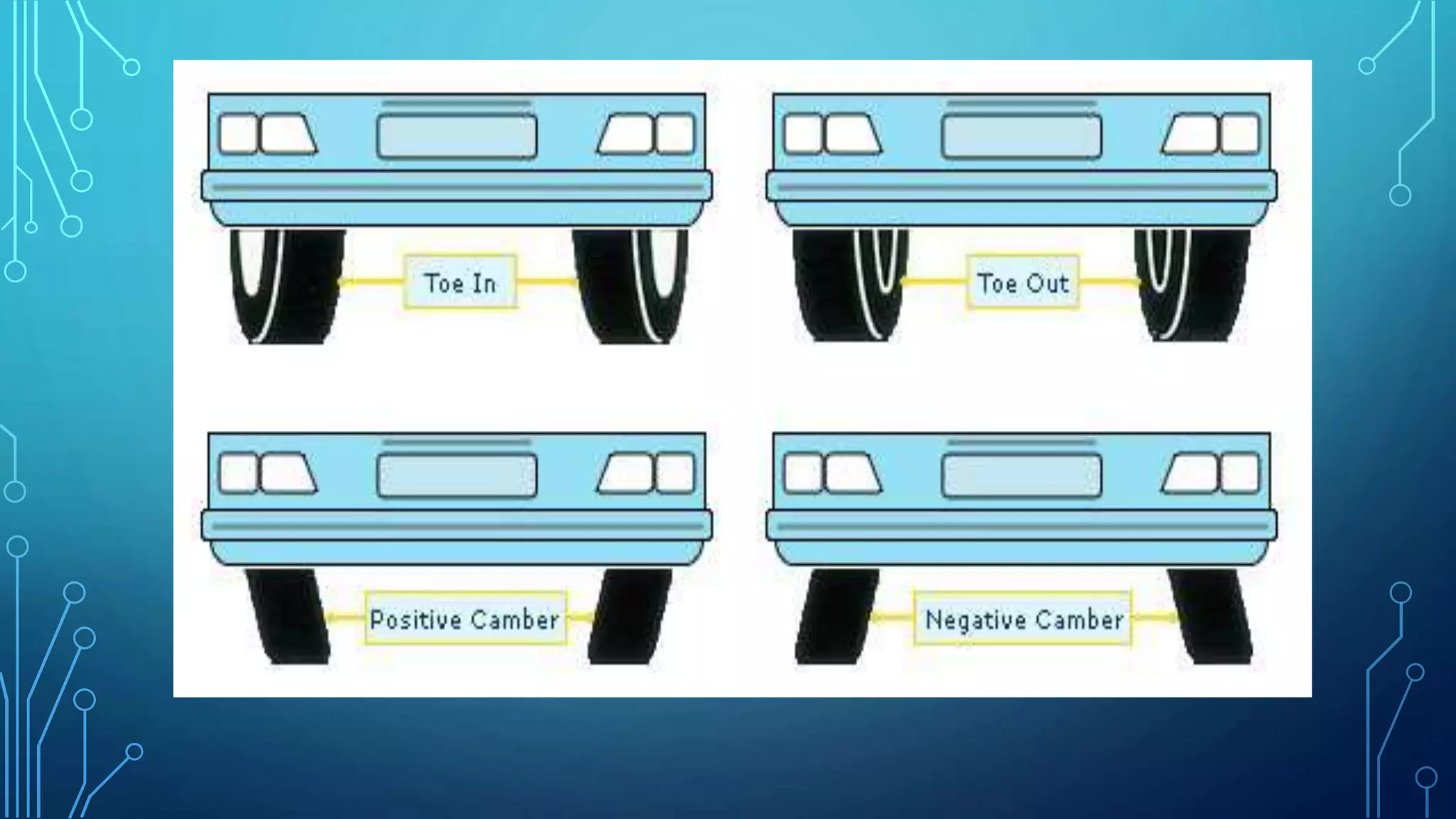
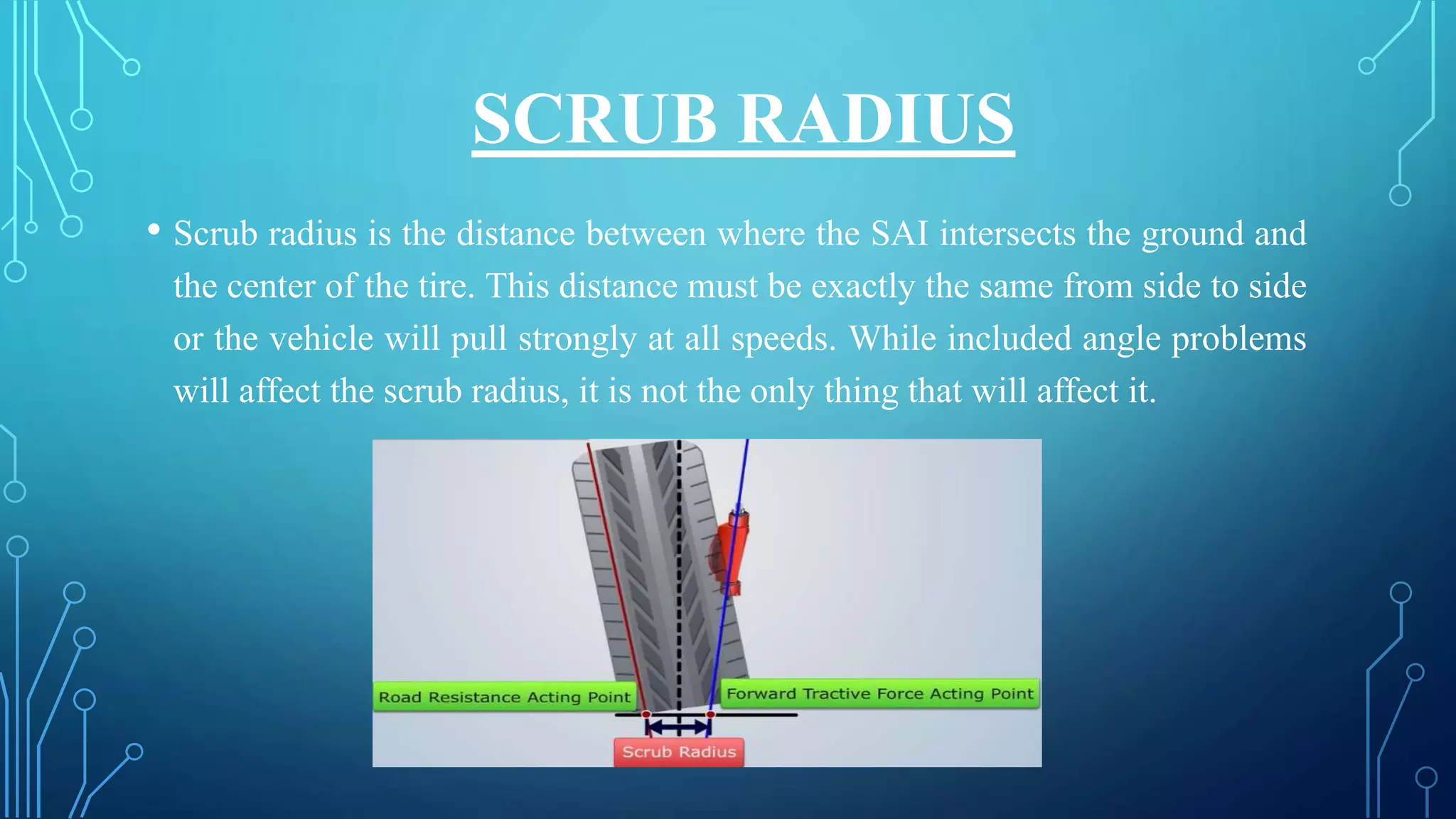
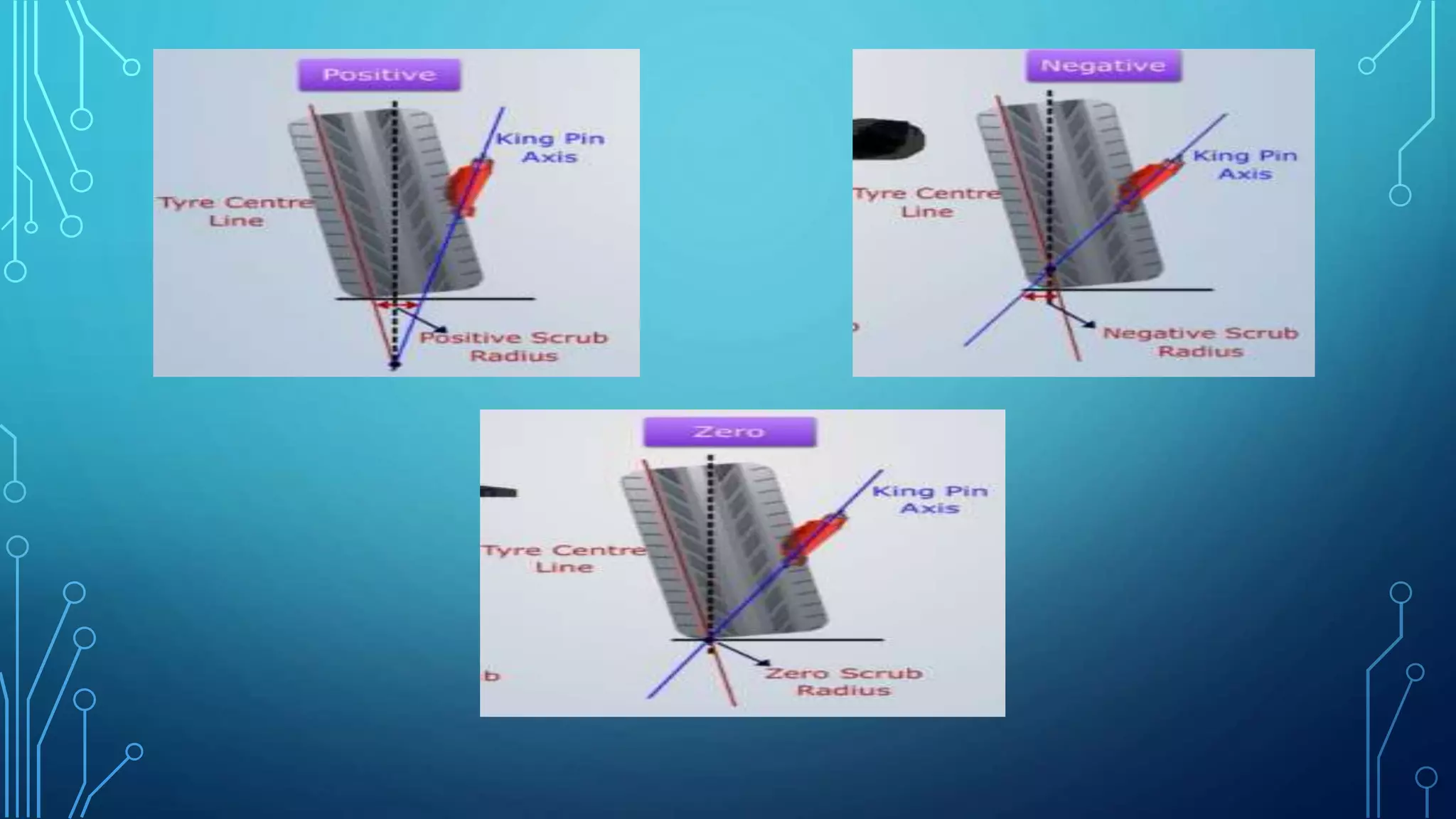
The document discusses the requirements of a good steering system, including that it should be accurate, easy to handle, and require minimal effort. It also covers various aspects of wheel alignment such as camber angle, caster angle, toe-in/toe-out, and scrub radius that impact tire wear and vehicle stability. Proper wheel alignment reduces tire wear, improves gas mileage and safety, and prevents pulling to one side.