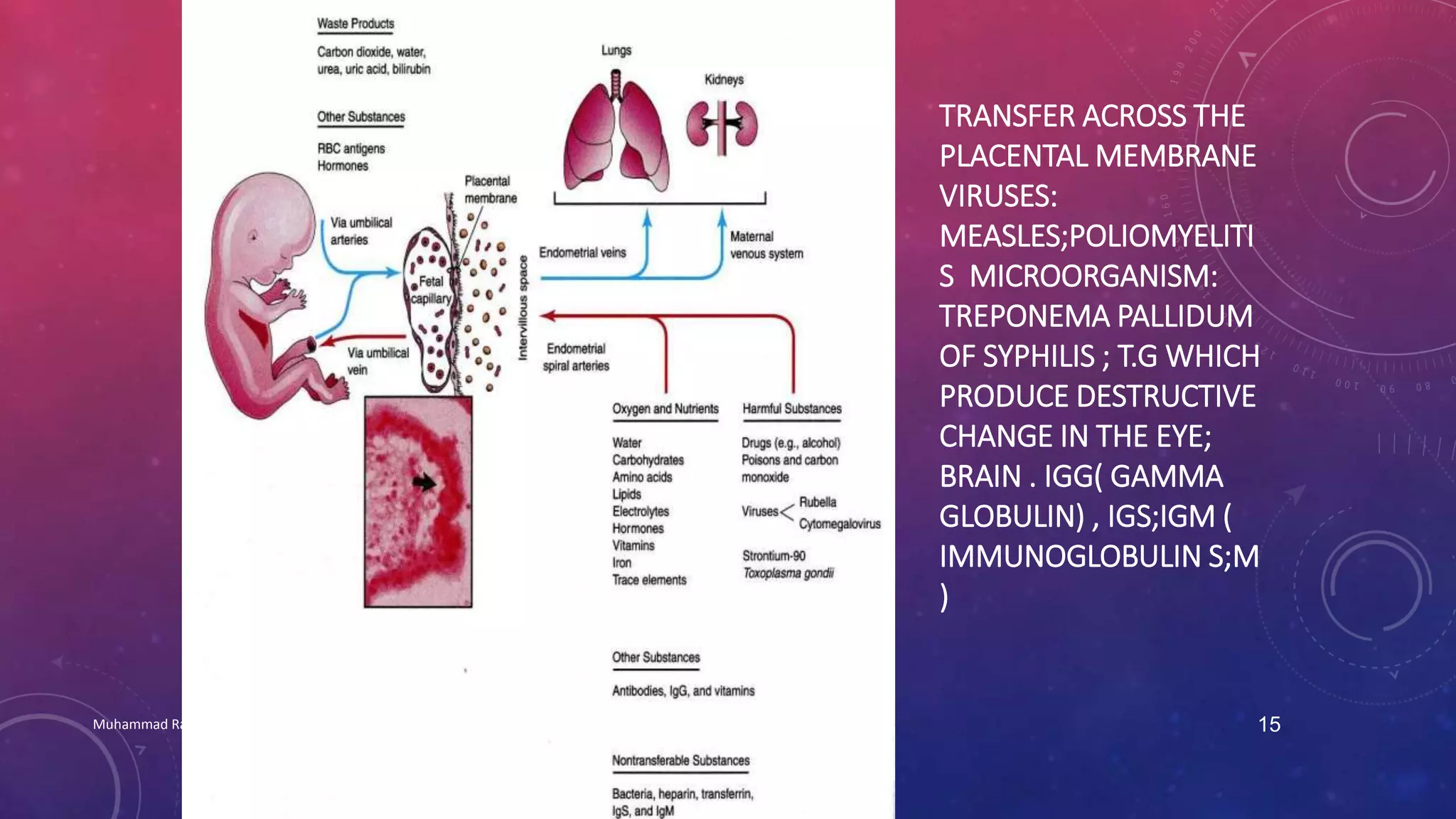
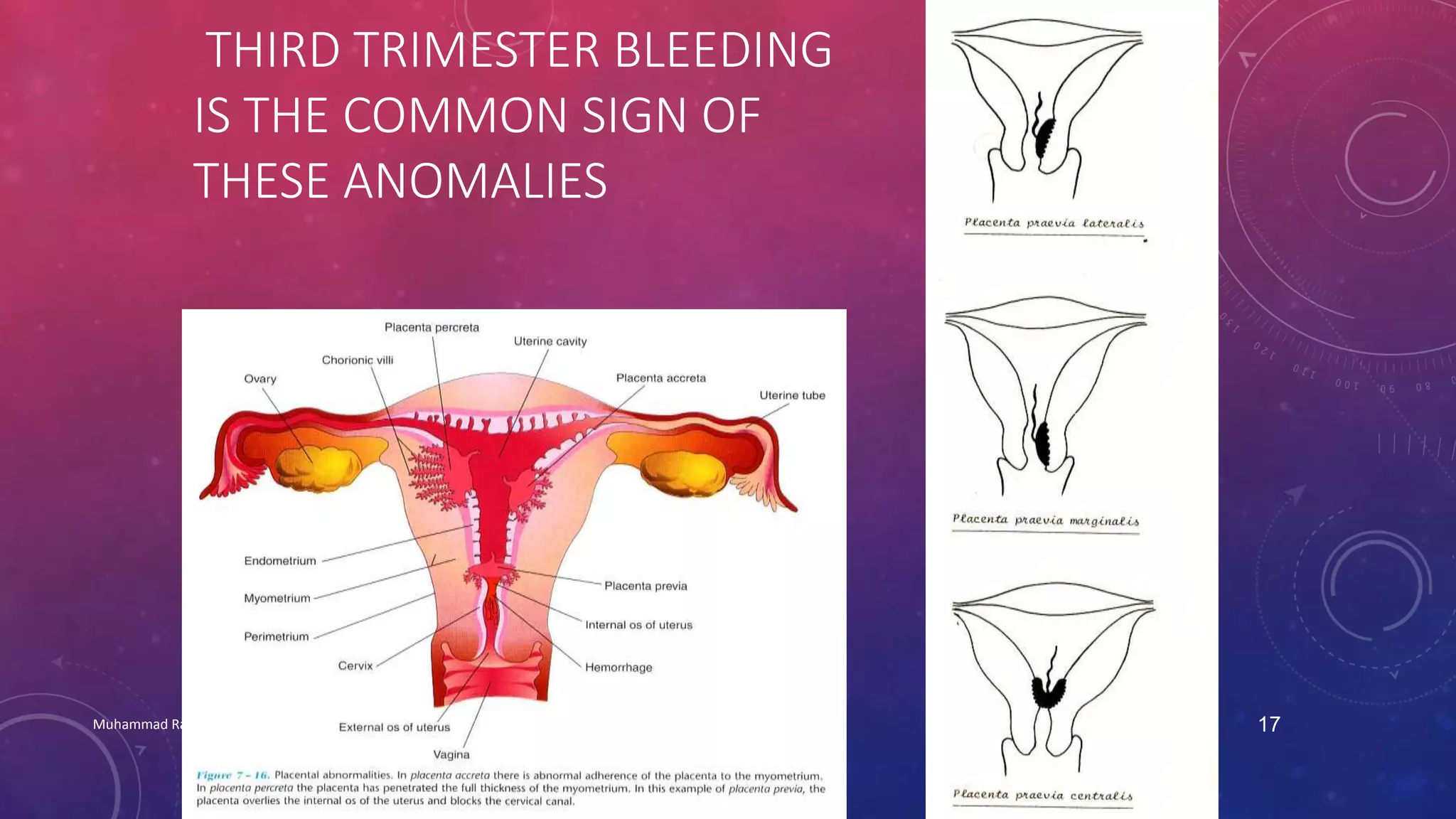
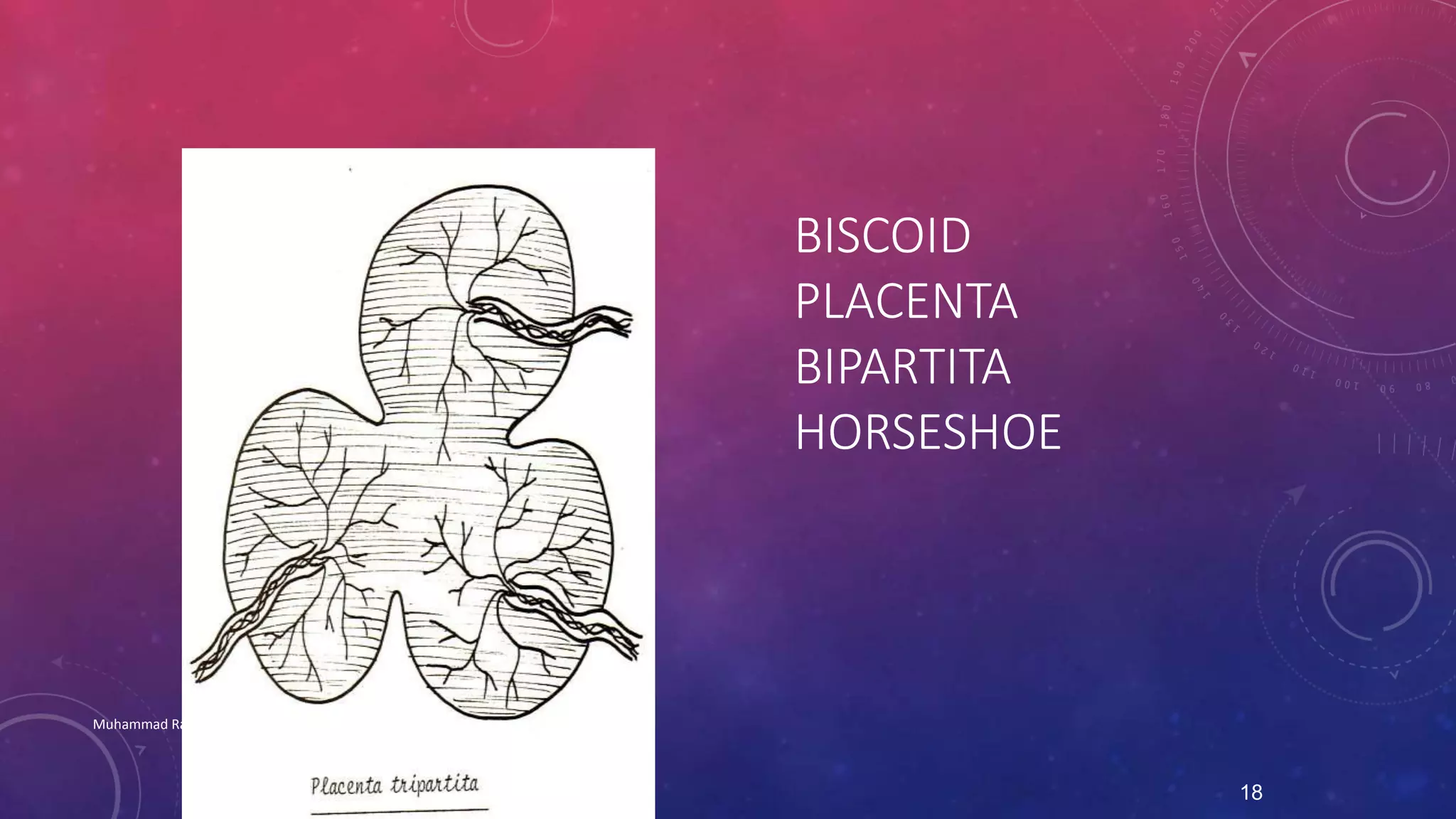
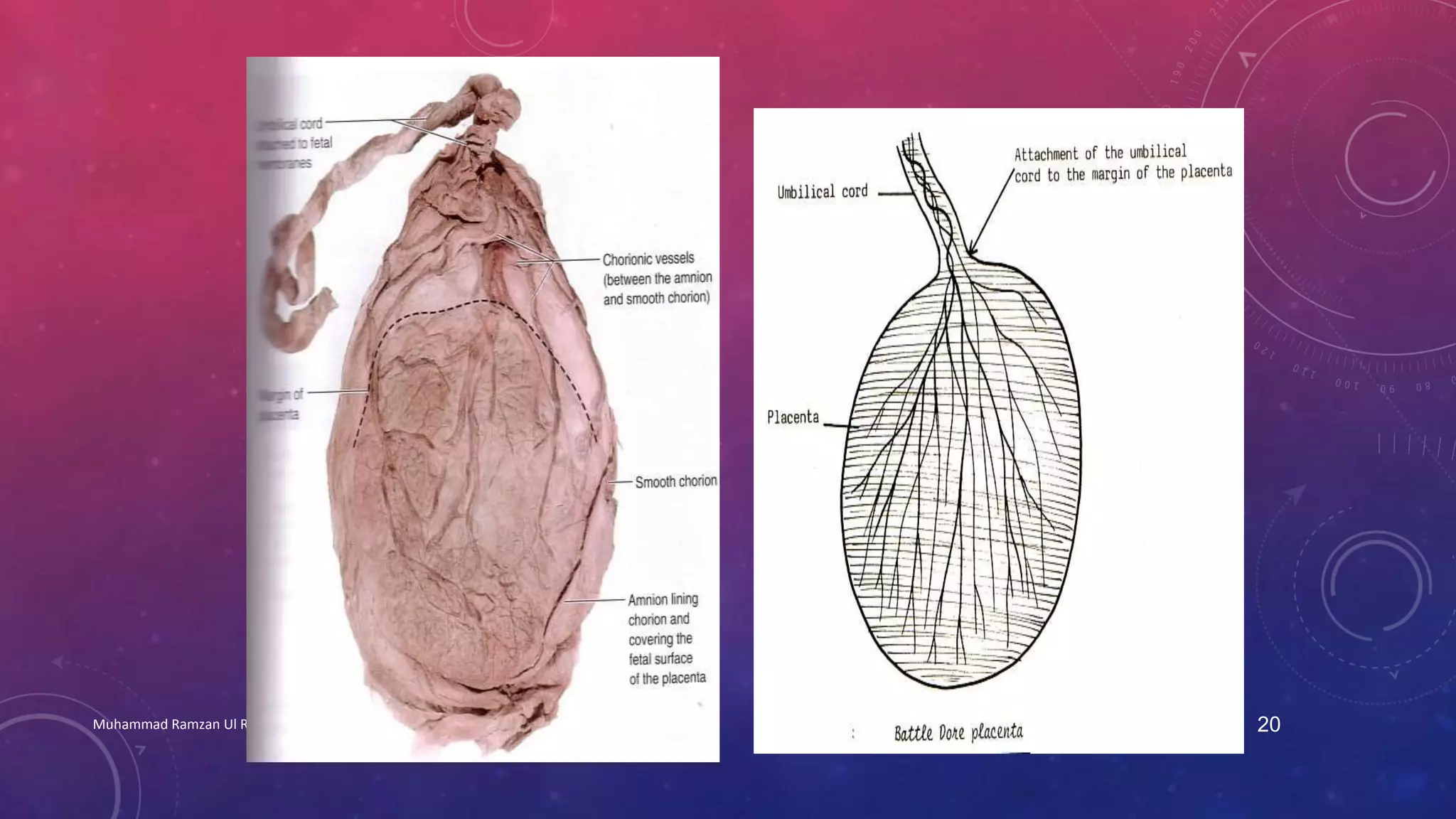
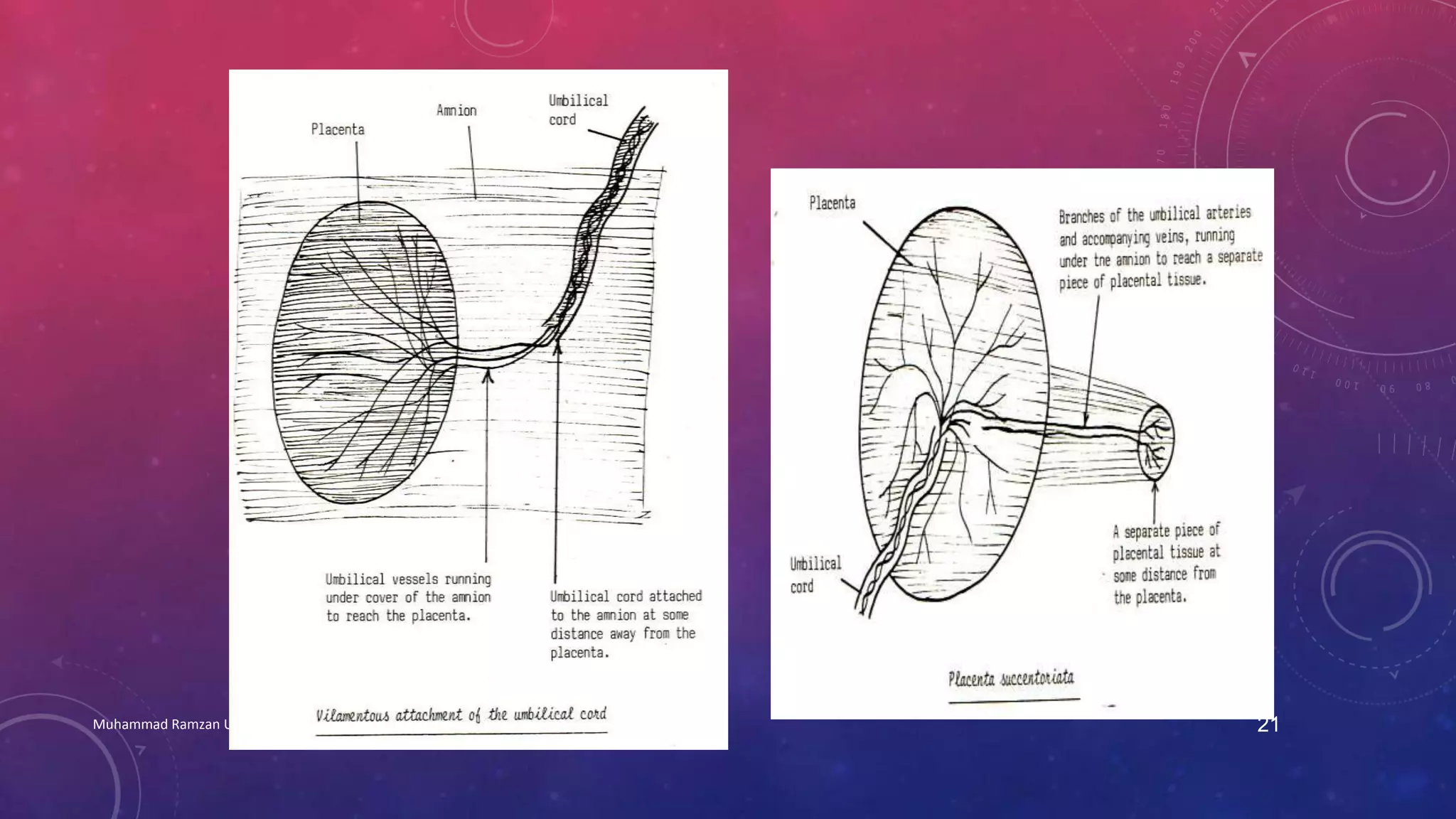
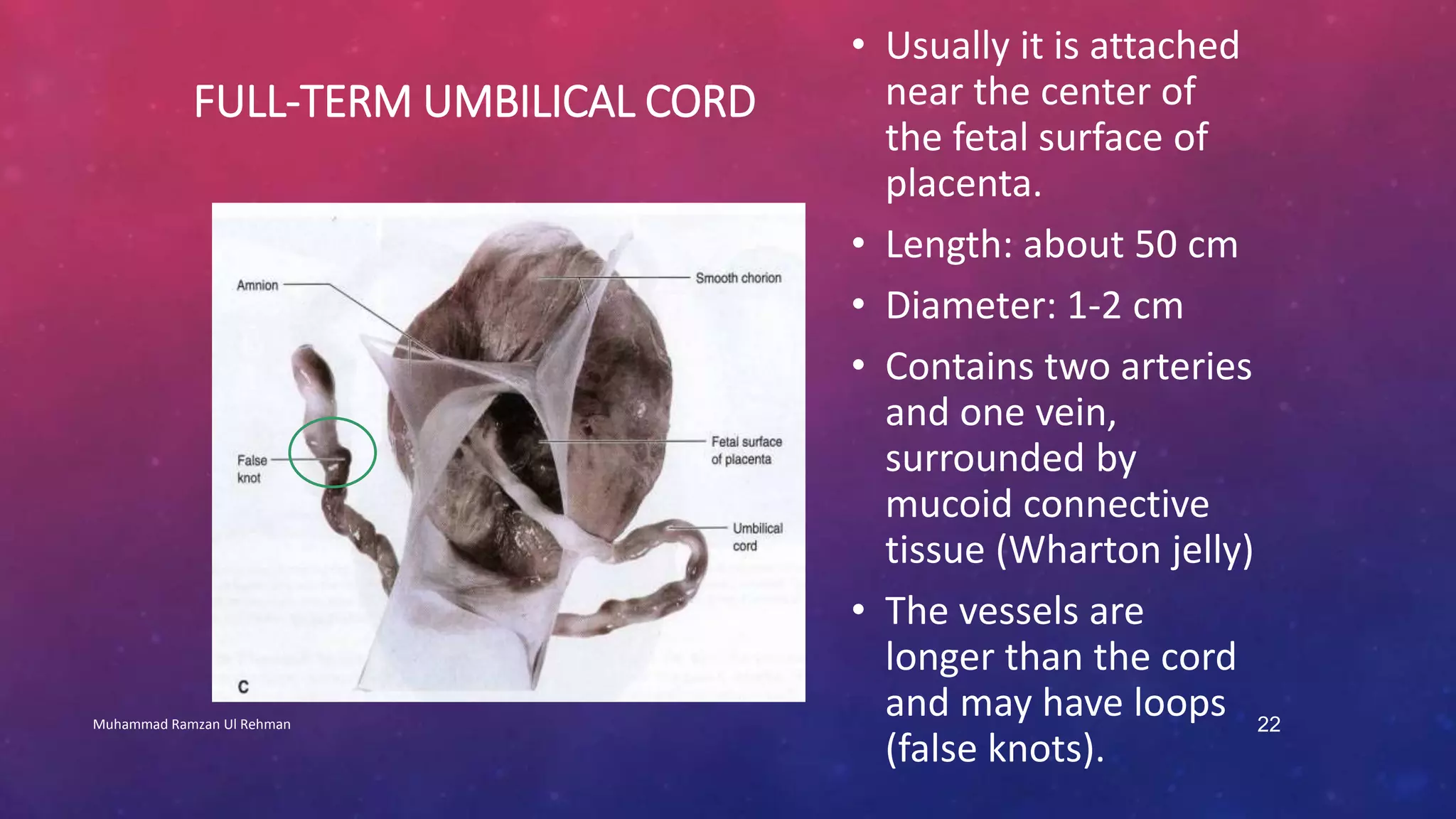
The placenta is a fetomaternal organ with fetal and maternal components that functions to protect the fetus, provide nutrition, aid respiration, perform excretion, and produce hormones. It develops from the chorionic sac and endometrium. In early development, chorionic villi form and connect to the embryo's circulatory system. Later, the villous chorion develops into the fetal part of the placenta while the decidua basalis forms the maternal part. At term, the placenta has a discoid shape and cotyledons, and the umbilical cord connects it to the fetus for nutrient/waste exchange across the placental membrane.