The document discusses early embryonic development during the second week of pregnancy. Key events include:
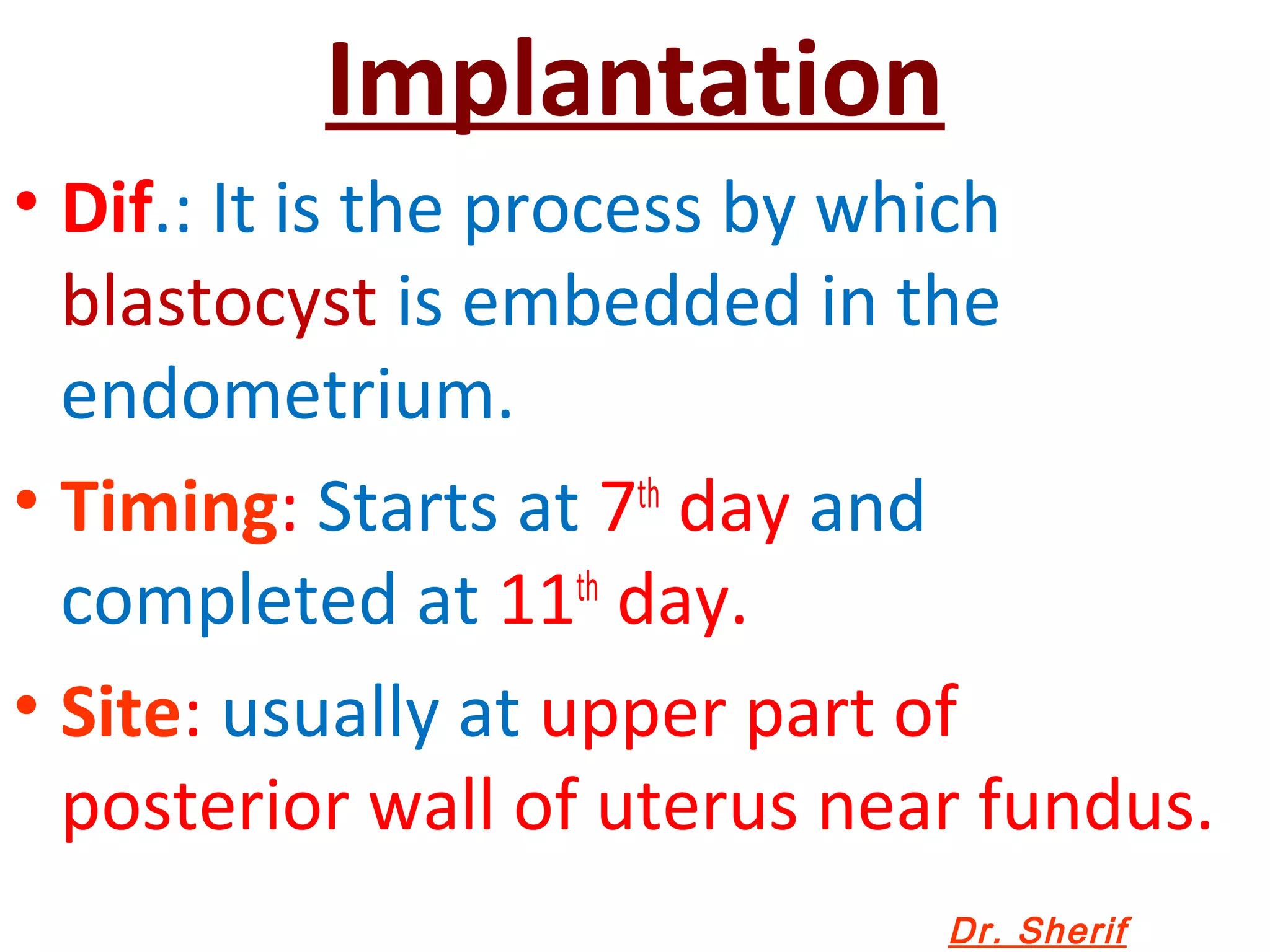
- Implantation of the blastocyst in the endometrium is completed by day 7.
- The blastocyst forms an inner cell mass (embryoblast) and outer cell mass (trophoblast).
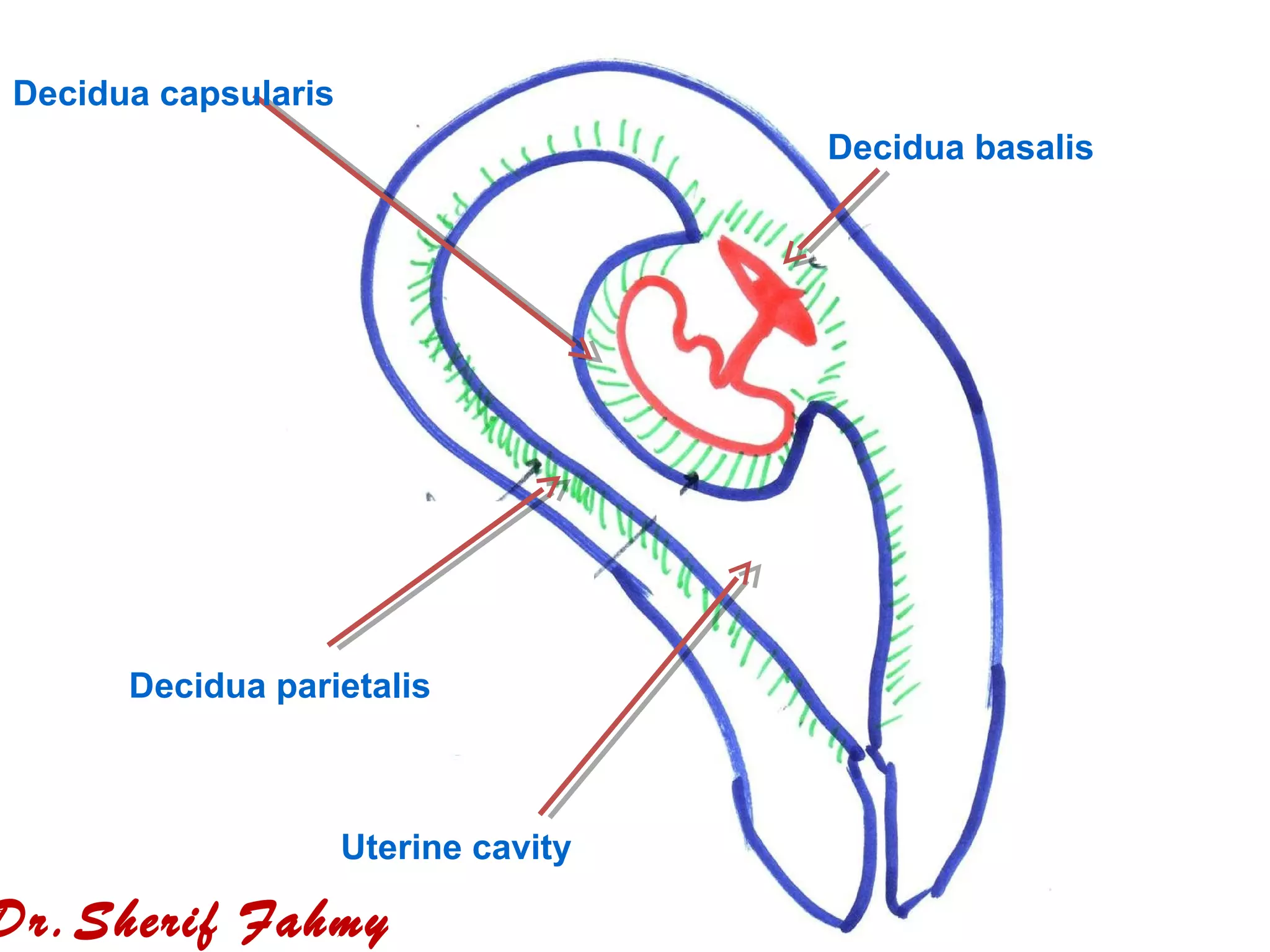
- By day 13, structures have formed including the amniotic cavity, yolk sac, chorionic villi, and connecting stalk between the embryo and placenta.
- Through this week, the embryonic disc splits into two layers and the trophoblast splits into an inner and outer layer. This lays the foundation for further organ development.