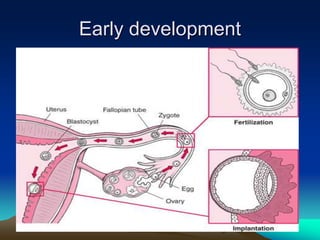
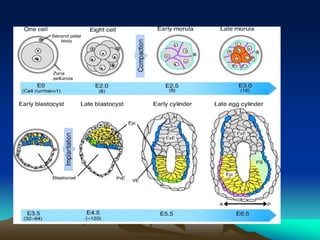
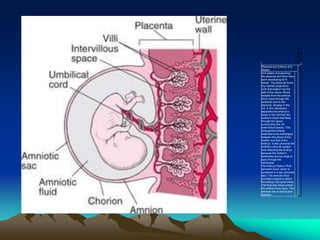
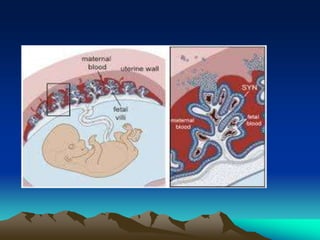
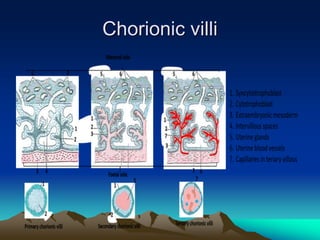
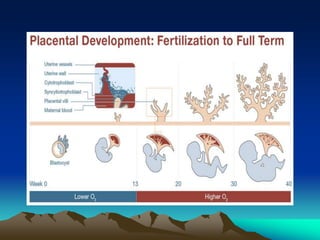
The placenta develops from trophoblast cells of the embryo. It forms chorionic villi which branch into tertiary villi containing fetal blood vessels. The placenta supports fetal growth through nutrient and gas exchange between maternal and fetal blood across the thin placental membrane. It also produces hormones like HCG, progesterone and estrogen essential for maintaining pregnancy. The mature placenta has a fetal side and a maternal side with cotyledons and septa. It transfers nutrients, gases, antibodies and metabolites while acting as a barrier and producing hormones throughout gestation. Exposure to certain chemicals, drugs or infections during pregnancy can potentially cause fetal abnormalities known as teratogenesis.













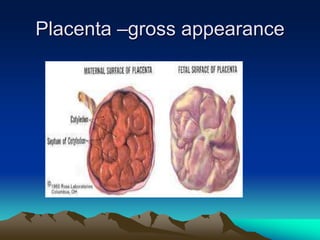

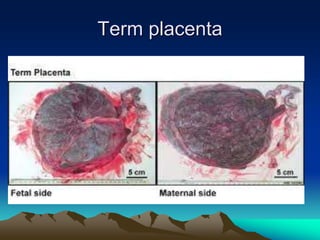
![Mature placenta
• Shape circular
• Weight -500-600 gms[1/6th of fetus]
• Diameter 15 to 20 cms
• Thickness -2 to 3 cms
• Surfaces –
– fetal surface
– Maternal surface](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/placenta-240301160937-db0620f1/85/placenta-pptuploading-to-download-a-pptfor-22-320.jpg)




![Functions of placenta.
• Transfer of nutrients.
• Respiration.[Oxygen and CO2 exchange]
• Transfer of antibodies.
• Production of hormones.
– HCG, HPL, estradiol, progesterone, Human chorionic
thyrotropin.
– Chorionic ACTH,
• Production of non specific pregnancy associated
proteins and hormones.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/placenta-240301160937-db0620f1/85/placenta-pptuploading-to-download-a-pptfor-28-320.jpg)
















