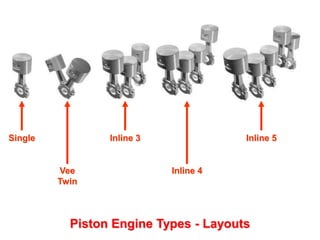
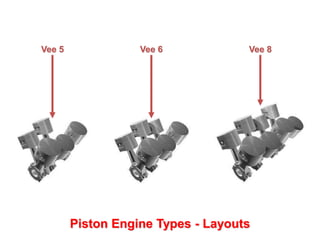
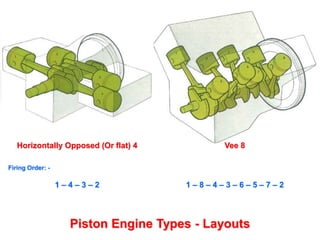
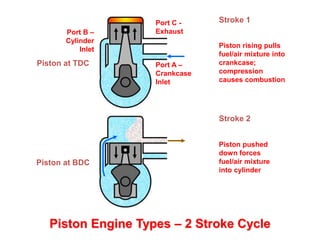
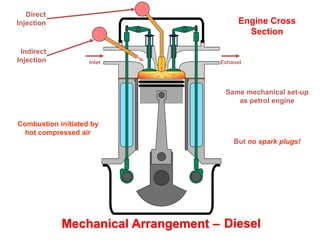
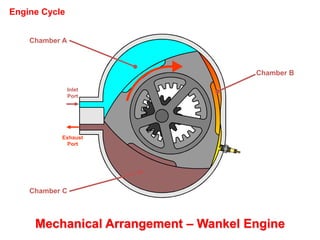
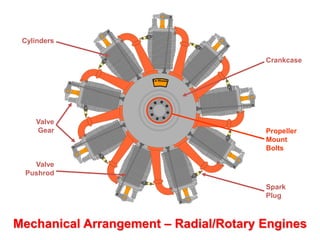
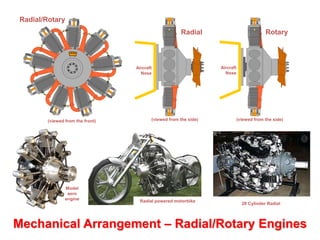
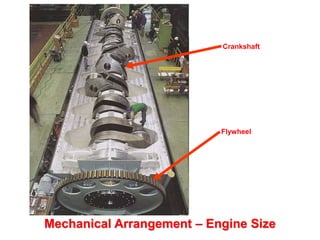
This document discusses different types of piston engine configurations and layouts including single inline, Vee, horizontally opposed, and radial arrangements. It also covers 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine cycles, mechanical arrangements of petrol, diesel, Wankel, and radial engines including locations of intake, exhaust, pistons, crankshafts, and other components. Finally, it notes the wide range of sizes for piston engines from very small to large aircraft engines.